Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage local, independent couriers to provide flexible and rapid last-mile logistics, enhancing customer reach and reducing delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers use automated, small-scale warehouses close to urban areas to increase efficiency and speed in order processing while minimizing inventory holding costs. Explore how integrating these innovative solutions can transform supply chain strategies and boost operational performance.
Why it is important
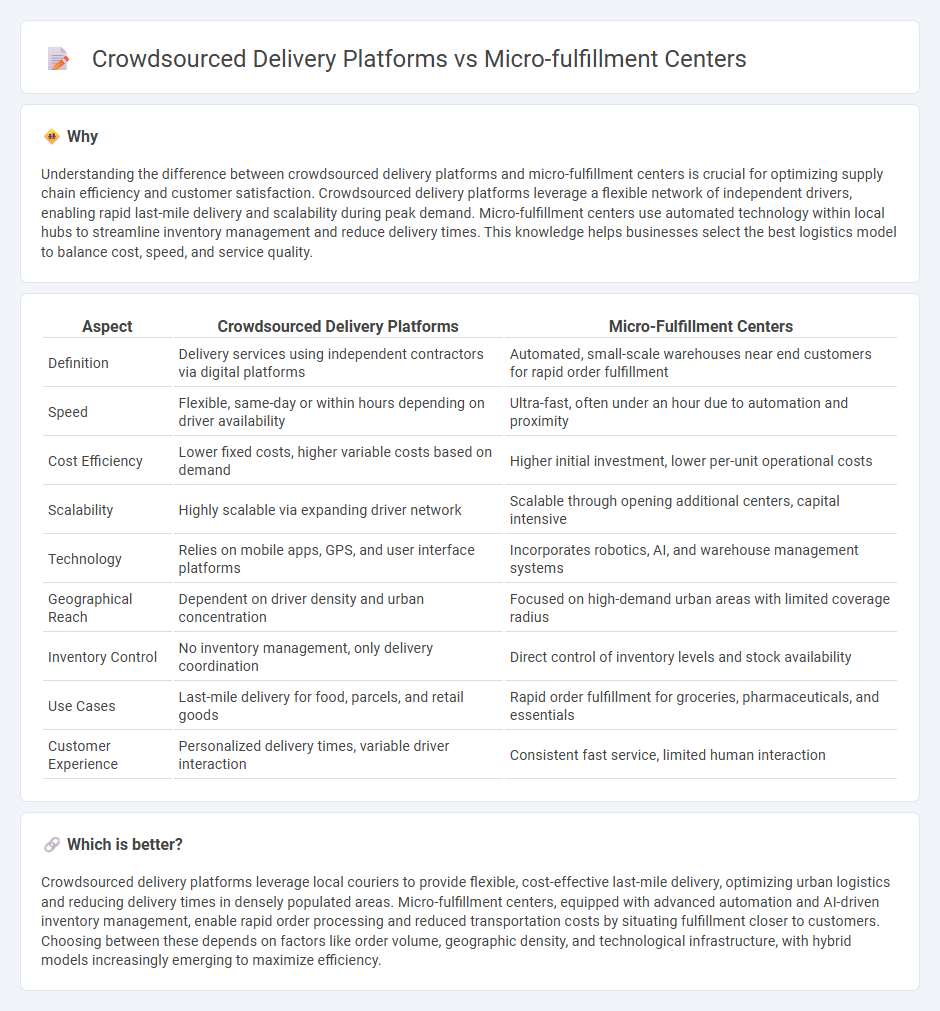
Understanding the difference between crowdsourced delivery platforms and micro-fulfillment centers is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage a flexible network of independent drivers, enabling rapid last-mile delivery and scalability during peak demand. Micro-fulfillment centers use automated technology within local hubs to streamline inventory management and reduce delivery times. This knowledge helps businesses select the best logistics model to balance cost, speed, and service quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crowdsourced Delivery Platforms | Micro-Fulfillment Centers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery services using independent contractors via digital platforms | Automated, small-scale warehouses near end customers for rapid order fulfillment |
| Speed | Flexible, same-day or within hours depending on driver availability | Ultra-fast, often under an hour due to automation and proximity |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fixed costs, higher variable costs based on demand | Higher initial investment, lower per-unit operational costs |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via expanding driver network | Scalable through opening additional centers, capital intensive |
| Technology | Relies on mobile apps, GPS, and user interface platforms | Incorporates robotics, AI, and warehouse management systems |
| Geographical Reach | Dependent on driver density and urban concentration | Focused on high-demand urban areas with limited coverage radius |
| Inventory Control | No inventory management, only delivery coordination | Direct control of inventory levels and stock availability |
| Use Cases | Last-mile delivery for food, parcels, and retail goods | Rapid order fulfillment for groceries, pharmaceuticals, and essentials |
| Customer Experience | Personalized delivery times, variable driver interaction | Consistent fast service, limited human interaction |
Which is better?
Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage local couriers to provide flexible, cost-effective last-mile delivery, optimizing urban logistics and reducing delivery times in densely populated areas. Micro-fulfillment centers, equipped with advanced automation and AI-driven inventory management, enable rapid order processing and reduced transportation costs by situating fulfillment closer to customers. Choosing between these depends on factors like order volume, geographic density, and technological infrastructure, with hybrid models increasingly emerging to maximize efficiency.
Connection
Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage local, on-demand drivers to enhance the last-mile delivery speed and flexibility, while micro-fulfillment centers strategically located near urban areas enable rapid order processing and inventory management. This integration reduces delivery times and operational costs by synchronizing dense inventory hubs with a scalable network of independent couriers. Together, they optimize supply chain efficiency through real-time fulfillment and responsive distribution tailored to dynamic consumer demand.
Key Terms
Automation
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage advanced robotics and AI-driven systems to automate inventory management, picking, and packing processes, significantly reducing order fulfillment time and labor costs. Crowdsourced delivery platforms rely on decentralized human couriers coordinated through digital apps, emphasizing flexible last-mile delivery but limited automation in order processing. Explore the latest innovations and efficiency comparisons between these two models to understand their impact on the future of e-commerce logistics.
Last-mile delivery
Micro-fulfillment centers streamline last-mile delivery by positioning small, automated warehouses close to urban consumers, significantly reducing delivery time and costs compared to traditional large-scale distribution hubs. Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage a network of freelance drivers or couriers, offering flexible, on-demand shipping with varying levels of reliability and scalability depending on the density of the driver network. Explore how these two models reshape the efficiency and customer experience in last-mile delivery.
Gig economy
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automated, localized warehouses enabling rapid order processing within urban areas, supporting gig economy workers by reducing delivery times and increasing order volume consistency. Crowdsourced delivery platforms utilize independent gig workers for flexible, on-demand last-mile logistics, capitalizing on workforce scalability but often facing challenges with reliability and quality control. Explore the evolving dynamics of these models in reshaping gig economy logistics efficiency and worker engagement.
Source and External Links
Micro-Fulfillment Explained: Key Benefits and Strategies for Ecommerce Success - Micro-fulfillment centers are small, highly compact warehouses (3,000 to 10,000 square feet) located near consumers in urban areas; they enable faster delivery and supply chain efficiency by storing high-demand products for rapid shipping, significantly reducing last-mile delivery time and cost.
Micro-Fulfilment: In-Depth Guide + 7 Real Examples - Leading companies like Gopuff and ShopRite use micro-fulfillment centers to rapidly fulfill orders and adapt inventory in real time, enhancing operational efficiency and customer convenience through options like curbside pickup and home delivery.
What Are Micro Fulfillment Centers? - Micro-fulfillment centers typically hold only the top-selling products and achieve faster inventory turnover (8-10 times per year) compared to traditional warehouses, using automated or manual picking to fulfill tight turnaround orders, especially in grocery retailing where one MFC per 10 grocery stores is predicted by 2030.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com