Ghost warehousing leverages underutilized storage spaces to enhance supply chain efficiency without the need for physical storefronts, enabling flexible and cost-effective inventory management. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, technology-driven hubs located close to end consumers, designed to accelerate order processing and last-mile delivery in urban environments. Explore the benefits and operational differences between these innovative logistics solutions to optimize your distribution strategy.
Why it is important
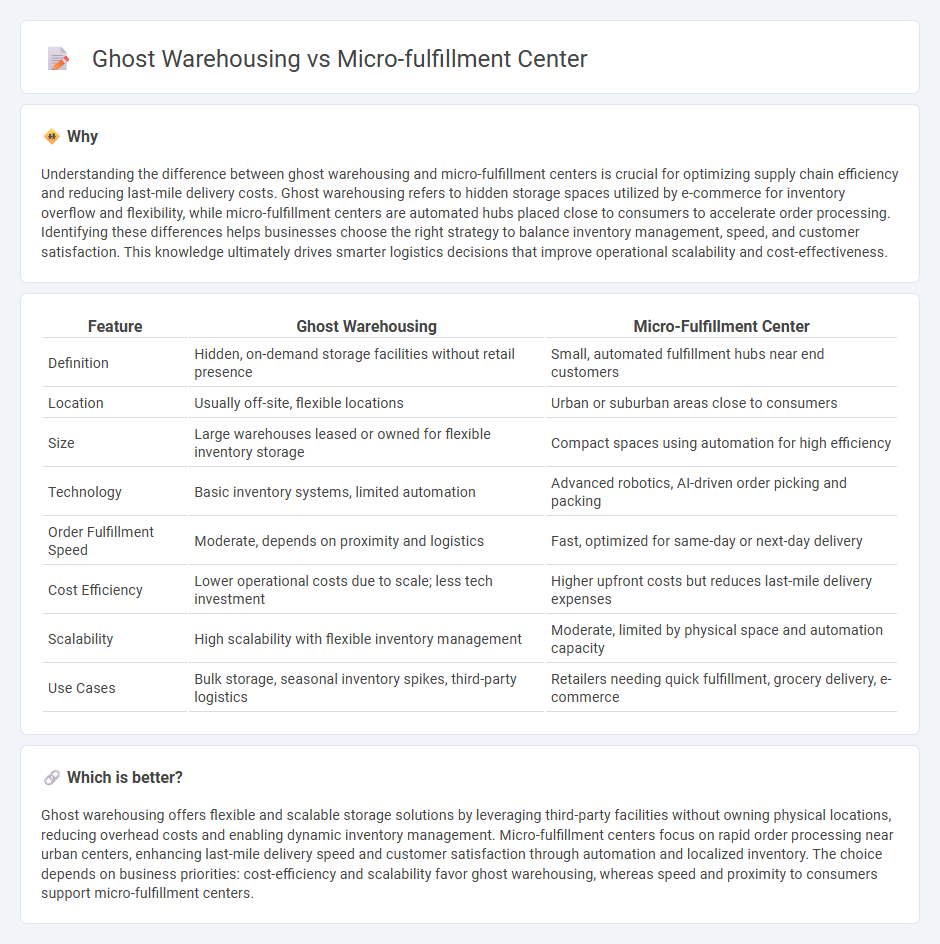
Understanding the difference between ghost warehousing and micro-fulfillment centers is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing last-mile delivery costs. Ghost warehousing refers to hidden storage spaces utilized by e-commerce for inventory overflow and flexibility, while micro-fulfillment centers are automated hubs placed close to consumers to accelerate order processing. Identifying these differences helps businesses choose the right strategy to balance inventory management, speed, and customer satisfaction. This knowledge ultimately drives smarter logistics decisions that improve operational scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ghost Warehousing | Micro-Fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hidden, on-demand storage facilities without retail presence | Small, automated fulfillment hubs near end customers |
| Location | Usually off-site, flexible locations | Urban or suburban areas close to consumers |
| Size | Large warehouses leased or owned for flexible inventory storage | Compact spaces using automation for high efficiency |
| Technology | Basic inventory systems, limited automation | Advanced robotics, AI-driven order picking and packing |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Moderate, depends on proximity and logistics | Fast, optimized for same-day or next-day delivery |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs due to scale; less tech investment | Higher upfront costs but reduces last-mile delivery expenses |
| Scalability | High scalability with flexible inventory management | Moderate, limited by physical space and automation capacity |
| Use Cases | Bulk storage, seasonal inventory spikes, third-party logistics | Retailers needing quick fulfillment, grocery delivery, e-commerce |
Which is better?
Ghost warehousing offers flexible and scalable storage solutions by leveraging third-party facilities without owning physical locations, reducing overhead costs and enabling dynamic inventory management. Micro-fulfillment centers focus on rapid order processing near urban centers, enhancing last-mile delivery speed and customer satisfaction through automation and localized inventory. The choice depends on business priorities: cost-efficiency and scalability favor ghost warehousing, whereas speed and proximity to consumers support micro-fulfillment centers.
Connection
Ghost warehousing and micro-fulfillment centers are interconnected through their focus on optimizing inventory management and accelerating last-mile delivery. Both concepts leverage technology-driven automation and data analytics to enhance storage efficiency and order accuracy within compact urban spaces. This synergy reduces operational costs and improves customer satisfaction by enabling faster, more flexible fulfillment.
Key Terms
Micro-fulfillment center:
Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated warehouses located near urban areas, designed to accelerate order fulfillment for e-commerce and retail businesses. By utilizing robotics and AI-driven inventory management, these centers minimize delivery times and reduce last-mile logistics costs. Discover how micro-fulfillment centers are transforming supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Automated picking
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automated picking technologies like robotic arms and conveyors to accelerate order processing in urban retail hubs, reducing delivery times significantly. Ghost warehousing employs similar automation but operates as centralized facilities without direct customer interfaces, optimizing storage and inventory management for multiple e-commerce clients. Explore how automated picking transforms supply chain efficiency in both models to enhance your logistics strategy.
Urban proximity
Micro-fulfillment centers optimize urban proximity by situating automated, compact warehouses close to high-demand city centers, reducing last-mile delivery times and costs. Ghost warehousing operates similar urban-based storage facilities but emphasizes flexible, multi-tenant usage that adapts to fluctuating retail and e-commerce needs. Explore how leveraging urban proximity transforms fulfillment strategies and urban logistics efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Are Micro Fulfillment Centers? - City National Bank - Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are small warehouses, typically 3,000 to 10,000 square feet, storing up to 15,000 items with compact designs for rapid shipping, often located in urban areas or within stores to enable fast product turnover and meet high customer expectations.
Micro fulfillment center: How it helps retailers speed up fulfillment - Micro fulfillment centers are small-scale, often automated facilities close to consumers that enable faster order fulfillment and can be standalone or integrated into existing stores, storing limited inventory for rapid delivery, typically holding about 24-48 hours' worth of stock.
Walgreens to increase stores serviced by micro-fulfillment centers - Walgreens is expanding its use of automated micro-fulfillment centers to increase operational efficiency and speed prescription delivery, highlighting the growing adoption of MFCs by retailers to improve last-mile fulfillment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com