Middle mile optimization focuses on enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of transporting goods between warehouses and distribution centers, reducing transit time and fuel consumption. Transshipment involves transferring shipments from one mode of transportation to another at intermediate points to optimize routing and consolidate loads. Explore how these strategies can significantly improve supply chain performance and reduce operational costs.
Why it is important
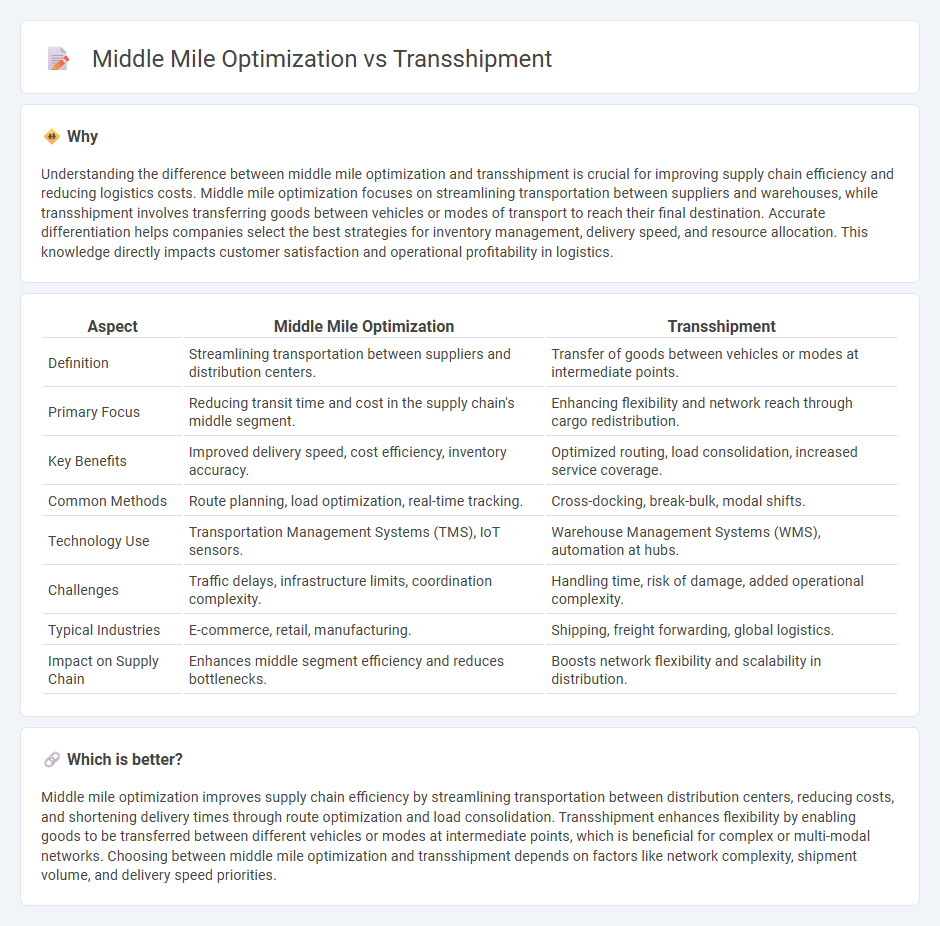
Understanding the difference between middle mile optimization and transshipment is crucial for improving supply chain efficiency and reducing logistics costs. Middle mile optimization focuses on streamlining transportation between suppliers and warehouses, while transshipment involves transferring goods between vehicles or modes of transport to reach their final destination. Accurate differentiation helps companies select the best strategies for inventory management, delivery speed, and resource allocation. This knowledge directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational profitability in logistics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Middle Mile Optimization | Transshipment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Streamlining transportation between suppliers and distribution centers. | Transfer of goods between vehicles or modes at intermediate points. |
| Primary Focus | Reducing transit time and cost in the supply chain's middle segment. | Enhancing flexibility and network reach through cargo redistribution. |
| Key Benefits | Improved delivery speed, cost efficiency, inventory accuracy. | Optimized routing, load consolidation, increased service coverage. |
| Common Methods | Route planning, load optimization, real-time tracking. | Cross-docking, break-bulk, modal shifts. |
| Technology Use | Transportation Management Systems (TMS), IoT sensors. | Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), automation at hubs. |
| Challenges | Traffic delays, infrastructure limits, coordination complexity. | Handling time, risk of damage, added operational complexity. |
| Typical Industries | E-commerce, retail, manufacturing. | Shipping, freight forwarding, global logistics. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Enhances middle segment efficiency and reduces bottlenecks. | Boosts network flexibility and scalability in distribution. |
Which is better?
Middle mile optimization improves supply chain efficiency by streamlining transportation between distribution centers, reducing costs, and shortening delivery times through route optimization and load consolidation. Transshipment enhances flexibility by enabling goods to be transferred between different vehicles or modes at intermediate points, which is beneficial for complex or multi-modal networks. Choosing between middle mile optimization and transshipment depends on factors like network complexity, shipment volume, and delivery speed priorities.
Connection
Middle mile optimization improves logistics efficiency by streamlining the transport of goods between suppliers and distribution centers, reducing transit times and costs. Transshipment plays a crucial role in this process by enabling the transfer of cargo between different vehicles or transportation modes at intermediate hubs, facilitating better route management and load consolidation. Together, these strategies enhance supply chain responsiveness and reduce overall freight expenses.
Key Terms
Cross-docking
Cross-docking significantly enhances middle mile optimization by minimizing storage time and accelerating the transshipment process, ensuring goods move swiftly from inbound to outbound transportation. This method reduces handling costs, mitigates inventory holding, and improves supply chain efficiency by aligning inbound and outbound freight schedules. Discover how leveraging cross-docking strategies can transform your logistics operations and boost overall performance.
Consolidation
Transshipment facilitates consolidation by transferring shipments between carriers or modes at intermediate points, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery efficiency in the supply chain. Middle mile optimization centers on streamlining the movement of goods from warehouses to distribution centers, maximizing load consolidation to minimize empty miles and enhance route efficiency. Explore effective consolidation strategies to boost supply chain performance and reduce operational costs.
Hub-and-spoke
The hub-and-spoke model streamlines transshipment by consolidating shipments at central hubs before dispatching them to final destinations, reducing costs and improving delivery times. Middle mile optimization focuses on enhancing routes and load efficiency between hubs and spokes to maximize transportation resources and minimize transit delays. Explore more about leveraging hub-and-spoke strategies for superior supply chain performance.
Source and External Links
Transshipment - Wikipedia - Transshipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
What is Transshipment? - MSC - Transshipment involves unloading cargo from one vessel and reloading it onto another at an intermediate port, serving as a hub before final delivery and often used to avoid congestion or customize cargo.
What is Transshipment? Complete guide [+lease containers] - Transshipment is the process where cargo containers are moved from one vessel to another at an intermediary hub during transit to their final port of discharge, enabling shipping routes without direct connections.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com