Senior living cohabitation offers shared housing that promotes independence and social interaction among elderly residents, often in a more affordable setting than traditional care facilities. Adult foster care provides personalized, family-style caregiving in a private home, focusing on individualized support for seniors with specific health or mobility needs. Explore the key differences to determine which senior housing option best suits your needs.
Why it is important
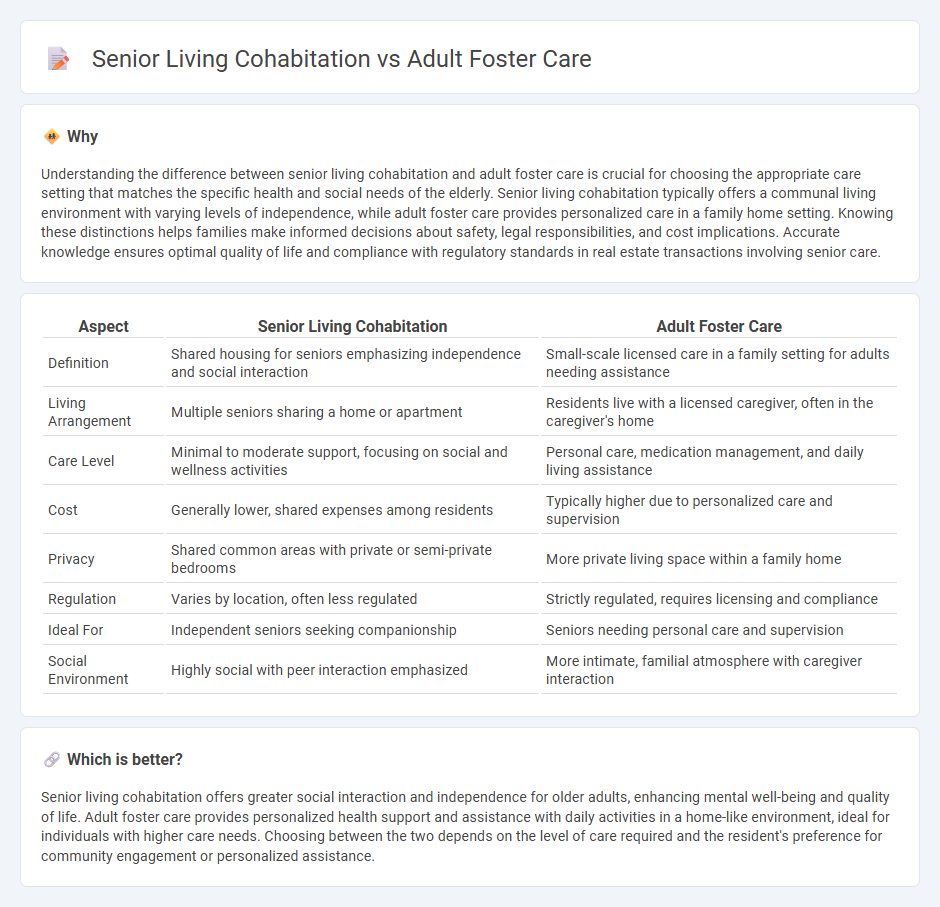
Understanding the difference between senior living cohabitation and adult foster care is crucial for choosing the appropriate care setting that matches the specific health and social needs of the elderly. Senior living cohabitation typically offers a communal living environment with varying levels of independence, while adult foster care provides personalized care in a family home setting. Knowing these distinctions helps families make informed decisions about safety, legal responsibilities, and cost implications. Accurate knowledge ensures optimal quality of life and compliance with regulatory standards in real estate transactions involving senior care.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Senior Living Cohabitation | Adult Foster Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared housing for seniors emphasizing independence and social interaction | Small-scale licensed care in a family setting for adults needing assistance |
| Living Arrangement | Multiple seniors sharing a home or apartment | Residents live with a licensed caregiver, often in the caregiver's home |
| Care Level | Minimal to moderate support, focusing on social and wellness activities | Personal care, medication management, and daily living assistance |
| Cost | Generally lower, shared expenses among residents | Typically higher due to personalized care and supervision |
| Privacy | Shared common areas with private or semi-private bedrooms | More private living space within a family home |
| Regulation | Varies by location, often less regulated | Strictly regulated, requires licensing and compliance |
| Ideal For | Independent seniors seeking companionship | Seniors needing personal care and supervision |
| Social Environment | Highly social with peer interaction emphasized | More intimate, familial atmosphere with caregiver interaction |
Which is better?
Senior living cohabitation offers greater social interaction and independence for older adults, enhancing mental well-being and quality of life. Adult foster care provides personalized health support and assistance with daily activities in a home-like environment, ideal for individuals with higher care needs. Choosing between the two depends on the level of care required and the resident's preference for community engagement or personalized assistance.
Connection
Senior living cohabitation and adult foster care both provide supportive, community-based housing options tailored to older adults requiring assistance with daily activities. They emphasize personalized care in a social environment, enhancing quality of life while reducing the need for institutional settings. These models often utilize shared resources and caregivers to optimize care efficiency and affordability.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations for adult foster care and senior living cohabitation differ significantly, with adult foster care facilities often categorized under residential care or group home zoning, allowing for smaller, home-like settings. Senior living cohabitation arrangements typically face stricter zoning ordinances due to their larger scale and communal living environments, which may require special permits or be confined to specific zones. Explore detailed local zoning laws to understand the legal requirements and restrictions for each type of senior housing option.
Occupancy Limits
Adult foster care typically enforces strict occupancy limits, often capping the number of residents based on state regulations to ensure personalized care and safety. Senior living cohabitation arrangements generally allow more flexible occupancy, accommodating a broader range of living setups from shared apartments to communal homes. Explore the specific occupancy rules and benefits of each option to determine the ideal living environment for seniors.
Licensing Requirements
Adult foster care typically requires state-specific licensing that mandates compliance with health, safety, and staffing standards to ensure personalized care for residents. Senior living cohabitation arrangements often face fewer regulatory constraints, as they may not involve formal caregiving services but emphasize shared living accommodations. Explore further to understand the detailed licensing criteria and how they impact care quality and resident rights.
Source and External Links
What is Adult Foster Care? - Discusses the benefits and suitability of adult foster care for individuals needing assistance with daily activities without requiring intense medical care.
Adult Foster Care: How It Works, Financial Assistance & More - Provides information on how adult foster care works, its costs, and available financial assistance options including Medicaid.
Your Guide to Adult Foster Care Homes - Offers a comprehensive guide to adult foster care homes, including what they are, services offered, and costs involved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com