Leaseback programs offer property owners immediate liquidity by selling their asset and leasing it back, ensuring uninterrupted use while freeing up capital. Concession agreements involve transferring property rights to an operator for a specific period, who manages and generates revenue under agreed terms, often seen in public-private partnerships. Explore the nuances and benefits of these strategies to optimize your real estate investment.
Why it is important
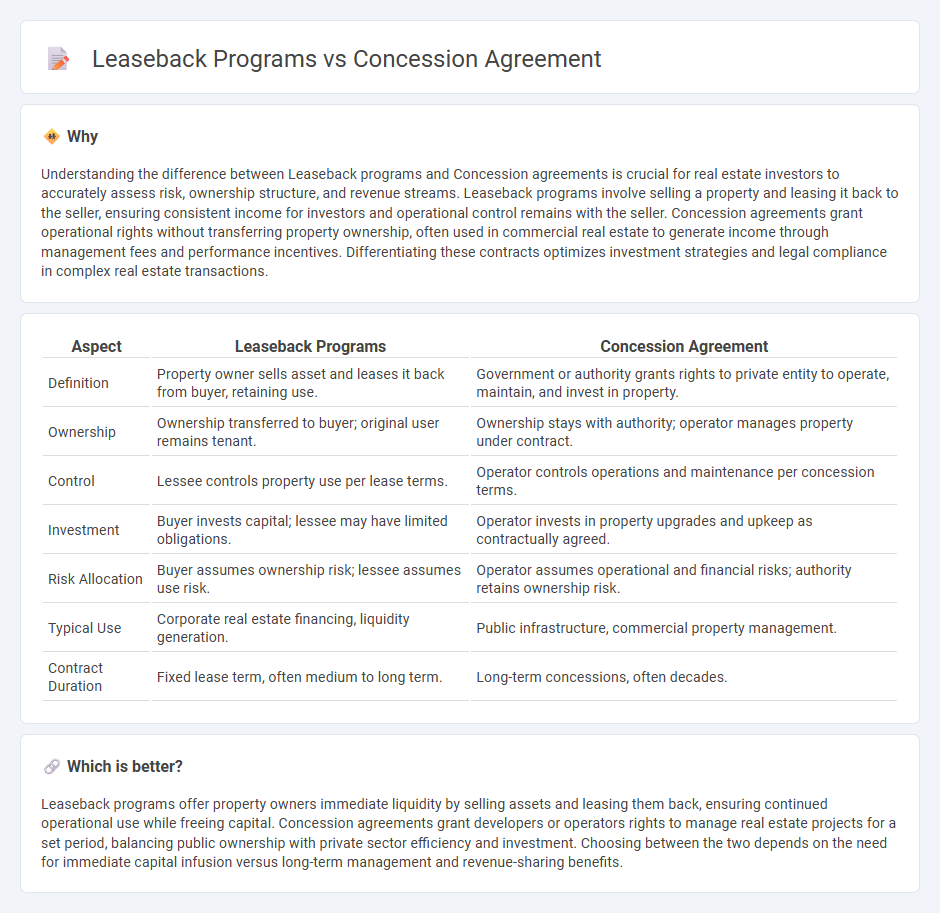
Understanding the difference between Leaseback programs and Concession agreements is crucial for real estate investors to accurately assess risk, ownership structure, and revenue streams. Leaseback programs involve selling a property and leasing it back to the seller, ensuring consistent income for investors and operational control remains with the seller. Concession agreements grant operational rights without transferring property ownership, often used in commercial real estate to generate income through management fees and performance incentives. Differentiating these contracts optimizes investment strategies and legal compliance in complex real estate transactions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Leaseback Programs | Concession Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Property owner sells asset and leases it back from buyer, retaining use. | Government or authority grants rights to private entity to operate, maintain, and invest in property. |
| Ownership | Ownership transferred to buyer; original user remains tenant. | Ownership stays with authority; operator manages property under contract. |
| Control | Lessee controls property use per lease terms. | Operator controls operations and maintenance per concession terms. |
| Investment | Buyer invests capital; lessee may have limited obligations. | Operator invests in property upgrades and upkeep as contractually agreed. |
| Risk Allocation | Buyer assumes ownership risk; lessee assumes use risk. | Operator assumes operational and financial risks; authority retains ownership risk. |
| Typical Use | Corporate real estate financing, liquidity generation. | Public infrastructure, commercial property management. |
| Contract Duration | Fixed lease term, often medium to long term. | Long-term concessions, often decades. |
Which is better?
Leaseback programs offer property owners immediate liquidity by selling assets and leasing them back, ensuring continued operational use while freeing capital. Concession agreements grant developers or operators rights to manage real estate projects for a set period, balancing public ownership with private sector efficiency and investment. Choosing between the two depends on the need for immediate capital infusion versus long-term management and revenue-sharing benefits.
Connection
Leaseback programs and concession agreements intersect in real estate by enabling asset owners to monetize properties while retaining operational control. Leaseback programs allow sellers to lease back their property immediately after sale, ensuring continuous use and income generation. Concession agreements grant rights to operate and manage real estate assets, often linked with leaseback structures to optimize long-term revenue and development potential.
Key Terms
Ownership Transfer
Concession agreements involve transferring temporary operational rights of an asset to a concessionaire while ownership remains with the original entity. Leaseback programs entail selling an asset to a buyer and then leasing it back, resulting in an ownership transfer to the buyer. Explore more about how ownership transfer impacts financial and operational strategies in both models.
Revenue Sharing
Concession agreements involve a private entity operating and managing a public asset in exchange for sharing revenue generated with the asset owner, typically a government. Leaseback programs allow asset owners to sell their property and then lease it back, generating upfront capital while paying rent over time, with less emphasis on revenue sharing. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model maximizes financial performance for your specific asset portfolio.
Lease Duration
Leaseback programs typically feature shorter lease durations, often ranging from 5 to 15 years, providing flexibility for property owners to regain control after the term ends. Concession agreements generally involve longer lease periods, sometimes spanning 20 to 50 years, enabling investors to secure steady returns over extended timeframes. Discover how lease duration impacts financial strategy and risk management in real estate deals.
Source and External Links
Concession (contract) - A concession or concession agreement is a grant of rights, land, property, or facility by a government or entity, often involving public services.
Concession Agreement Template - Provides a template for concession agreements, which outline the rights, responsibilities, and obligations between the resource owner and the operator.
Concession Agreements - Public Private Partnership - Discusses concession agreements in the context of railways, involving construction, maintenance, and operation with major investment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com