Infill development maximizes underutilized urban land by constructing new buildings within existing neighborhoods, enhancing property values and urban density without expanding city boundaries. Adaptive reuse preserves historic structures by repurposing them for modern use, combining sustainability with cultural conservation. Discover how these strategies transform cities and offer innovative solutions in real estate.
Why it is important
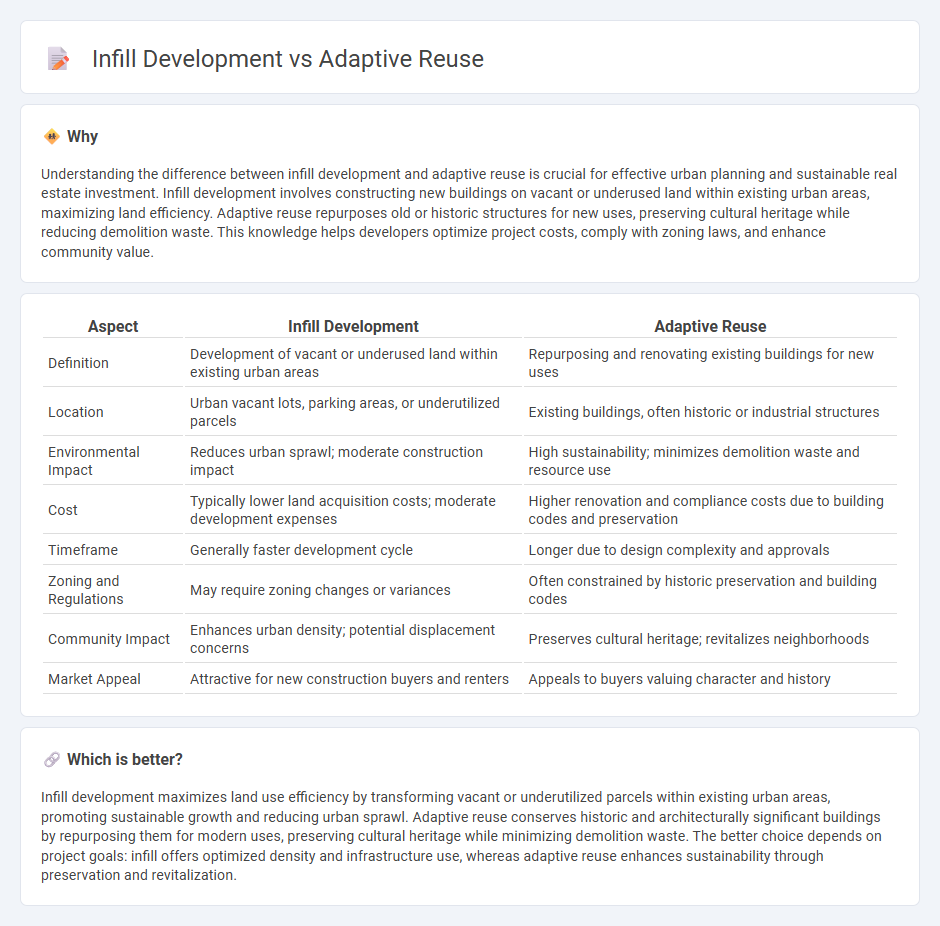
Understanding the difference between infill development and adaptive reuse is crucial for effective urban planning and sustainable real estate investment. Infill development involves constructing new buildings on vacant or underused land within existing urban areas, maximizing land efficiency. Adaptive reuse repurposes old or historic structures for new uses, preserving cultural heritage while reducing demolition waste. This knowledge helps developers optimize project costs, comply with zoning laws, and enhance community value.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Infill Development | Adaptive Reuse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development of vacant or underused land within existing urban areas | Repurposing and renovating existing buildings for new uses |
| Location | Urban vacant lots, parking areas, or underutilized parcels | Existing buildings, often historic or industrial structures |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces urban sprawl; moderate construction impact | High sustainability; minimizes demolition waste and resource use |
| Cost | Typically lower land acquisition costs; moderate development expenses | Higher renovation and compliance costs due to building codes and preservation |
| Timeframe | Generally faster development cycle | Longer due to design complexity and approvals |
| Zoning and Regulations | May require zoning changes or variances | Often constrained by historic preservation and building codes |
| Community Impact | Enhances urban density; potential displacement concerns | Preserves cultural heritage; revitalizes neighborhoods |
| Market Appeal | Attractive for new construction buyers and renters | Appeals to buyers valuing character and history |
Which is better?
Infill development maximizes land use efficiency by transforming vacant or underutilized parcels within existing urban areas, promoting sustainable growth and reducing urban sprawl. Adaptive reuse conserves historic and architecturally significant buildings by repurposing them for modern uses, preserving cultural heritage while minimizing demolition waste. The better choice depends on project goals: infill offers optimized density and infrastructure use, whereas adaptive reuse enhances sustainability through preservation and revitalization.
Connection
Infill development and adaptive reuse both focus on maximizing land efficiency within urban areas by repurposing existing spaces to meet current needs. Infill development utilizes vacant or underused parcels within built-up environments, while adaptive reuse transforms obsolete buildings into functional properties, often preserving architectural heritage. These strategies reduce urban sprawl and promote sustainable growth through revitalizing infrastructure and enhancing community value.
Key Terms
Zoning
Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings in compliance with zoning regulations that may require special permits or variances due to changes in building use. Infill development focuses on constructing new buildings on vacant or underutilized parcels within existing zones, often benefiting from streamlined approvals in areas with compatible land use designations. Explore zoning considerations further to understand the feasibility and regulatory impact on both adaptive reuse and infill development projects.
Historic Preservation
Adaptive reuse preserves historic buildings by repurposing existing structures for new functions, maintaining architectural heritage and cultural significance. Infill development involves constructing new buildings on vacant or underutilized urban lots, often complementing historic districts while optimizing land use. Explore how these strategies balance growth and conservation in historic preservation.
Land Utilization
Adaptive reuse maximizes land utilization by repurposing existing structures, reducing the need for new land consumption and minimizing urban sprawl. Infill development enhances land efficiency by developing vacant or underused parcels within established urban areas, promoting density and sustainable growth. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how each strategy impacts urban planning and resource management.
Source and External Links
Adaptive reuse - Wikipedia - Adaptive reuse is the process of reusing an existing building for a different purpose than originally designed, allowing preservation of historic features while extending the building's life and reducing environmental impact through reuse rather than demolition.
What is adaptive reuse (and why is it important)? - Adaptive reuse refers to repurposing buildings at the end of their lifespan for new uses, maintaining cultural and historical elements, and serving as a sustainable alternative to demolition by reducing CO2 emissions.
A Complete Guide to Adaptive Reuse in 2023 - MBH Architects - Adaptive reuse includes various types such as renovation, integration, and preservation, focusing on sustainable renovation or addition to existing buildings for new functions after their original use has ended.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com