Last mile logistics hubs optimize delivery efficiency by positioning distribution centers near key transportation routes on city outskirts, reducing transit times and costs. Urban infill warehouses focus on repurposing underutilized city spaces within dense urban areas to support rapid, localized delivery and meet growing e-commerce demand. Discover how these real estate strategies transform supply chain dynamics and urban planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between last mile logistics hubs and urban infill warehouses is crucial for optimizing real estate investments and operational efficiency in the supply chain. Last mile logistics hubs focus on rapid distribution close to consumer markets, reducing delivery times and costs. Urban infill warehouses repurpose underutilized urban spaces to support local inventory storage and minimize transportation distances. Recognizing their distinct roles helps developers and investors tailor strategies for market demand and accessibility.
Comparison Table
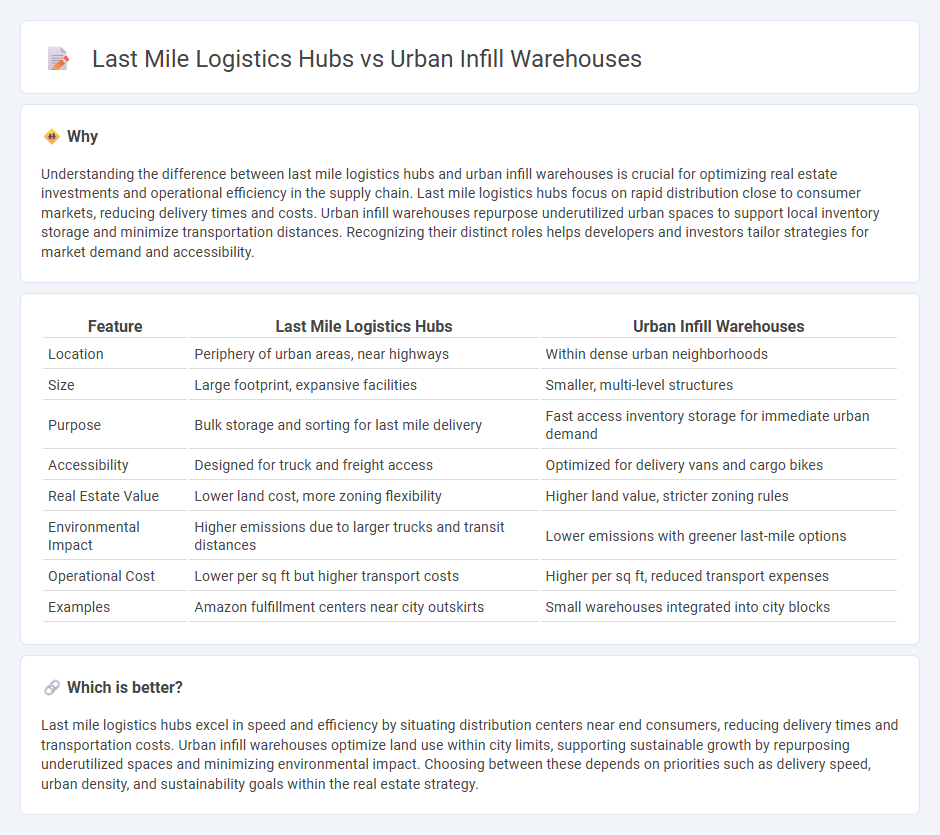
| Feature | Last Mile Logistics Hubs | Urban Infill Warehouses |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Periphery of urban areas, near highways | Within dense urban neighborhoods |
| Size | Large footprint, expansive facilities | Smaller, multi-level structures |
| Purpose | Bulk storage and sorting for last mile delivery | Fast access inventory storage for immediate urban demand |
| Accessibility | Designed for truck and freight access | Optimized for delivery vans and cargo bikes |
| Real Estate Value | Lower land cost, more zoning flexibility | Higher land value, stricter zoning rules |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions due to larger trucks and transit distances | Lower emissions with greener last-mile options |
| Operational Cost | Lower per sq ft but higher transport costs | Higher per sq ft, reduced transport expenses |
| Examples | Amazon fulfillment centers near city outskirts | Small warehouses integrated into city blocks |
Which is better?
Last mile logistics hubs excel in speed and efficiency by situating distribution centers near end consumers, reducing delivery times and transportation costs. Urban infill warehouses optimize land use within city limits, supporting sustainable growth by repurposing underutilized spaces and minimizing environmental impact. Choosing between these depends on priorities such as delivery speed, urban density, and sustainability goals within the real estate strategy.
Connection
Last mile logistics hubs optimize the delivery process by reducing transit times and costs in dense urban areas. Urban infill warehouses strategically utilize underused city spaces, increasing proximity to consumers and enabling faster order fulfillment. Integrating these facilities enhances supply chain efficiency, meeting rising e-commerce demands and reducing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Urban infill warehouses often face stricter zoning regulations compared to last mile logistics hubs, as they must comply with mixed-use district restrictions and noise ordinances in densely populated areas. Last mile logistics hubs are typically located near major transportation networks and enjoy more lenient zoning to facilitate rapid delivery operations. Explore zoning strategies shaping the future of urban logistics for deeper insights.
Proximity to Population Centers
Urban infill warehouses are strategically located within city boundaries, maximizing proximity to dense population centers and enabling rapid delivery times. Last mile logistics hubs, while often positioned near urban fringes, prioritize access to transportation networks for efficient distribution but may be farther from end consumers. Explore how these location strategies impact delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Transportation Infrastructure
Urban infill warehouses leverage existing transportation infrastructure by situating inventory closer to dense population centers, thus reducing last-mile delivery times and transportation costs. Last mile logistics hubs emphasize strategic locations near major highways and transit nodes to optimize large-scale distribution efficiency and connectivity. Explore detailed insights to understand their impacts on transportation networks and urban mobility.
Source and External Links
Making room for industrial infill: Maximizing existing urban infrastructure supports sustainable growth - This article discusses how industrial infill developments, including warehouses, are crucial for urban sustainability by maximizing existing infrastructure and adapting to e-commerce demands.
It's Not All About Urban Infill - This report highlights the trend of industrial tenants preferring exurban areas over urban infill locations, but notes the potential for renovating older urban warehouses to capitalize on local demand.
Why Infill Industrial Properties Outperform in Today's Market - Infill industrial properties, like urban warehouses, are outperforming due to strong demand for logistics and fulfillment infrastructure near densely populated areas, driven by e-commerce growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com