Digital twins provide a dynamic, real-time virtual replica of physical properties, enhancing predictive maintenance and energy efficiency beyond traditional CAD's static 3D modeling capabilities. CAD focuses on precise architectural design and structural details, while digital twins integrate live sensor data for ongoing monitoring and operational optimization. Explore the transformative impact of digital twins in real estate management and design innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twins and CAD is crucial in real estate because digital twins provide real-time, dynamic simulations of properties, while CAD offers static, detailed design blueprints. Digital twins enable property managers and investors to monitor building performance and maintenance needs, enhancing decision-making and cost efficiency. CAD remains essential for initial architectural planning and construction documentation. Mastering both tools optimizes property development, management, and value assessment.
Comparison Table
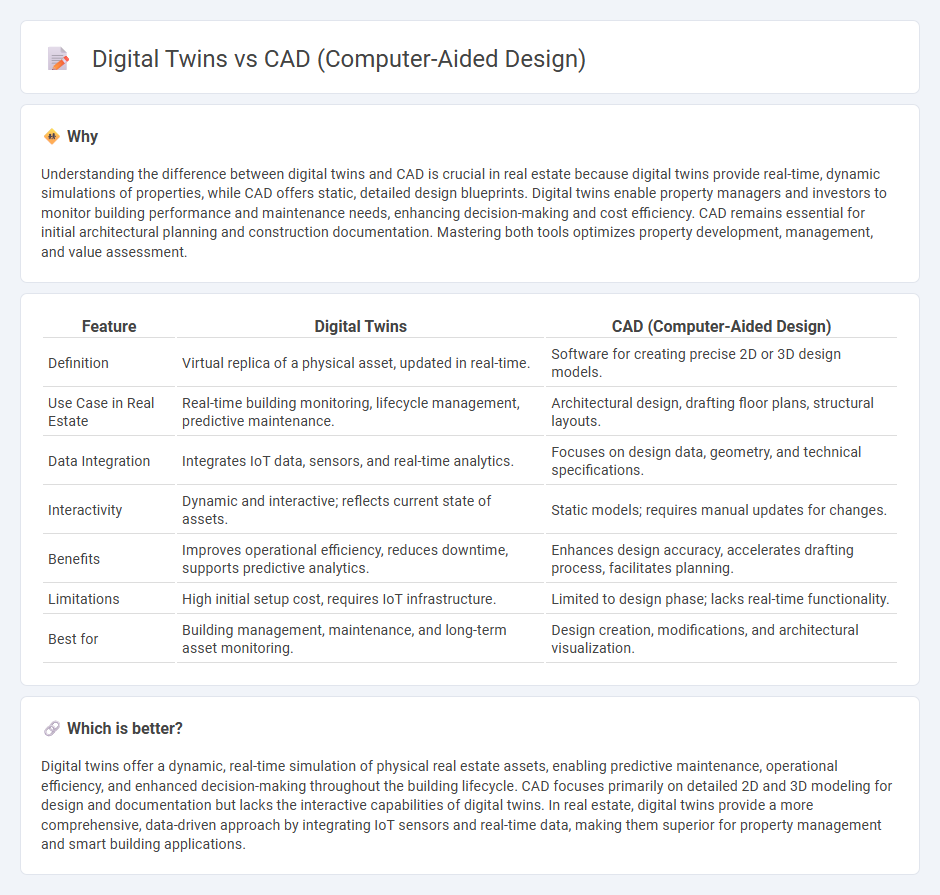
| Feature | Digital Twins | CAD (Computer-Aided Design) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of a physical asset, updated in real-time. | Software for creating precise 2D or 3D design models. |
| Use Case in Real Estate | Real-time building monitoring, lifecycle management, predictive maintenance. | Architectural design, drafting floor plans, structural layouts. |
| Data Integration | Integrates IoT data, sensors, and real-time analytics. | Focuses on design data, geometry, and technical specifications. |
| Interactivity | Dynamic and interactive; reflects current state of assets. | Static models; requires manual updates for changes. |
| Benefits | Improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime, supports predictive analytics. | Enhances design accuracy, accelerates drafting process, facilitates planning. |
| Limitations | High initial setup cost, requires IoT infrastructure. | Limited to design phase; lacks real-time functionality. |
| Best for | Building management, maintenance, and long-term asset monitoring. | Design creation, modifications, and architectural visualization. |
Which is better?
Digital twins offer a dynamic, real-time simulation of physical real estate assets, enabling predictive maintenance, operational efficiency, and enhanced decision-making throughout the building lifecycle. CAD focuses primarily on detailed 2D and 3D modeling for design and documentation but lacks the interactive capabilities of digital twins. In real estate, digital twins provide a more comprehensive, data-driven approach by integrating IoT sensors and real-time data, making them superior for property management and smart building applications.
Connection
Digital twins utilize CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models to create precise, interactive replicas of real estate properties, enabling accurate simulations and real-time monitoring. Integrating CAD data ensures detailed architectural and structural representations, improving facility management and predictive maintenance. This connection enhances project planning, reduces construction errors, and optimizes building performance throughout the property lifecycle.
Key Terms
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) primarily facilitates the creation of detailed 2D and 3D architectural drawings, essential for visualizing building components and structural elements. Digital twins integrate BIM (Building Information Modeling) data with real-time sensor inputs to provide a dynamic, virtual replica of a building for enhanced facility management and performance monitoring. Explore how the convergence of CAD, BIM, and digital twins is revolutionizing construction workflows and asset lifecycle management.
Visualization
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) enables detailed 2D and 3D modeling essential for precise engineering and architectural plans, focusing primarily on design creation and modification. Digital twins extend visualization by integrating real-time data and simulations, offering dynamic, interactive representations that reflect operational performance and environmental changes. Explore the evolving capabilities of digital twins versus traditional CAD to enhance visualization in digital engineering.
Data Synchronization
Data synchronization in CAD systems ensures real-time updating of design modifications across teams, maintaining consistency in geometry, annotations, and metadata. Digital twins leverage continuous data integration from IoT sensors and operational systems to reflect accurate, up-to-date virtual replicas of physical assets. Explore how seamless data synchronization bridges CAD precision with digital twin functionality for enhanced design and lifecycle management.
Source and External Links
What is CAD (Computer-Aided Design)? | Definition from TechTarget - CAD is computer-based software used to create 2D drawings and 3D models to aid design processes, allowing visualization, modification, and optimization of products before physical production.
Computer-aided design - Wikipedia - CAD helps in creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design, integrating with other digital product development tools like CAE, CAM, and PDM for comprehensive product lifecycle management.
CAD Software | 2D and 3D Computer-Aided Design - Autodesk - CAD software enables diverse professionals to draft detailed 2D and 3D models and plans, improving collaboration, accuracy, and productivity, with cloud-based options facilitating real-time multiuser access and project management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com