Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing the distance trucks travel without cargo, thereby cutting fuel costs and carbon emissions. Shared trucking involves multiple shippers collaborating to fill truck capacity, optimizing routes and reducing overall transportation expenses. Discover how integrating these strategies can transform logistics efficiency.
Why it is important
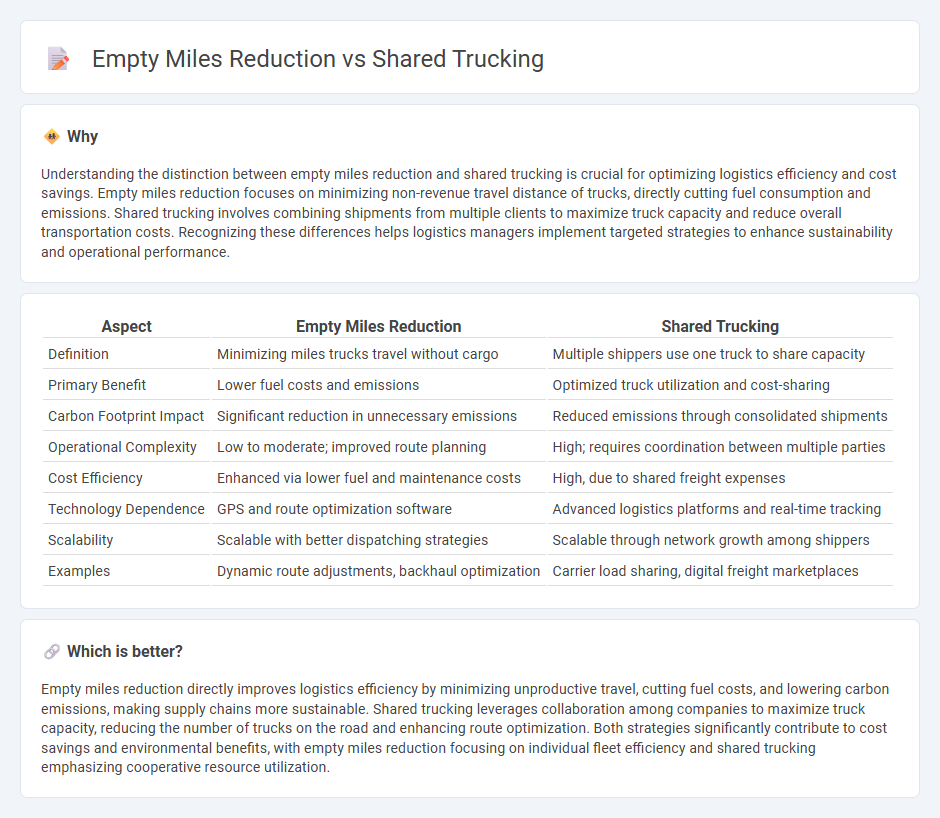
Understanding the distinction between empty miles reduction and shared trucking is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and cost savings. Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing non-revenue travel distance of trucks, directly cutting fuel consumption and emissions. Shared trucking involves combining shipments from multiple clients to maximize truck capacity and reduce overall transportation costs. Recognizing these differences helps logistics managers implement targeted strategies to enhance sustainability and operational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Shared Trucking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing miles trucks travel without cargo | Multiple shippers use one truck to share capacity |
| Primary Benefit | Lower fuel costs and emissions | Optimized truck utilization and cost-sharing |
| Carbon Footprint Impact | Significant reduction in unnecessary emissions | Reduced emissions through consolidated shipments |
| Operational Complexity | Low to moderate; improved route planning | High; requires coordination between multiple parties |
| Cost Efficiency | Enhanced via lower fuel and maintenance costs | High, due to shared freight expenses |
| Technology Dependence | GPS and route optimization software | Advanced logistics platforms and real-time tracking |
| Scalability | Scalable with better dispatching strategies | Scalable through network growth among shippers |
| Examples | Dynamic route adjustments, backhaul optimization | Carrier load sharing, digital freight marketplaces |
Which is better?
Empty miles reduction directly improves logistics efficiency by minimizing unproductive travel, cutting fuel costs, and lowering carbon emissions, making supply chains more sustainable. Shared trucking leverages collaboration among companies to maximize truck capacity, reducing the number of trucks on the road and enhancing route optimization. Both strategies significantly contribute to cost savings and environmental benefits, with empty miles reduction focusing on individual fleet efficiency and shared trucking emphasizing cooperative resource utilization.
Connection
Reducing empty miles directly enhances shared trucking efficiency by maximizing load utilization and minimizing unproductive travel distances. Shared trucking platforms optimize route planning and cargo matching, enabling multiple shipments to be consolidated into fewer trips. This synergy decreases operational costs, lowers carbon emissions, and improves overall supply chain sustainability.
Key Terms
Load Consolidation
Load consolidation enhances shared trucking efficiency by combining multiple shipments into a single truckload, significantly reducing empty miles and improving fuel economy. This strategy leverages advanced routing algorithms and real-time data to maximize truck capacity utilization, lowering operational costs and carbon emissions. Discover how load consolidation drives sustainable logistics solutions and optimizes transportation networks.
Backhauling
Backhauling optimizes shared trucking by utilizing return trips to transport goods, significantly reducing empty miles and lowering operational costs. Efficient route planning and load matching systems enhance backhaul opportunities, enabling carriers to maximize truck capacity and reduce carbon emissions. Explore how backhauling innovations drive sustainability and profitability in freight logistics.
Route Optimization
Shared trucking leverages collaborative logistics by combining freight loads from multiple shippers, significantly reducing empty miles and enhancing route optimization efficiency. Advanced route optimization algorithms integrate real-time data and traffic patterns to dynamically adjust routes, resulting in fuel savings, lower emissions, and improved delivery times. Explore how cutting-edge route optimization tools can revolutionize shared trucking operations and minimize empty miles in your supply chain.
Source and External Links
A look under the hood: Breaking down two real Shared Truckloads - Shared Truckload (STL) combines shipments from multiple companies into one truck without terminal stops, offering cost savings, environmental benefits, and improved efficiency through automated matching technology.
Shared Truckload Explained: When & How to Use It - Shared Truckload merges freight from various shippers into a single trailer, providing faster, more reliable service than LTL at comparable prices, with sustainability benefits and ideal for shipments of 1 to 12 pallets.
How Shared Transportation Networks Boost Efficiency - Shared dedicated transportation networks combine freight from multiple shippers going to similar destinations, lowering costs, reducing emissions, and improving delivery reliability through optimized routes and load sharing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com