Green leases prioritize sustainability by integrating energy efficiency and environmental performance clauses that benefit both landlords and tenants through reduced operating costs and enhanced property value. Absolute net leases impose full responsibility on tenants for all property expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, offering landlords minimal risk and consistent income. Discover the key differences and benefits of green leases versus absolute net leases to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
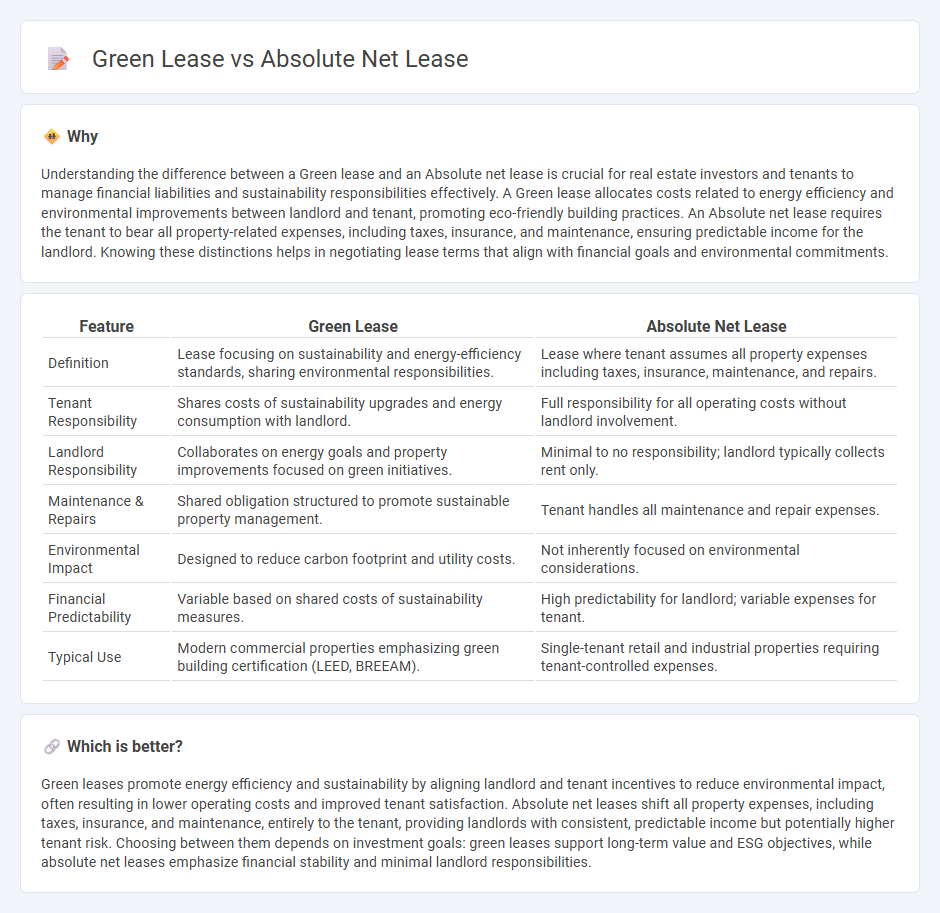
Understanding the difference between a Green lease and an Absolute net lease is crucial for real estate investors and tenants to manage financial liabilities and sustainability responsibilities effectively. A Green lease allocates costs related to energy efficiency and environmental improvements between landlord and tenant, promoting eco-friendly building practices. An Absolute net lease requires the tenant to bear all property-related expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, ensuring predictable income for the landlord. Knowing these distinctions helps in negotiating lease terms that align with financial goals and environmental commitments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Lease | Absolute Net Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease focusing on sustainability and energy-efficiency standards, sharing environmental responsibilities. | Lease where tenant assumes all property expenses including taxes, insurance, maintenance, and repairs. |
| Tenant Responsibility | Shares costs of sustainability upgrades and energy consumption with landlord. | Full responsibility for all operating costs without landlord involvement. |
| Landlord Responsibility | Collaborates on energy goals and property improvements focused on green initiatives. | Minimal to no responsibility; landlord typically collects rent only. |
| Maintenance & Repairs | Shared obligation structured to promote sustainable property management. | Tenant handles all maintenance and repair expenses. |
| Environmental Impact | Designed to reduce carbon footprint and utility costs. | Not inherently focused on environmental considerations. |
| Financial Predictability | Variable based on shared costs of sustainability measures. | High predictability for landlord; variable expenses for tenant. |
| Typical Use | Modern commercial properties emphasizing green building certification (LEED, BREEAM). | Single-tenant retail and industrial properties requiring tenant-controlled expenses. |
Which is better?
Green leases promote energy efficiency and sustainability by aligning landlord and tenant incentives to reduce environmental impact, often resulting in lower operating costs and improved tenant satisfaction. Absolute net leases shift all property expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, entirely to the tenant, providing landlords with consistent, predictable income but potentially higher tenant risk. Choosing between them depends on investment goals: green leases support long-term value and ESG objectives, while absolute net leases emphasize financial stability and minimal landlord responsibilities.
Connection
Green leases and absolute net leases intersect by integrating sustainability requirements with financial responsibilities, encouraging tenants to adopt eco-friendly practices while covering all property expenses. Both lease types influence operational efficiency and cost allocation, with green leases focusing on energy savings and environmental impact, and absolute net leases transferring maintenance and risk obligations entirely to tenants. This connection drives landlords and tenants toward sustainable property management strategies that balance economic and environmental benefits.
Key Terms
Operating Expenses
Absolute net leases require tenants to cover all operating expenses, including property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, minimizing landlord responsibilities. Green leases integrate sustainability clauses, encouraging shared operational cost savings through energy efficiency and environmental initiatives. Explore how these lease structures impact operating expenses and tenant-landlord collaboration for a deeper understanding.
Maintenance Responsibility
Absolute net leases assign full maintenance responsibility, including structural repairs and operating expenses, to the tenant, minimizing landlord obligations and ensuring predictable income streams. Green leases incorporate sustainability clauses requiring both landlords and tenants to collaboratively manage energy efficiency, reduce waste, and share maintenance duties aligned with environmental goals. Explore how these lease structures impact financial risk and operational control in commercial real estate.
Sustainability Requirements
Absolute net leases allocate all property expenses, including maintenance, taxes, and insurance, to tenants, often overlooking sustainability requirements in lease agreements. Green leases explicitly incorporate environmental performance standards and sustainability obligations, promoting energy efficiency, waste reduction, and eco-friendly practices in commercial properties. Explore the key differences and advantages of these lease types to align real estate strategies with sustainability goals.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Absolute Net Lease in Commercial Real Estate - This article explains how an absolute net lease places significant financial responsibility on the tenant, including property taxes, insurance, maintenance, and structural repairs.
What is an absolute net lease in real estate? - This piece describes the absolute net lease as a type of commercial lease where the tenant covers all property-related expenses, including taxes, insurance, maintenance, and major repairs.
Understanding the Absolute NNN Lease: A Comprehensive Guide - This guide outlines the absolute NNN lease, which places extensive responsibility on the tenant for all property expenses and operations, giving the landlord a passive role.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com