Quick commerce prioritizes speed by delivering products within minutes or hours, leveraging local micro-fulfillment centers and advanced real-time inventory management systems. Traditional e-commerce relies on centralized warehouses and longer delivery windows, often spanning several days, focusing on broader geographic reach and bulk shipping. Explore how these contrasting logistics models impact consumer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and traditional e-commerce is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies and meeting consumer expectations. Quick commerce prioritizes ultra-fast delivery within minutes or hours, demanding localized inventory and advanced last-mile logistics, whereas traditional e-commerce focuses on broader product variety with longer delivery times. Precise knowledge of these models enables logistics firms to allocate resources effectively, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. This distinction also drives innovations in warehousing, transportation, and order fulfillment systems tailored to each commerce type.
Comparison Table
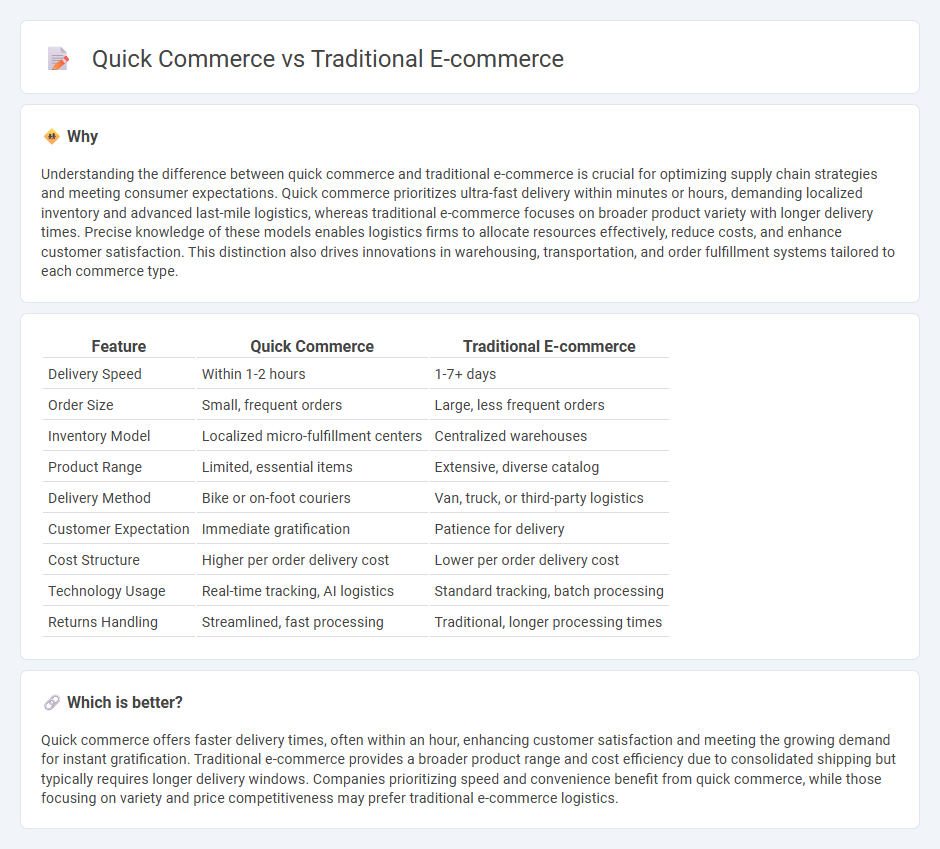
| Feature | Quick Commerce | Traditional E-commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | Within 1-2 hours | 1-7+ days |
| Order Size | Small, frequent orders | Large, less frequent orders |
| Inventory Model | Localized micro-fulfillment centers | Centralized warehouses |
| Product Range | Limited, essential items | Extensive, diverse catalog |
| Delivery Method | Bike or on-foot couriers | Van, truck, or third-party logistics |
| Customer Expectation | Immediate gratification | Patience for delivery |
| Cost Structure | Higher per order delivery cost | Lower per order delivery cost |
| Technology Usage | Real-time tracking, AI logistics | Standard tracking, batch processing |
| Returns Handling | Streamlined, fast processing | Traditional, longer processing times |
Which is better?
Quick commerce offers faster delivery times, often within an hour, enhancing customer satisfaction and meeting the growing demand for instant gratification. Traditional e-commerce provides a broader product range and cost efficiency due to consolidated shipping but typically requires longer delivery windows. Companies prioritizing speed and convenience benefit from quick commerce, while those focusing on variety and price competitiveness may prefer traditional e-commerce logistics.
Connection
Quick commerce leverages advanced logistics networks and real-time inventory management systems originally developed for traditional e-commerce to expedite order fulfillment. Both models rely heavily on last-mile delivery optimization, warehousing strategies, and supply chain integration to meet consumer demand efficiently. The seamless integration of data analytics and automated sorting technologies connects quick commerce operations with traditional e-commerce platforms, enhancing overall delivery speed and customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
Delivery Time
Traditional e-commerce typically offers delivery times ranging from 2 to 7 days, prioritizing inventory consolidation and cost efficiency. Quick commerce emphasizes ultra-fast delivery, often within 30 minutes to 2 hours, by leveraging local warehouses and advanced logistics technology. Explore the key differences in delivery speed and customer impact to understand which model suits your business needs.
Inventory Management
Traditional e-commerce relies on centralized warehouses with extensive inventory, leading to longer delivery times but broader product availability. Quick commerce focuses on hyper-local, small-scale inventory stored in micro-fulfillment centers, enabling rapid delivery within minutes. Discover how these approaches impact supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Last-mile Fulfillment
Traditional e-commerce relies heavily on centralized warehousing and slower delivery timelines, often spanning several days to complete last-mile fulfillment. Quick commerce, by contrast, emphasizes ultrafast delivery through localized micro-fulfillment centers or dark stores, enabling delivery times as short as 10 to 30 minutes. Explore more to understand how last-mile strategies can transform customer experience and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Difference between Traditional Commerce and E-commerce - Traditional e-commerce involves buying or selling products/services electronically using the internet, contrasting with traditional commerce where transactions occur face-to-face without internet involvement, typically in physical markets or stores.
Quick Commerce vs. Traditional E-Commerce - Traditional e-commerce uses large warehouses and courier services to ship products, offers customers more time to research, and typically provides a wider range of products at lower costs compared to quick commerce's focus on instant delivery.
E-commerce vs Traditional commerce vs Social commerce - Traditional commerce takes place at a geographical location allowing customers to physically choose goods, whereas e-commerce conducts buying and selling online through product images and descriptions, with delivery arranged for the customer.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com