Reducing empty miles in logistics minimizes fuel consumption and operational costs by ensuring trucks carry loads on return trips rather than traveling empty. Multi-stop routing optimizes delivery sequences, increasing route efficiency and vehicle utilization through strategic planning of multiple deliveries per trip. Explore how balancing empty miles reduction with multi-stop routing enhances overall supply chain performance and sustainability.
Why it is important
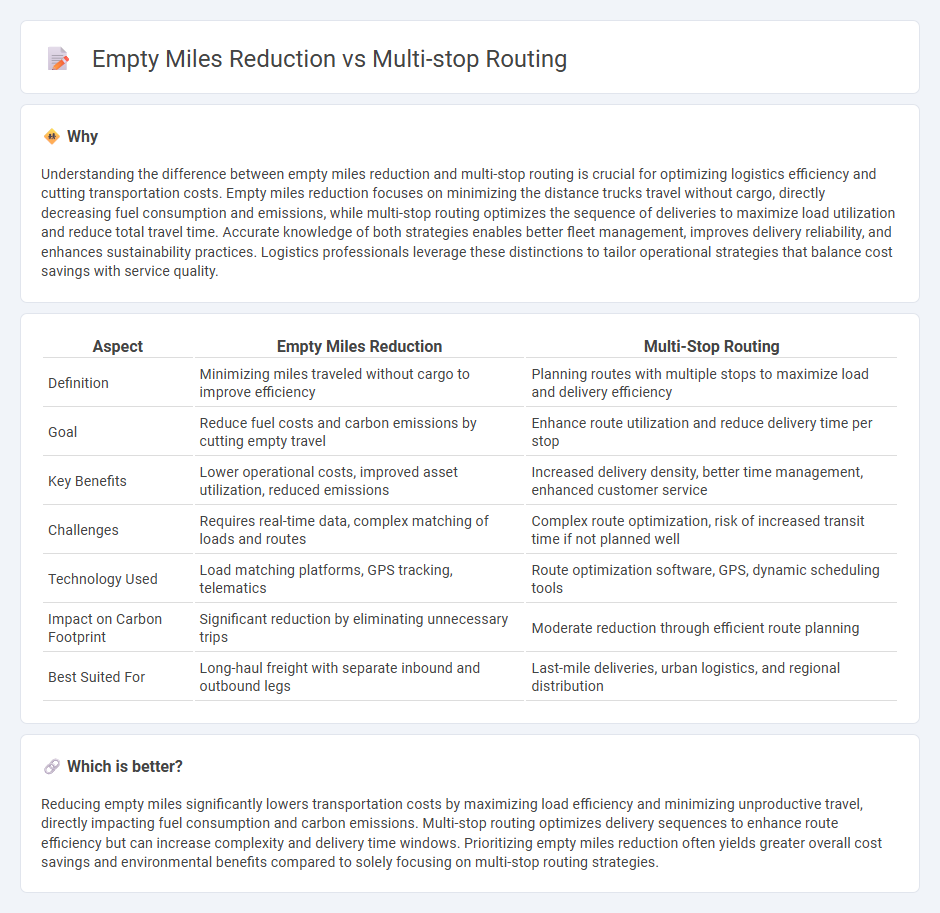
Understanding the difference between empty miles reduction and multi-stop routing is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and cutting transportation costs. Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing the distance trucks travel without cargo, directly decreasing fuel consumption and emissions, while multi-stop routing optimizes the sequence of deliveries to maximize load utilization and reduce total travel time. Accurate knowledge of both strategies enables better fleet management, improves delivery reliability, and enhances sustainability practices. Logistics professionals leverage these distinctions to tailor operational strategies that balance cost savings with service quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Multi-Stop Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing miles traveled without cargo to improve efficiency | Planning routes with multiple stops to maximize load and delivery efficiency |
| Goal | Reduce fuel costs and carbon emissions by cutting empty travel | Enhance route utilization and reduce delivery time per stop |
| Key Benefits | Lower operational costs, improved asset utilization, reduced emissions | Increased delivery density, better time management, enhanced customer service |
| Challenges | Requires real-time data, complex matching of loads and routes | Complex route optimization, risk of increased transit time if not planned well |
| Technology Used | Load matching platforms, GPS tracking, telematics | Route optimization software, GPS, dynamic scheduling tools |
| Impact on Carbon Footprint | Significant reduction by eliminating unnecessary trips | Moderate reduction through efficient route planning |
| Best Suited For | Long-haul freight with separate inbound and outbound legs | Last-mile deliveries, urban logistics, and regional distribution |
Which is better?
Reducing empty miles significantly lowers transportation costs by maximizing load efficiency and minimizing unproductive travel, directly impacting fuel consumption and carbon emissions. Multi-stop routing optimizes delivery sequences to enhance route efficiency but can increase complexity and delivery time windows. Prioritizing empty miles reduction often yields greater overall cost savings and environmental benefits compared to solely focusing on multi-stop routing strategies.
Connection
Empty miles reduction significantly lowers transportation costs and carbon emissions by minimizing non-revenue travel distances. Multi-stop routing enhances route efficiency by consolidating deliveries and pickups into optimized paths, directly contributing to fewer empty miles. Together, these strategies improve fleet utilization and operational sustainability in logistics management.
Key Terms
Route Optimization
Multi-stop routing enhances route optimization by efficiently sequencing multiple delivery points, minimizing total travel distance and time. Empty miles reduction targets the elimination of non-revenue-generating travel, directly lowering fuel costs and carbon emissions. Explore advanced route optimization strategies to improve logistics efficiency and sustainability.
Backhauling
Multi-stop routing enhances delivery efficiency by optimizing stops to reduce total travel distance, while empty miles reduction targets minimizing non-revenue generating trips, especially in backhauling. Backhauling allows carriers to transport goods on return trips, thereby cutting down on empty miles and improving overall fleet utilization. Explore how integrating multi-stop routing with backhauling strategies can maximize operational savings and boost sustainability.
Load Consolidation
Load consolidation plays a crucial role in multi-stop routing by efficiently combining shipments to maximize vehicle capacity and reduce the number of trips. This approach directly impacts empty miles reduction by minimizing unproductive travel distances, leading to lower fuel consumption and operational costs. Explore how advanced load consolidation techniques can optimize your logistics strategy and drive significant cost savings.
Source and External Links
Multi-Stop Route Planning: Tips for Optimized Directions | FarEye - A multi-stop route planner is a sophisticated tool that uses advanced algorithms to optimize delivery routes with multiple stops, reducing travel time, fuel consumption, and improving delivery efficiency by dynamically adjusting routes in real time based on factors like traffic and priorities.
Route Planner - MyRouteOnline - MyRouteOnline offers a multi-stop route planner that creates the quickest and most efficient driving routes between multiple destinations, utilizing Google Maps API to ensure accurate distance and time calculations and allowing users to import locations or enter them manually.
Multi-Stop Route Planner - Apps on Google Play - Maposcope's Multi-Stop Route Planner app automates delivery route planning by determining the fastest order of stops with real-time traffic updates, customizable priorities, service times, and the ability to save and share detailed route reports with estimated times of arrival.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com