Dynamic routing adapts to real-time network conditions by automatically selecting the best paths for data transmission, enhancing efficiency and reducing congestion. Constraint-based routing, on the other hand, optimizes routes based on predefined criteria like bandwidth, latency, or policy rules to meet specific performance or security requirements. Explore more to understand which routing strategy suits your logistics network needs best.
Why it is important
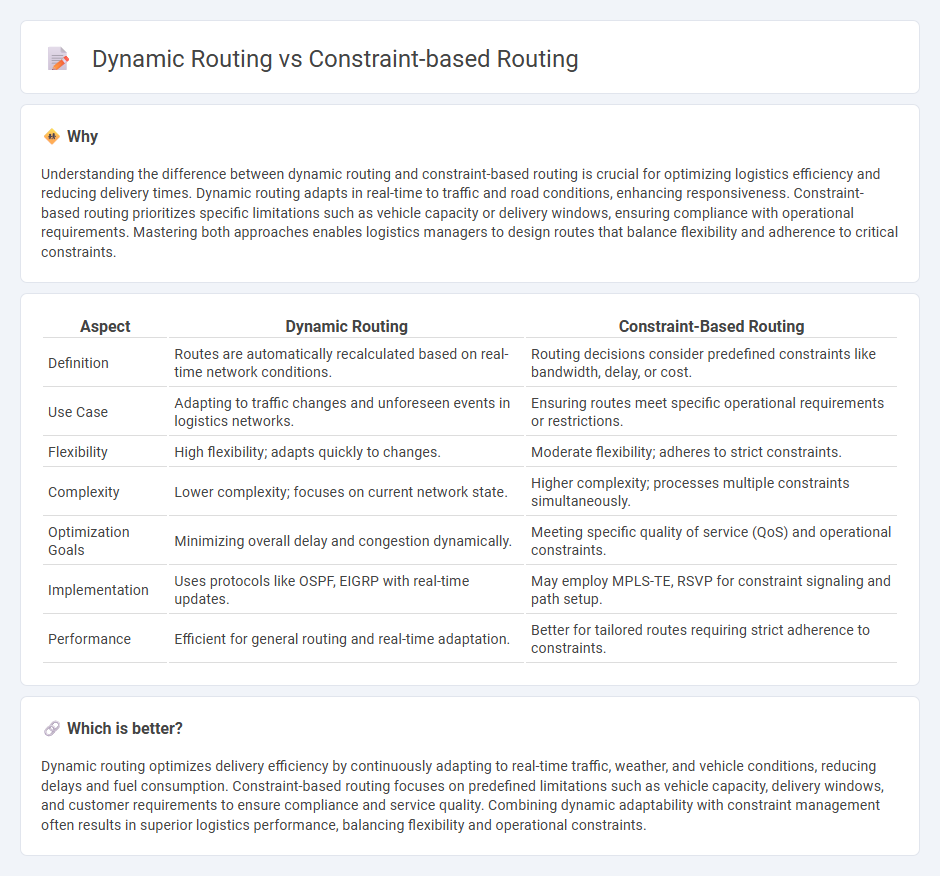
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and constraint-based routing is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and reducing delivery times. Dynamic routing adapts in real-time to traffic and road conditions, enhancing responsiveness. Constraint-based routing prioritizes specific limitations such as vehicle capacity or delivery windows, ensuring compliance with operational requirements. Mastering both approaches enables logistics managers to design routes that balance flexibility and adherence to critical constraints.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dynamic Routing | Constraint-Based Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Routes are automatically recalculated based on real-time network conditions. | Routing decisions consider predefined constraints like bandwidth, delay, or cost. |
| Use Case | Adapting to traffic changes and unforeseen events in logistics networks. | Ensuring routes meet specific operational requirements or restrictions. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; adapts quickly to changes. | Moderate flexibility; adheres to strict constraints. |
| Complexity | Lower complexity; focuses on current network state. | Higher complexity; processes multiple constraints simultaneously. |
| Optimization Goals | Minimizing overall delay and congestion dynamically. | Meeting specific quality of service (QoS) and operational constraints. |
| Implementation | Uses protocols like OSPF, EIGRP with real-time updates. | May employ MPLS-TE, RSVP for constraint signaling and path setup. |
| Performance | Efficient for general routing and real-time adaptation. | Better for tailored routes requiring strict adherence to constraints. |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing optimizes delivery efficiency by continuously adapting to real-time traffic, weather, and vehicle conditions, reducing delays and fuel consumption. Constraint-based routing focuses on predefined limitations such as vehicle capacity, delivery windows, and customer requirements to ensure compliance and service quality. Combining dynamic adaptability with constraint management often results in superior logistics performance, balancing flexibility and operational constraints.
Connection
Dynamic routing and constraint-based routing are interconnected through their shared goal of optimizing logistics networks by adapting route decisions in real time based on changing conditions and predefined constraints such as delivery windows, vehicle capacity, and traffic regulations. Dynamic routing leverages real-time data inputs like traffic congestion and road closures, while constraint-based routing integrates specific operational restrictions to ensure feasible and efficient route planning. Together, they enhance logistics efficiency by minimizing travel time, reducing fuel consumption, and improving on-time delivery performance.
Key Terms
Constraint-Based Routing:
Constraint-based routing optimizes network traffic by considering specific requirements such as bandwidth, latency, and policy constraints, rather than relying solely on shortest path metrics like dynamic routing protocols do. It leverages resources like Traffic Engineering databases and explicitly defines paths to meet service level agreements (SLAs) and improve overall network performance and reliability. Explore how constraint-based routing can enhance your network's efficiency and control.
Resource Allocation
Constraint-based routing optimizes resource allocation by considering network constraints such as bandwidth, latency, and link availability to ensure efficient traffic management and adherence to quality of service (QoS) requirements. Dynamic routing adapts paths based on real-time network conditions, dynamically redistributing resources to prevent congestion and maximize overall network utilization. Explore further to understand how these routing techniques impact network performance and resource efficiency.
Rule-Based Scheduling
Constraint-based routing utilizes predefined rules and metrics to determine optimal network paths, ensuring specific requirements such as bandwidth, latency, or security are adhered to. Dynamic routing, in contrast, relies on real-time network state information and adaptive algorithms to update routes automatically based on current conditions, often prioritizing overall efficiency and load balancing. Explore further to understand how rule-based scheduling integrates with these routing techniques for enhanced network performance and control.
Source and External Links
Constraint-Based Routing in the Internet: Basic Principles and Recent Research - Constraint-based routing (CBR) is a class of routing algorithms that selects network paths based on a set of requirements or constraints, including policies and quality of service (QoS), aiming to satisfy these while optimizing costs, load balancing, or security.
Overview of Constraint-Based Path Selection Algorithms for QoS Routing - Constraint-based routing focuses on finding paths meeting multiple QoS constraints, a complex NP-complete problem often solved with heuristic algorithms such as restricted shortest path and multi-constrained path approaches.
Constraint-based Routing Label Distribution Protocol - CR-LDP is an extension of the Label Distribution Protocol used to establish label-switched paths in MPLS networks based on constraints like QoS and explicit routing requirements for traffic engineering, though it has been deprecated in favor of RSVP-TE since 2003.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com