Milk run logistics optimizes supply chain efficiency by consolidating multiple deliveries into a single trip, reducing transportation costs and minimizing inventory levels. Transshipment involves transferring goods at intermediate nodes, facilitating flexible routing and improving delivery speed across complex networks. Discover the key differences to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
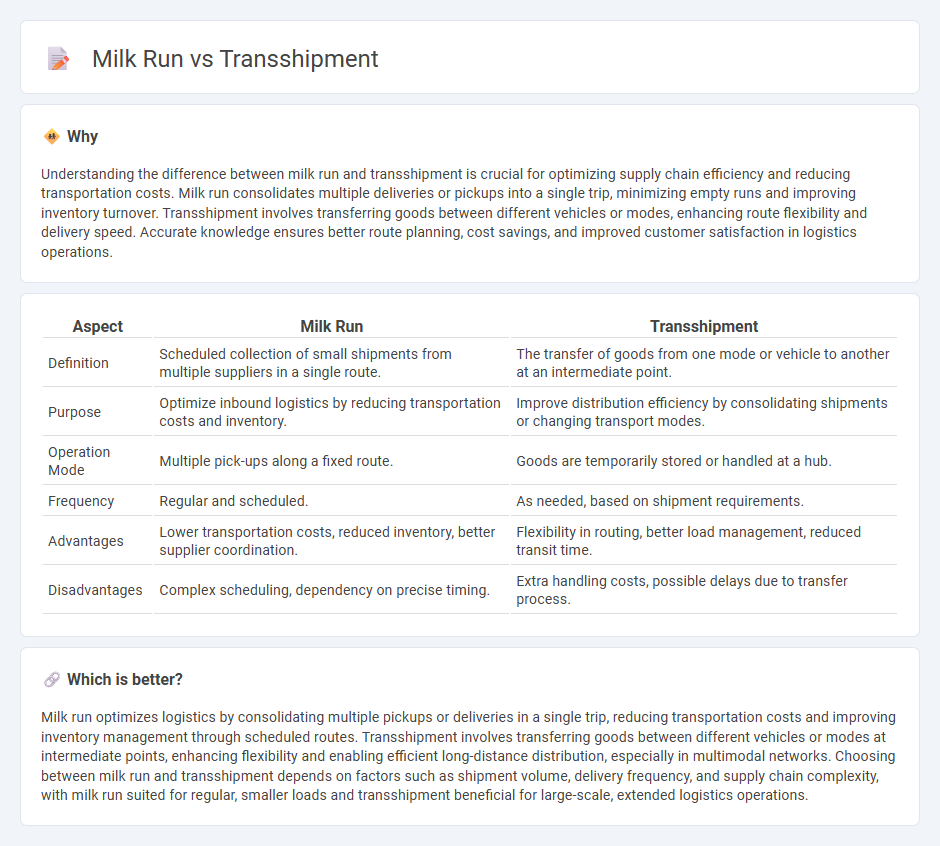
Understanding the difference between milk run and transshipment is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Milk run consolidates multiple deliveries or pickups into a single trip, minimizing empty runs and improving inventory turnover. Transshipment involves transferring goods between different vehicles or modes, enhancing route flexibility and delivery speed. Accurate knowledge ensures better route planning, cost savings, and improved customer satisfaction in logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Milk Run | Transshipment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled collection of small shipments from multiple suppliers in a single route. | The transfer of goods from one mode or vehicle to another at an intermediate point. |
| Purpose | Optimize inbound logistics by reducing transportation costs and inventory. | Improve distribution efficiency by consolidating shipments or changing transport modes. |
| Operation Mode | Multiple pick-ups along a fixed route. | Goods are temporarily stored or handled at a hub. |
| Frequency | Regular and scheduled. | As needed, based on shipment requirements. |
| Advantages | Lower transportation costs, reduced inventory, better supplier coordination. | Flexibility in routing, better load management, reduced transit time. |
| Disadvantages | Complex scheduling, dependency on precise timing. | Extra handling costs, possible delays due to transfer process. |
Which is better?
Milk run optimizes logistics by consolidating multiple pickups or deliveries in a single trip, reducing transportation costs and improving inventory management through scheduled routes. Transshipment involves transferring goods between different vehicles or modes at intermediate points, enhancing flexibility and enabling efficient long-distance distribution, especially in multimodal networks. Choosing between milk run and transshipment depends on factors such as shipment volume, delivery frequency, and supply chain complexity, with milk run suited for regular, smaller loads and transshipment beneficial for large-scale, extended logistics operations.
Connection
Milk run logistics optimizes supply chain efficiency by consolidating multiple shipments into a single route, reducing transportation costs and minimizing inventory levels. Transshipment plays a crucial role in this process by facilitating the transfer of goods between different vehicles or transportation modes at intermediate points. Together, milk run and transshipment enhance distribution networks by improving delivery frequency and flexibility while reducing lead times in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Transshipment:
Transshipment involves transferring goods from one mode of transport to another at an intermediate point, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing shipping costs. It plays a crucial role in global logistics, enabling consolidation of cargo and minimizing delivery times. Discover more about how transshipment can enhance your supply chain operations.
Hub-and-spoke
Transshipment in a hub-and-spoke model centralizes cargo at a hub where goods are sorted and redirected to their final destinations, optimizing route efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Milk run logistics complement this by enabling scheduled pickups and deliveries along fixed routes, minimizing inventory levels and improving supply chain reliability. Explore how integrating these strategies enhances overall distribution network performance.
Intermediate handling
Intermediate handling in transshipment involves transferring goods between different transport modes or vehicles at a transfer point, optimizing load consolidation and route efficiency. Milk run logistics focus on scheduled, multi-stop pickups and deliveries, minimizing inventory levels and enhancing supply chain responsiveness through repeated intermediate handling activities. Explore the detailed differences in intermediate handling to optimize your supply chain operations.
Source and External Links
Transshipment - Wikipedia - Transshipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
Transshipment: Meaning, process, types and more - Amazon - Transshipment involves unloading cargo from one vessel and reloading it into another during its journey from origin to final destination, passing through customs and documentation at an intermediate port.
What is Transshipment? Complete guide [+lease containers] - Transshipment is a supply chain process where containers are transferred at an intermediary hub from one vessel to another, essential when direct shipping routes are unavailable, exemplified by transport from South Africa to the Philippines via Singapore.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com