Urban consolidation centers streamline last-mile delivery by centralizing goods from multiple suppliers to reduce traffic congestion and emissions in city centers. Distribution centers focus on large-scale storage and order fulfillment, serving broader regions with extensive inventory management systems. Explore the key differences and benefits of each facility to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
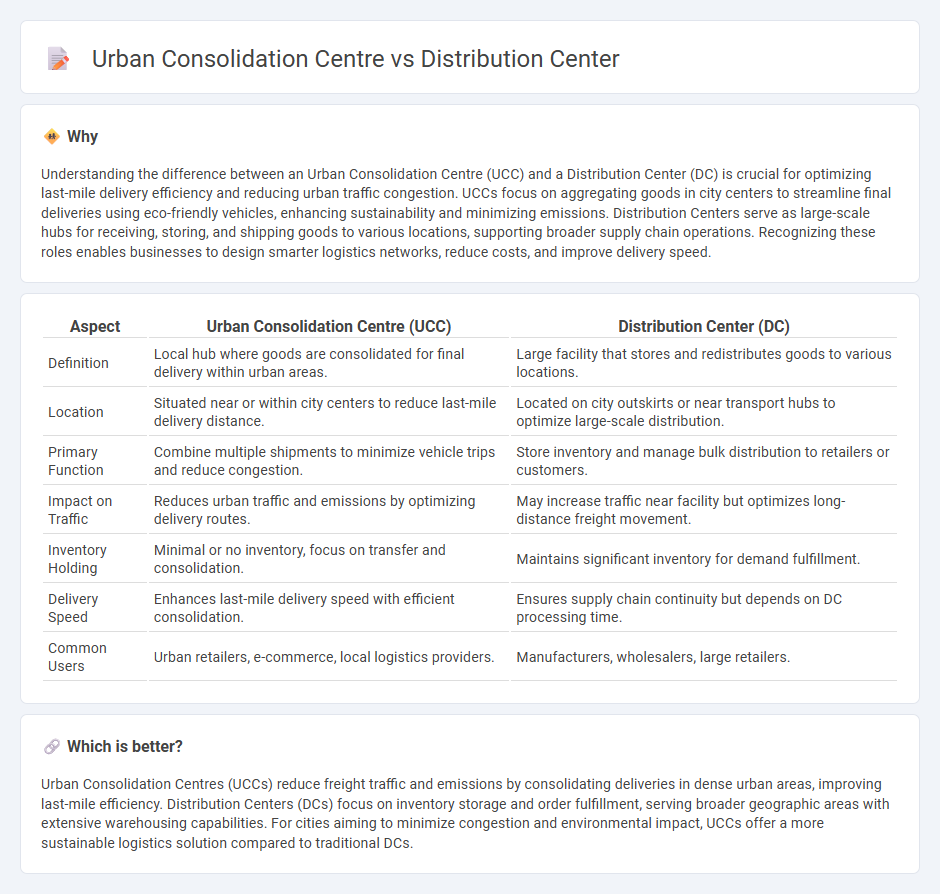
Understanding the difference between an Urban Consolidation Centre (UCC) and a Distribution Center (DC) is crucial for optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency and reducing urban traffic congestion. UCCs focus on aggregating goods in city centers to streamline final deliveries using eco-friendly vehicles, enhancing sustainability and minimizing emissions. Distribution Centers serve as large-scale hubs for receiving, storing, and shipping goods to various locations, supporting broader supply chain operations. Recognizing these roles enables businesses to design smarter logistics networks, reduce costs, and improve delivery speed.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Consolidation Centre (UCC) | Distribution Center (DC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Local hub where goods are consolidated for final delivery within urban areas. | Large facility that stores and redistributes goods to various locations. |
| Location | Situated near or within city centers to reduce last-mile delivery distance. | Located on city outskirts or near transport hubs to optimize large-scale distribution. |
| Primary Function | Combine multiple shipments to minimize vehicle trips and reduce congestion. | Store inventory and manage bulk distribution to retailers or customers. |
| Impact on Traffic | Reduces urban traffic and emissions by optimizing delivery routes. | May increase traffic near facility but optimizes long-distance freight movement. |
| Inventory Holding | Minimal or no inventory, focus on transfer and consolidation. | Maintains significant inventory for demand fulfillment. |
| Delivery Speed | Enhances last-mile delivery speed with efficient consolidation. | Ensures supply chain continuity but depends on DC processing time. |
| Common Users | Urban retailers, e-commerce, local logistics providers. | Manufacturers, wholesalers, large retailers. |
Which is better?
Urban Consolidation Centres (UCCs) reduce freight traffic and emissions by consolidating deliveries in dense urban areas, improving last-mile efficiency. Distribution Centers (DCs) focus on inventory storage and order fulfillment, serving broader geographic areas with extensive warehousing capabilities. For cities aiming to minimize congestion and environmental impact, UCCs offer a more sustainable logistics solution compared to traditional DCs.
Connection
Urban consolidation centers (UCCs) streamline last-mile logistics by consolidating goods from multiple suppliers to reduce delivery trips within congested city areas. Distribution centers (DCs) serve as key inventory hubs where products are received, stored, and sorted before being dispatched to UCCs. The integration between DCs and UCCs enhances supply chain efficiency, lowers transportation costs, and minimizes urban traffic congestion.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Distribution centers centralize inventory storage and facilitate bulk shipments to retail locations, optimizing stock levels and reducing delivery times for large-scale operations. Urban consolidation centres focus on consolidating deliveries within city environments, minimizing urban congestion and enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency while maintaining precise inventory tracking to meet local demand fluctuations. Explore how integrating these facilities can streamline inventory management and improve supply chain agility.
Last-Mile Delivery
Distribution centers serve as large-scale hubs managing inventory storage and outbound logistics, often located on city peripheries to facilitate bulk transportation. Urban consolidation centers operate within city limits to aggregate shipments, reducing delivery vehicles' trips and minimizing congestion in last-mile delivery networks. Explore how integrating these systems enhances efficiency and sustainability in urban logistics.
Cross-Docking
Distribution centers primarily serve as centralized nodes for inventory storage, order processing, and last-mile delivery, whereas urban consolidation centres (UCCs) focus on aggregating shipments to optimize freight transport within city limits. Cross-docking is a critical operation in UCCs, enabling direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transport with minimal or no storage, reducing delivery times and urban traffic congestion. Explore more about how cross-docking innovations in urban consolidation centres can enhance supply chain efficiency and sustainability.
Source and External Links
Distribution Centers Explained - Distribution centers are logistics facilities that store, pick, pack, and ship finished goods efficiently to customers, acting as a key hub in the modern supply chain to speed delivery by centralizing inventory closer to customers.
What Is a Distribution Center and How Do They Work? - A distribution center is a facility where goods are received, quality checked, stored temporarily, managed, and then shipped timely to resellers or end users, often using equipment and staff to handle inventory and orders effectively.
Warehouse vs. Distribution Center Explained - WiSys - A distribution center is distinct from a warehouse by its active role in order fulfillment including receiving, product mixing, cross-docking, packaging, and shipping goods quickly to customers or retail locations rather than simply storing them long-term.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com