Freight marketplaces provide a digital platform connecting shippers and carriers with transparent pricing, real-time tracking, and streamlined booking processes. Spot markets focus on immediate, short-term freight contracts often driven by urgent demand fluctuations and dynamic pricing. Explore more to understand how these models impact supply chain efficiency and cost management.
Why it is important
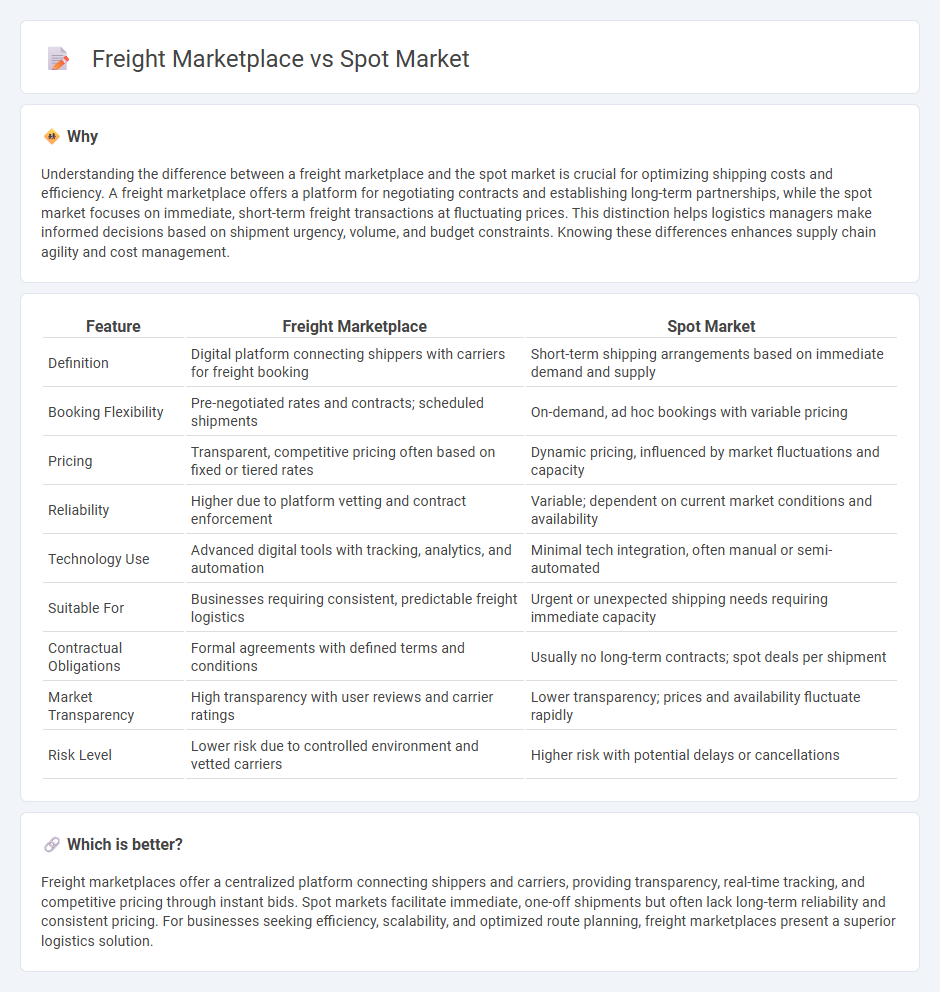
Understanding the difference between a freight marketplace and the spot market is crucial for optimizing shipping costs and efficiency. A freight marketplace offers a platform for negotiating contracts and establishing long-term partnerships, while the spot market focuses on immediate, short-term freight transactions at fluctuating prices. This distinction helps logistics managers make informed decisions based on shipment urgency, volume, and budget constraints. Knowing these differences enhances supply chain agility and cost management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Freight Marketplace | Spot Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital platform connecting shippers with carriers for freight booking | Short-term shipping arrangements based on immediate demand and supply |
| Booking Flexibility | Pre-negotiated rates and contracts; scheduled shipments | On-demand, ad hoc bookings with variable pricing |
| Pricing | Transparent, competitive pricing often based on fixed or tiered rates | Dynamic pricing, influenced by market fluctuations and capacity |
| Reliability | Higher due to platform vetting and contract enforcement | Variable; dependent on current market conditions and availability |
| Technology Use | Advanced digital tools with tracking, analytics, and automation | Minimal tech integration, often manual or semi-automated |
| Suitable For | Businesses requiring consistent, predictable freight logistics | Urgent or unexpected shipping needs requiring immediate capacity |
| Contractual Obligations | Formal agreements with defined terms and conditions | Usually no long-term contracts; spot deals per shipment |
| Market Transparency | High transparency with user reviews and carrier ratings | Lower transparency; prices and availability fluctuate rapidly |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to controlled environment and vetted carriers | Higher risk with potential delays or cancellations |
Which is better?
Freight marketplaces offer a centralized platform connecting shippers and carriers, providing transparency, real-time tracking, and competitive pricing through instant bids. Spot markets facilitate immediate, one-off shipments but often lack long-term reliability and consistent pricing. For businesses seeking efficiency, scalability, and optimized route planning, freight marketplaces present a superior logistics solution.
Connection
The freight marketplace and spot market are interconnected through real-time matching of shippers and carriers for immediate transportation needs. Spot markets facilitate dynamic pricing based on current supply and demand, which freight marketplaces leverage to optimize shipment allocations. This integration enhances efficiency, reduces deadhead miles, and provides transparency in freight logistics operations.
Key Terms
Real-time Pricing
Spot market pricing fluctuates based on immediate supply and demand, offering shippers and carriers real-time rates for freight services. Freight marketplaces aggregate these dynamic prices from multiple carriers to provide transparent, competitive bids instantly. Explore how real-time pricing in freight marketplaces can optimize your shipping costs and improve efficiency.
Load Matching
The spot market enables immediate shipment contracts based on real-time pricing, allowing shippers and carriers to quickly match loads with available trucks for urgent freight needs. Freight marketplaces utilize advanced algorithms and data analytics to optimize load matching by connecting multiple shippers and carriers in a centralized platform, enhancing efficiency and reducing empty miles. Explore how load matching innovations in these platforms can streamline logistics and reduce transportation costs.
Carrier Network
Spot markets in freight operate through immediate, demand-driven transactions connecting shippers with available carriers in real-time, optimizing route efficiency and reducing empty miles. Freight marketplaces, such as Uber Freight or Convoy, leverage digital carrier networks to provide scalable access to vetted carriers, enhanced transparency, and dynamic pricing based on live supply and demand data. Explore how carrier network integration in these platforms revolutionizes freight logistics and boosts operational agility.
Source and External Links
Spot Market Definition and Meaning - A spot market is a public financial market where commodities, securities, or currencies are bought and sold for immediate delivery and settlement, typically within two business days, based on current supply and demand.
What Is the Spot Market & How Does It Work? - The spot market is where buyers and sellers make an immediate exchange, with delivery occurring simultaneously with payment, reflecting real-time prices for commodities, stocks, or currencies.
Spot Market - Overview, Characteristics, and Types - The spot market, also called the cash market, is where financial instruments and commodities are traded for immediate delivery and payment, usually settling within two working days, contrasting with futures markets where delivery is scheduled for a future date.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com