Co-living spaces offer flexible, amenity-rich rentals designed for individuals seeking affordability and community in urban settings, while co-housing emphasizes jointly owned, resident-managed neighborhoods promoting long-term collaboration and shared resources. Each model caters to different lifestyles, with co-living focusing on convenience and social interaction, and co-housing prioritizing sustainable living and community governance. Explore the unique benefits and challenges of co-living spaces versus co-housing to determine which suits your real estate needs best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between co-living spaces and co-housing is crucial for making informed real estate decisions that align with lifestyle preferences and investment goals. Co-living spaces offer flexible, fully furnished accommodations with shared amenities, ideal for transient residents and young professionals seeking convenience. Co-housing focuses on intentional communities with private homes and communal areas, fostering long-term relationships and collaborative living. Recognizing these distinctions helps buyers and renters select properties that best suit their social needs and financial expectations.
Comparison Table
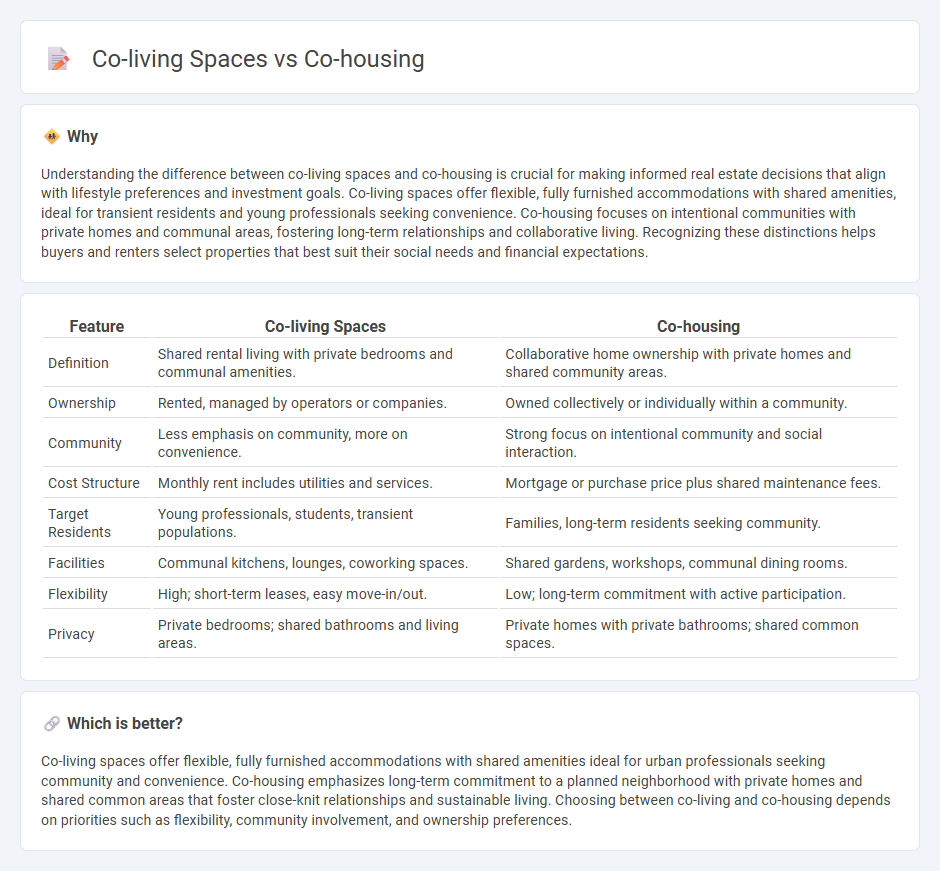
| Feature | Co-living Spaces | Co-housing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared rental living with private bedrooms and communal amenities. | Collaborative home ownership with private homes and shared community areas. |
| Ownership | Rented, managed by operators or companies. | Owned collectively or individually within a community. |
| Community | Less emphasis on community, more on convenience. | Strong focus on intentional community and social interaction. |
| Cost Structure | Monthly rent includes utilities and services. | Mortgage or purchase price plus shared maintenance fees. |
| Target Residents | Young professionals, students, transient populations. | Families, long-term residents seeking community. |
| Facilities | Communal kitchens, lounges, coworking spaces. | Shared gardens, workshops, communal dining rooms. |
| Flexibility | High; short-term leases, easy move-in/out. | Low; long-term commitment with active participation. |
| Privacy | Private bedrooms; shared bathrooms and living areas. | Private homes with private bathrooms; shared common spaces. |
Which is better?
Co-living spaces offer flexible, fully furnished accommodations with shared amenities ideal for urban professionals seeking community and convenience. Co-housing emphasizes long-term commitment to a planned neighborhood with private homes and shared common areas that foster close-knit relationships and sustainable living. Choosing between co-living and co-housing depends on priorities such as flexibility, community involvement, and ownership preferences.
Connection
Co-living spaces and co-housing share a fundamental focus on community-oriented residential models that optimize affordability and social interaction in real estate. Both concepts emphasize shared amenities and collaborative living environments, fostering a sense of belonging and efficient use of urban spaces. These housing trends address the increasing demand for flexible, cost-effective solutions in high-density cities, transforming traditional real estate development approaches.
Key Terms
Shared Amenities
Co-housing communities emphasize shared amenities such as community gardens, kitchens, and recreational areas designed to foster long-term neighbor interactions and collective responsibility. Co-living spaces typically offer fully furnished private rooms with shared common areas including lounges, kitchens, and coworking spaces, targeting convenience and social engagement for short to medium-term stays. Explore more about how shared amenities influence community dynamics and resident experiences in co-housing and co-living models.
Private Units
Co-housing communities typically feature private units with individual kitchens and bathrooms, promoting both autonomy and social interaction through shared common spaces. In co-living spaces, residents often have private bedrooms but share bathrooms and kitchen facilities, emphasizing affordability and community connectivity. Explore how private unit designs in these models impact lifestyle and personal privacy.
Community Governance
Community governance in co-housing emphasizes resident-led decision-making, shared responsibilities, and consensus-building to foster a strong sense of ownership and collaboration among members. In contrast, co-living spaces often rely on centralized management or external operators, resulting in less direct involvement from residents in governance processes. Discover how the nuances of community governance shape the lived experience in co-housing and co-living by exploring their distinct models further.
Source and External Links
Cohousing - Wikipedia - Cohousing is an intentional, self-governing community where residents live in private homes with shared spaces, offering social, practical, and environmental benefits.
Embracing Community: The Rise of Co-Housing and Co-Living Spaces in Austin, TX - This article explores the growth of co-housing and co-living spaces in Austin, driven by factors like affordability and community spirit.
The Cohousing Association of America - The Cohousing Association provides information and resources on cohousing, emphasizing its benefits despite challenges like affordability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com