Urban consolidation centers reduce delivery costs and emissions by consolidating shipments closer to city centers, improving last-mile logistics efficiency. Regional warehouses optimize inventory storage and distribution on a larger scale, supporting broader geographic coverage and bulk shipments. Explore the advantages and strategic applications of both solutions in modern logistics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between urban consolidation centers and regional warehouses is crucial for optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency and reducing transportation costs in logistics operations. Urban consolidation centers focus on centralizing shipments within cities to minimize congestion and emissions, while regional warehouses serve broader geographic areas, supporting inventory storage and distribution. This distinction enables logistics managers to tailor supply chain strategies to specific urban or regional demands, enhancing service speed and sustainability. Effective utilization of both facilities improves overall network responsiveness and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table
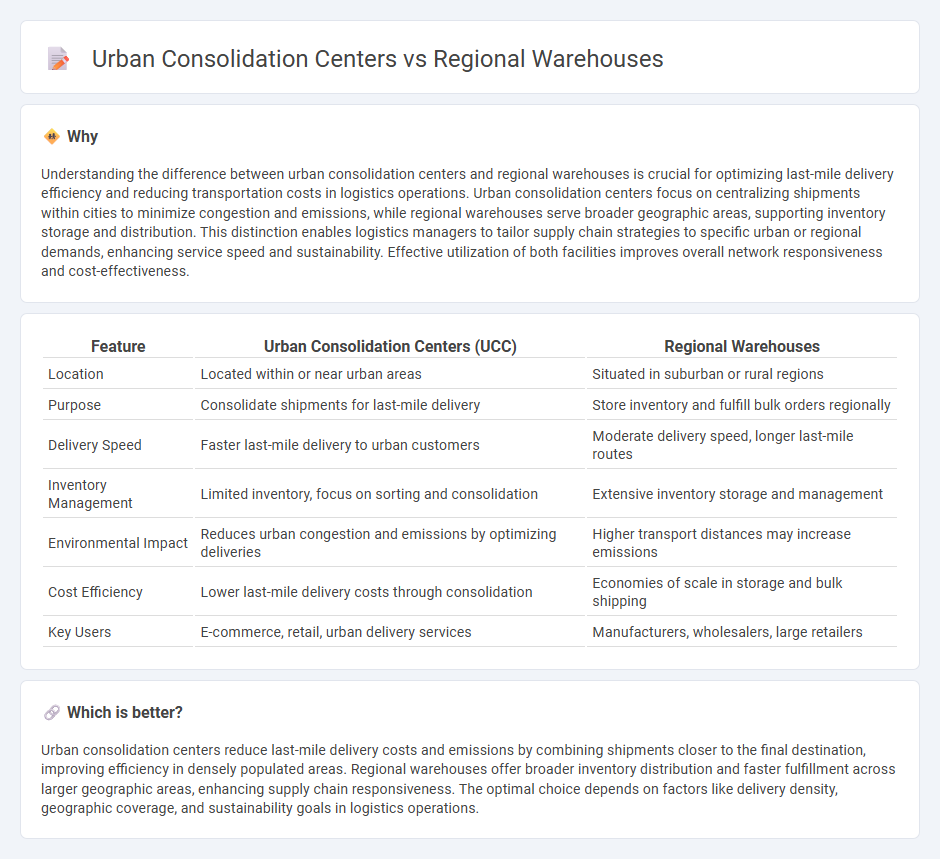
| Feature | Urban Consolidation Centers (UCC) | Regional Warehouses |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Located within or near urban areas | Situated in suburban or rural regions |
| Purpose | Consolidate shipments for last-mile delivery | Store inventory and fulfill bulk orders regionally |
| Delivery Speed | Faster last-mile delivery to urban customers | Moderate delivery speed, longer last-mile routes |
| Inventory Management | Limited inventory, focus on sorting and consolidation | Extensive inventory storage and management |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces urban congestion and emissions by optimizing deliveries | Higher transport distances may increase emissions |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower last-mile delivery costs through consolidation | Economies of scale in storage and bulk shipping |
| Key Users | E-commerce, retail, urban delivery services | Manufacturers, wholesalers, large retailers |
Which is better?
Urban consolidation centers reduce last-mile delivery costs and emissions by combining shipments closer to the final destination, improving efficiency in densely populated areas. Regional warehouses offer broader inventory distribution and faster fulfillment across larger geographic areas, enhancing supply chain responsiveness. The optimal choice depends on factors like delivery density, geographic coverage, and sustainability goals in logistics operations.
Connection
Urban consolidation centers and regional warehouses create an integrated logistics network that streamlines last-mile delivery by centralizing goods closer to urban consumers. Regional warehouses supply bulk inventory to urban consolidation centers, which then sort and consolidate shipments to reduce delivery trips and traffic congestion. This synergy enhances distribution efficiency, lowers transportation costs, and supports sustainable urban logistics solutions.
Key Terms
Distribution Network
Regional warehouses centralize inventory storage to optimize supply chain efficiency by serving broad geographic areas, reducing transportation costs for long-haul deliveries. Urban consolidation centers, located near city hubs, streamline last-mile delivery by aggregating shipments from multiple suppliers, decreasing urban congestion and delivery emissions. Explore how integrating these facilities can enhance distribution network performance and sustainability.
Last-Mile Delivery
Regional warehouses serve as large storage hubs situated on city outskirts, facilitating bulk inventory management and long-distance distribution, which reduces shipping costs and lead times for last-mile delivery. Urban consolidation centers, positioned within dense city areas, optimize last-mile logistics by aggregating shipments from multiple suppliers, minimizing delivery trips and reducing traffic congestion and emissions. Explore further to understand how choosing between these facilities can enhance efficiency and sustainability in last-mile delivery.
Inventory Centralization
Regional warehouses centralize inventory by storing large quantities of products in strategic locations to serve broad geographic areas efficiently. Urban consolidation centers concentrate inventory closer to end consumers, enabling faster last-mile delivery and reducing city traffic congestion. Explore the advantages and trade-offs of these inventory centralization strategies to optimize your logistics network.
Source and External Links
Regional warehouse: Supply chain advantages | AR Racking Inc - A regional warehouse is an intermediate storage facility that serves as a distribution point for a specific geographical region, offering benefits like inventory consolidation, reduced delivery times, cost optimization, and improved product availability by being closer to end consumers.
Regional Warehousing I Buske Logistics - Buske Logistics provides regional warehousing solutions offering strategic storage, fast delivery within key geographic areas, real-time tracking, efficient handling, and scalable capacity to enhance regional supply chains.
Regional warehouse for smaller distribution zones - Mecalux - Regional warehouses are designed to accommodate large vehicle flows and serve as distribution centers between urban hubs, enabling fast shipping to local stores and customers, exemplified by companies like Leroy Merlin and Motos Bordoy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com