Cold chain logistics involves the specialized transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods such as pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and bio-products, ensuring strict temperature controls from origin to destination. Drayage logistics focuses on the short-distance movement of freight, commonly between ports, rail yards, and warehouses, serving as a critical link in the supply chain for containerized cargo. Discover the distinct operational challenges and technological innovations driving efficiency in these vital logistics sectors.
Why it is important
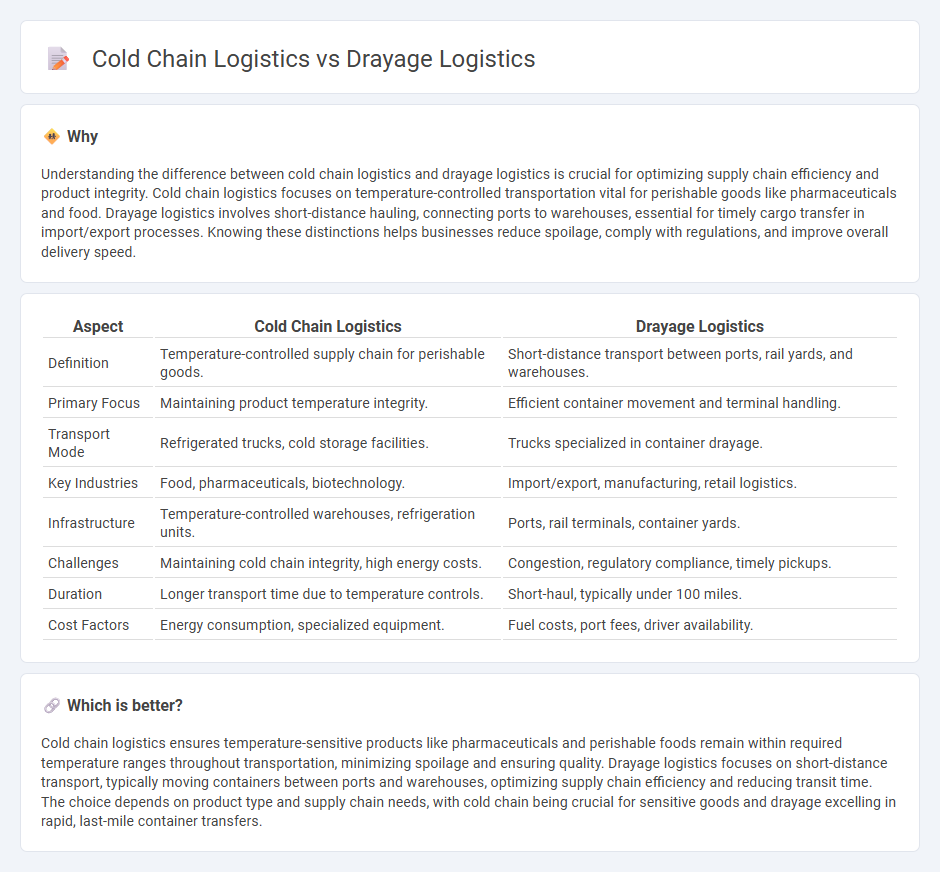
Understanding the difference between cold chain logistics and drayage logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and product integrity. Cold chain logistics focuses on temperature-controlled transportation vital for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food. Drayage logistics involves short-distance hauling, connecting ports to warehouses, essential for timely cargo transfer in import/export processes. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses reduce spoilage, comply with regulations, and improve overall delivery speed.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Drayage Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Short-distance transport between ports, rail yards, and warehouses. |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product temperature integrity. | Efficient container movement and terminal handling. |
| Transport Mode | Refrigerated trucks, cold storage facilities. | Trucks specialized in container drayage. |
| Key Industries | Food, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology. | Import/export, manufacturing, retail logistics. |
| Infrastructure | Temperature-controlled warehouses, refrigeration units. | Ports, rail terminals, container yards. |
| Challenges | Maintaining cold chain integrity, high energy costs. | Congestion, regulatory compliance, timely pickups. |
| Duration | Longer transport time due to temperature controls. | Short-haul, typically under 100 miles. |
| Cost Factors | Energy consumption, specialized equipment. | Fuel costs, port fees, driver availability. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods remain within required temperature ranges throughout transportation, minimizing spoilage and ensuring quality. Drayage logistics focuses on short-distance transport, typically moving containers between ports and warehouses, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing transit time. The choice depends on product type and supply chain needs, with cold chain being crucial for sensitive goods and drayage excelling in rapid, last-mile container transfers.
Connection
Cold chain logistics and drayage logistics are interconnected through the critical role drayage plays in efficiently transporting temperature-sensitive goods from ports to nearby storage or distribution centers. Maintaining strict temperature controls during drayage ensures the integrity of perishable items within the cold chain, reducing spoilage and compliance risks. This seamless integration optimizes supply chain operations by bridging maritime shipping and refrigerated storage with timely, short-distance cargo movement.
Key Terms
Drayage Logistics:
Drayage logistics involves the transport of goods over short distances, primarily moving containers between ports, rail yards, and warehouses, ensuring efficient last-mile delivery within supply chains. This sector relies heavily on precise scheduling, local regulations compliance, and rapid turnarounds to minimize demurrage charges and optimize cargo flow. Explore the intricacies of drayage logistics to understand its pivotal role in streamlining global trade operations.
Intermodal Containers
Drayage logistics specializes in the short-haul transportation of intermodal containers between ports, rail terminals, and warehouses, optimizing efficiency in cargo transfer. Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled handling and storage of perishable goods within intermodal containers, crucial for maintaining product quality during transit. Explore the nuances of both to enhance your supply chain strategy.
Port Operations
Drayage logistics involves the short-distance transportation of goods from ports to nearby warehouses, focusing on efficient container movement and turnaround times to reduce congestion and improve port throughput. Cold chain logistics centers on maintaining temperature-controlled environments throughout the supply chain, critical for perishable goods handled at ports with specialized refrigerated storage and equipment. Explore the intricacies of port operations to understand how drayage and cold chain logistics intersect and impact global trade efficiency.
Source and External Links
Drayage: Meaning, Importance, and Types - Drayage is short-haul transport within a single urban area that is critical in connecting cargo from ports to the next stage in the supply chain, influencing the entire shipping logistics process.
What is drayage? - Drayage involves freight transportation over short distances, mostly by truck, with various types such as port drayage, inter-carrier, intra-carrier, expedited, long-haul, shuttle, and door-to-door services to meet specific logistics needs.
What is Drayage? - Drayage connects different modes of long-haul transport through short-haul trucking, facilitating multimodal transport by moving freight containers between ports, rail yards, warehouses, and distribution centers, which is essential for global supply chains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com