Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining temperature-controlled environments to preserve the quality and safety of perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals and food products during transportation and storage. Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, recycling, or disposal, aiming to optimize resource use and minimize waste. Explore in-depth insights on cold chain and reverse logistics to enhance supply chain efficiency and sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cold chain and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and ensuring product integrity. Cold chain logistics focus on temperature-controlled transportation and storage to preserve perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food items. Reverse logistics handles the return, recycling, or disposal of products, minimizing waste and reducing costs. Proper management of both processes enhances customer satisfaction and sustainability in the logistics industry.
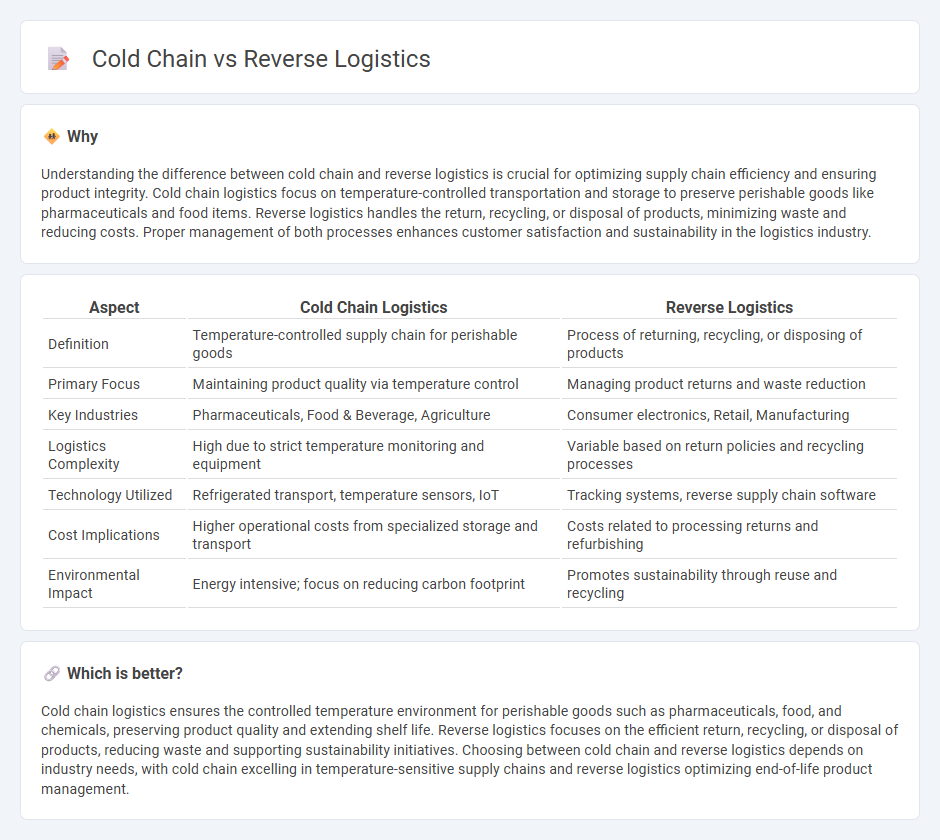
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods | Process of returning, recycling, or disposing of products |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product quality via temperature control | Managing product returns and waste reduction |
| Key Industries | Pharmaceuticals, Food & Beverage, Agriculture | Consumer electronics, Retail, Manufacturing |
| Logistics Complexity | High due to strict temperature monitoring and equipment | Variable based on return policies and recycling processes |
| Technology Utilized | Refrigerated transport, temperature sensors, IoT | Tracking systems, reverse supply chain software |
| Cost Implications | Higher operational costs from specialized storage and transport | Costs related to processing returns and refurbishing |
| Environmental Impact | Energy intensive; focus on reducing carbon footprint | Promotes sustainability through reuse and recycling |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures the controlled temperature environment for perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals, preserving product quality and extending shelf life. Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, or disposal of products, reducing waste and supporting sustainability initiatives. Choosing between cold chain and reverse logistics depends on industry needs, with cold chain excelling in temperature-sensitive supply chains and reverse logistics optimizing end-of-life product management.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled storage and transportation for perishable goods, maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain. Reverse logistics manages the return, recycling, and disposal of products, including expired or damaged cold chain items, to minimize waste and environmental impact. Integrating cold chain and reverse logistics optimizes asset recovery and sustainability in temperature-sensitive supply networks.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distribution center for return, repair, recycling, or disposal, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing waste. Key elements include product returns management, refurbishment, and sustainable disposal methods, which are critical for industries like electronics, retail, and automotive. Explore the comprehensive benefits and strategies of reverse logistics to improve your business sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics involves the process of managing product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to maximize value recovery and minimize waste, while cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled conditions during the storage and transportation of perishable goods. In returns management, reverse logistics focuses on efficient handling of returned items, whereas cold chain emphasizes maintaining product integrity through strict temperature controls during return transit. Explore detailed strategies and best practices to optimize returns management within both reverse logistics and cold chain frameworks.
Waste Disposal
Reverse logistics involves managing the return and proper disposal of products to minimize environmental impact, emphasizing efficient waste disposal processes to reduce landfill contributions. Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled environments throughout transportation and storage, preventing spoilage and reducing waste of perishable goods. Explore how these systems optimize waste disposal for sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the final destination (customer) back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or proper disposal, aiming to recapture value and enhance supply chain sustainability and efficiency.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages the return flow of goods from customers to sellers or manufacturers, including returns processing, refurbishments, and recycling, and varies by industry to optimize cost savings and sustainability.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics involves upstream movement of products for recapturing value or disposal, including returns, remanufacturing, and refurbishing, with growing importance due to environmental concerns and an expanding global market worth billions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com