Containerization revolutionizes logistics by enabling standardized, efficient transport of goods across multiple modes without handling the cargo itself, significantly reducing transit times and costs. Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining temperature-sensitive products within strict environmental conditions through specialized refrigerated containers and monitoring systems to ensure product integrity from origin to destination. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of containerization versus cold chain logistics to optimize supply chain performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between containerization and cold chain logistics is crucial for ensuring the integrity and security of goods during transportation. Containerization offers standardized, efficient handling of a wide range of products, while cold chain logistics specifically maintains temperature-sensitive items like pharmaceuticals and food at controlled temperatures. Proper knowledge prevents product spoilage, reduces losses, and ensures regulatory compliance. This distinction optimizes supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction in logistics management.
Comparison Table
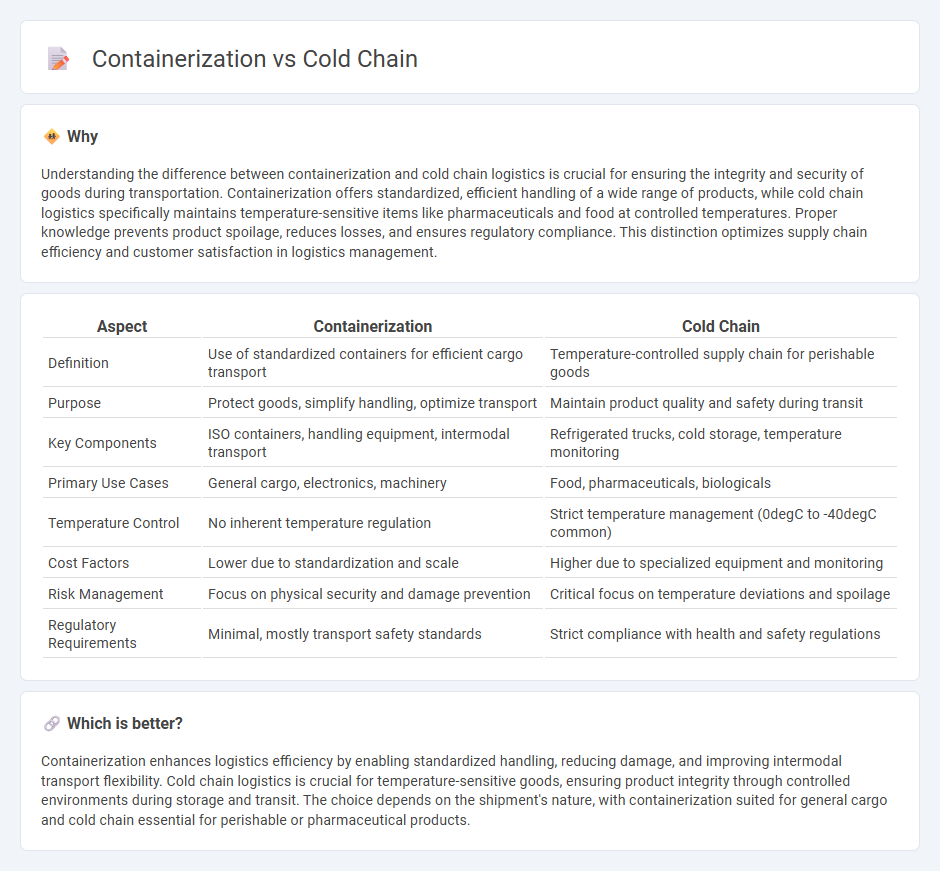
| Aspect | Containerization | Cold Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of standardized containers for efficient cargo transport | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods |
| Purpose | Protect goods, simplify handling, optimize transport | Maintain product quality and safety during transit |
| Key Components | ISO containers, handling equipment, intermodal transport | Refrigerated trucks, cold storage, temperature monitoring |
| Primary Use Cases | General cargo, electronics, machinery | Food, pharmaceuticals, biologicals |
| Temperature Control | No inherent temperature regulation | Strict temperature management (0degC to -40degC common) |
| Cost Factors | Lower due to standardization and scale | Higher due to specialized equipment and monitoring |
| Risk Management | Focus on physical security and damage prevention | Critical focus on temperature deviations and spoilage |
| Regulatory Requirements | Minimal, mostly transport safety standards | Strict compliance with health and safety regulations |
Which is better?
Containerization enhances logistics efficiency by enabling standardized handling, reducing damage, and improving intermodal transport flexibility. Cold chain logistics is crucial for temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring product integrity through controlled environments during storage and transit. The choice depends on the shipment's nature, with containerization suited for general cargo and cold chain essential for perishable or pharmaceutical products.
Connection
Containerization enhances the efficiency of cold chain logistics by providing standardized, insulated containers equipped with temperature control systems that maintain the integrity of perishable goods during transportation. The integration of refrigerated containers (reefers) ensures consistent cooling and reduces spoilage across long-distance supply chains, critical for pharmaceuticals, seafood, and fresh produce. This synergy between containerization and cold chain technology drives cost-effective, reliable, and scalable cold logistics solutions worldwide.
Key Terms
**Cold Chain:**
Cold chain logistics involves the temperature-controlled supply chain essential for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals, seafood, and produce, ensuring product integrity from origin to destination. It relies on refrigeration technologies, insulated packaging, and real-time temperature monitoring to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life. Discover more about the critical role of cold chain solutions in global trade and healthcare.
Refrigeration
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled transportation of perishable goods using refrigerated trucks, storage units, and specialized packaging to maintain product integrity from origin to destination. Containerization involves the use of standardized containers, often refrigerated (reefers), to facilitate efficient, large-scale shipping while preserving required cold temperatures throughout transit. Explore more about how refrigeration technologies innovate cold chain and containerization for global supply chains.
Temperature Monitoring
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods maintain a consistent environment, using specialized refrigerated storage and transport methods with real-time temperature monitoring systems. Containerization involves transporting goods in standardized containers, which can include refrigerated units (reefers) equipped with advanced temperature sensors and GPS tracking for precise climate control. Explore in-depth comparisons of cold chain and containerized temperature monitoring technologies to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
B.9 - The Cold Chain and its Logistics - This article discusses how the cold chain involves the transportation of temperature-sensitive products through thermal and refrigerated packaging methods across a supply chain.
Cold Chain Definition | UPS Supply Chain Solutions - The cold chain is a continuous temperature-controlled supply chain designed to preserve the life cycle of perishable products like foods, drugs, and chemicals.
Cold Chain - Wikipedia - The cold chain is a supply chain that uses refrigeration to maintain perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, produce, and other temperature-sensitive products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com