Biophilic design integrates natural elements such as plants, natural light, and organic materials to create living spaces that enhance well-being and foster a connection to nature. Bauhaus emphasizes minimalism, functionality, and geometric forms, focusing on simplicity and industrial materials to optimize space and utility. Explore how these contrasting design philosophies influence modern real estate development and property value.
Why it is important
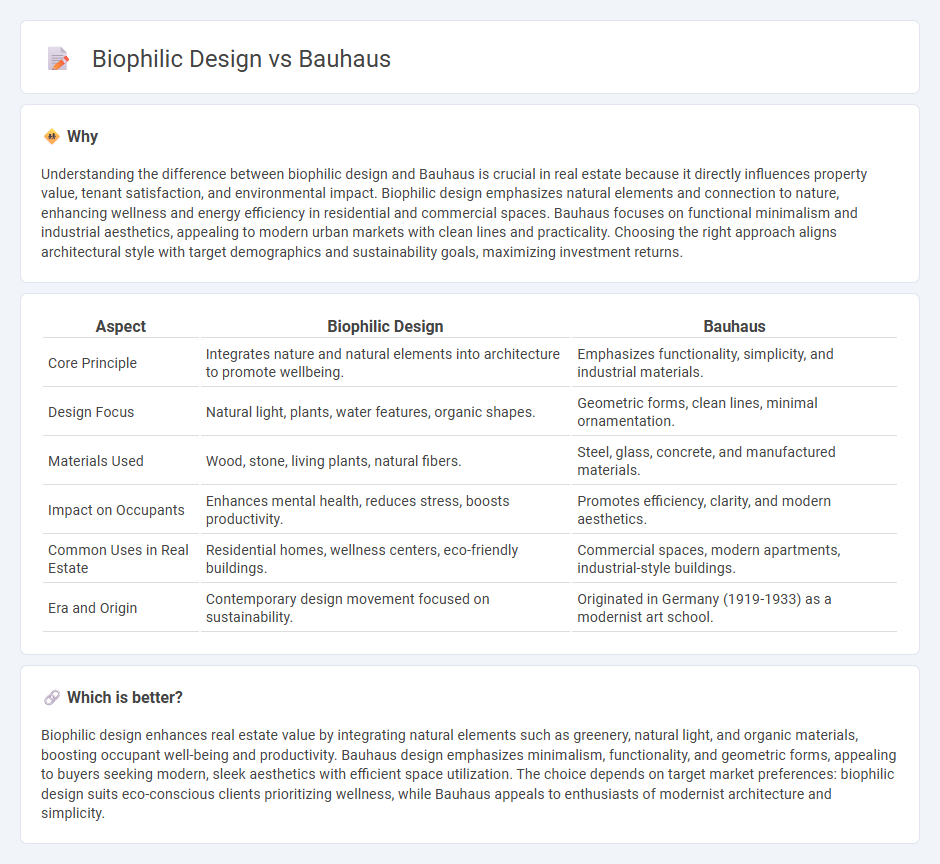
Understanding the difference between biophilic design and Bauhaus is crucial in real estate because it directly influences property value, tenant satisfaction, and environmental impact. Biophilic design emphasizes natural elements and connection to nature, enhancing wellness and energy efficiency in residential and commercial spaces. Bauhaus focuses on functional minimalism and industrial aesthetics, appealing to modern urban markets with clean lines and practicality. Choosing the right approach aligns architectural style with target demographics and sustainability goals, maximizing investment returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biophilic Design | Bauhaus |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Integrates nature and natural elements into architecture to promote wellbeing. | Emphasizes functionality, simplicity, and industrial materials. |
| Design Focus | Natural light, plants, water features, organic shapes. | Geometric forms, clean lines, minimal ornamentation. |
| Materials Used | Wood, stone, living plants, natural fibers. | Steel, glass, concrete, and manufactured materials. |
| Impact on Occupants | Enhances mental health, reduces stress, boosts productivity. | Promotes efficiency, clarity, and modern aesthetics. |
| Common Uses in Real Estate | Residential homes, wellness centers, eco-friendly buildings. | Commercial spaces, modern apartments, industrial-style buildings. |
| Era and Origin | Contemporary design movement focused on sustainability. | Originated in Germany (1919-1933) as a modernist art school. |
Which is better?
Biophilic design enhances real estate value by integrating natural elements such as greenery, natural light, and organic materials, boosting occupant well-being and productivity. Bauhaus design emphasizes minimalism, functionality, and geometric forms, appealing to buyers seeking modern, sleek aesthetics with efficient space utilization. The choice depends on target market preferences: biophilic design suits eco-conscious clients prioritizing wellness, while Bauhaus appeals to enthusiasts of modernist architecture and simplicity.
Connection
Biophilic design enhances real estate value by integrating natural elements that improve occupant well-being and energy efficiency, aligning with Bauhaus principles of functional simplicity and form follows function. Both design philosophies emphasize minimalism and seamless interaction between indoor and outdoor spaces, creating sustainable and aesthetically pleasing environments. Incorporating these concepts in property development can increase market appeal and promote healthier living conditions.
Key Terms
Minimalism (Bauhaus)
Bauhaus design emphasizes minimalism through functional, clean lines and a lack of ornamentation, focusing on simplicity, geometric shapes, and industrial materials such as steel and glass. This style aims to merge art with technology, promoting efficiency and clarity in architectural and interior design. Explore further to understand how Bauhaus minimalism contrasts with organic elements in biophilic design.
Nature Integration (Biophilic Design)
Biophilic design integrates natural elements such as sunlight, greenery, and natural materials to enhance well-being and productivity, contrasting Bauhaus's focus on minimalism and functional geometry. This design philosophy prioritizes human connection to nature through organic forms, textures, and patterns, supporting mental health and sustainability. Explore deeper into how biophilic design transforms spaces with nature-focused innovation.
Functionalism (Bauhaus)
Bauhaus design emphasizes functionalism through minimalist forms, geometric shapes, and an absence of ornamentation, prioritizing practicality and efficient use of materials. This approach contrasts with biophilic design, which integrates natural elements to foster emotional well-being and connection to nature. Explore how these design philosophies shape modern architecture and interior spaces.
Source and External Links
The Bauhaus, 1919-1933 - This essay from the Metropolitan Museum of Art explores the Bauhaus's core objective of uniting all arts and its evolution from a craft-based curriculum to focusing on mass production.
Bauhaus - Wikipedia's entry provides a comprehensive overview of the Bauhaus, including its history, key figures, and architectural influences.
Bauhaus - Tate's description highlights the Bauhaus as a revolutionary art school that sought to integrate art into everyday life through architecture and design.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com