Opportunity zone investing offers significant tax incentives by allowing investors to defer and potentially reduce capital gains taxes when investing in designated economically distressed areas. Syndication pools capital from multiple investors to fund large-scale real estate projects, providing access to high-value assets and diversified portfolios. Explore the unique benefits and strategies of both approaches to enhance your real estate investment portfolio.
Why it is important
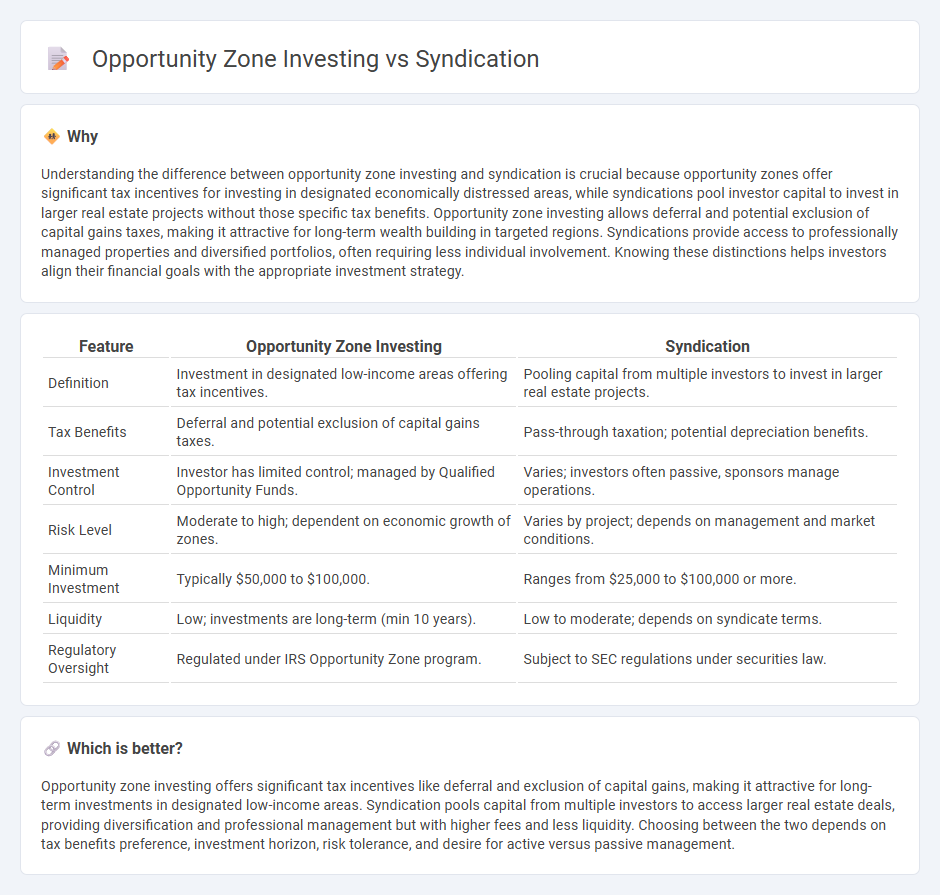
Understanding the difference between opportunity zone investing and syndication is crucial because opportunity zones offer significant tax incentives for investing in designated economically distressed areas, while syndications pool investor capital to invest in larger real estate projects without those specific tax benefits. Opportunity zone investing allows deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains taxes, making it attractive for long-term wealth building in targeted regions. Syndications provide access to professionally managed properties and diversified portfolios, often requiring less individual involvement. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their financial goals with the appropriate investment strategy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Opportunity Zone Investing | Syndication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in designated low-income areas offering tax incentives. | Pooling capital from multiple investors to invest in larger real estate projects. |
| Tax Benefits | Deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains taxes. | Pass-through taxation; potential depreciation benefits. |
| Investment Control | Investor has limited control; managed by Qualified Opportunity Funds. | Varies; investors often passive, sponsors manage operations. |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high; dependent on economic growth of zones. | Varies by project; depends on management and market conditions. |
| Minimum Investment | Typically $50,000 to $100,000. | Ranges from $25,000 to $100,000 or more. |
| Liquidity | Low; investments are long-term (min 10 years). | Low to moderate; depends on syndicate terms. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Regulated under IRS Opportunity Zone program. | Subject to SEC regulations under securities law. |
Which is better?
Opportunity zone investing offers significant tax incentives like deferral and exclusion of capital gains, making it attractive for long-term investments in designated low-income areas. Syndication pools capital from multiple investors to access larger real estate deals, providing diversification and professional management but with higher fees and less liquidity. Choosing between the two depends on tax benefits preference, investment horizon, risk tolerance, and desire for active versus passive management.
Connection
Opportunity zone investing leverages tax incentives by directing capital into designated low-income communities, while syndication pools funds from multiple investors to access larger, higher-value real estate projects within these zones. This strategic connection enables investors to minimize capital gains taxes and diversify risks through collective ownership of development or rehabilitation properties. Syndications in opportunity zones accelerate community revitalization by channeling substantial aggregated investments into impactful real estate ventures.
Key Terms
Passive Investors
Syndication investing involves pooling capital from multiple passive investors to invest in larger real estate projects, offering diversified risk and professional management. Opportunity Zone investing provides tax incentives by directing funds into designated low-income areas, allowing passive investors to defer and reduce capital gains taxes. Explore further to understand which strategy aligns best with your financial goals and tax benefits.
Tax Deferral
Tax deferral strategies in real estate syndication enable investors to postpone capital gains taxes through mechanisms like 1031 exchanges, maximizing investment growth. Opportunity zone investing offers deferral and potential reduction of capital gains taxes when capital is reinvested in designated low-income communities, with additional tax benefits after holding periods. Explore how these distinct tax deferral options can optimize your real estate investment portfolio.
Fund Structure
Syndication structures in real estate investing typically involve multiple investors pooling capital into a single entity, often a limited partnership or LLC, to acquire and manage properties collectively, optimizing risk diversification and management expertise. Opportunity zone investing, governed by specific IRS regulations, requires investments to be held in Qualified Opportunity Funds (QOFs) that follow strict timelines and reinvestment rules to qualify for tax incentives. Explore the detailed distinctions in fund structure and regulatory benefits to understand which strategy aligns with your investment goals.
Source and External Links
What Is Syndication? (Including Benefits and Types) - This article explains syndication in broadcasting as a method of distributing television shows to multiple stations, contrasting with centralized network distribution.
Broadcast syndication - This webpage describes broadcast syndication as the practice of licensing TV or radio programs to multiple stations rather than a single network, highlighting its evolution and impact on revenue.
Real Estate Syndication Guide & How Passive Investors Profit - This guide explains real estate syndication as a method where investors pool capital to purchase properties, allowing for fractional ownership and shared income.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com