Green corridors prioritize sustainable transportation by minimizing carbon emissions through optimized routes and eco-friendly modes, significantly reducing environmental impact. Inland ports serve as strategic logistics hubs away from traditional seaports, enhancing cargo handling efficiency and alleviating congestion while supporting multimodal transport networks. Explore the benefits and differences between green corridors and inland ports to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a green corridor and an inland port is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing environmental impact in logistics. Green corridors focus on sustainable transportation routes that minimize carbon emissions, while inland ports serve as strategic logistics hubs that facilitate cargo transfer away from congested seaports. Logistics professionals can leverage green corridors to achieve eco-friendly deliveries and use inland ports to enhance multimodal connectivity and reduce transit times. Knowledge of both concepts enables better planning, cost savings, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Comparison Table
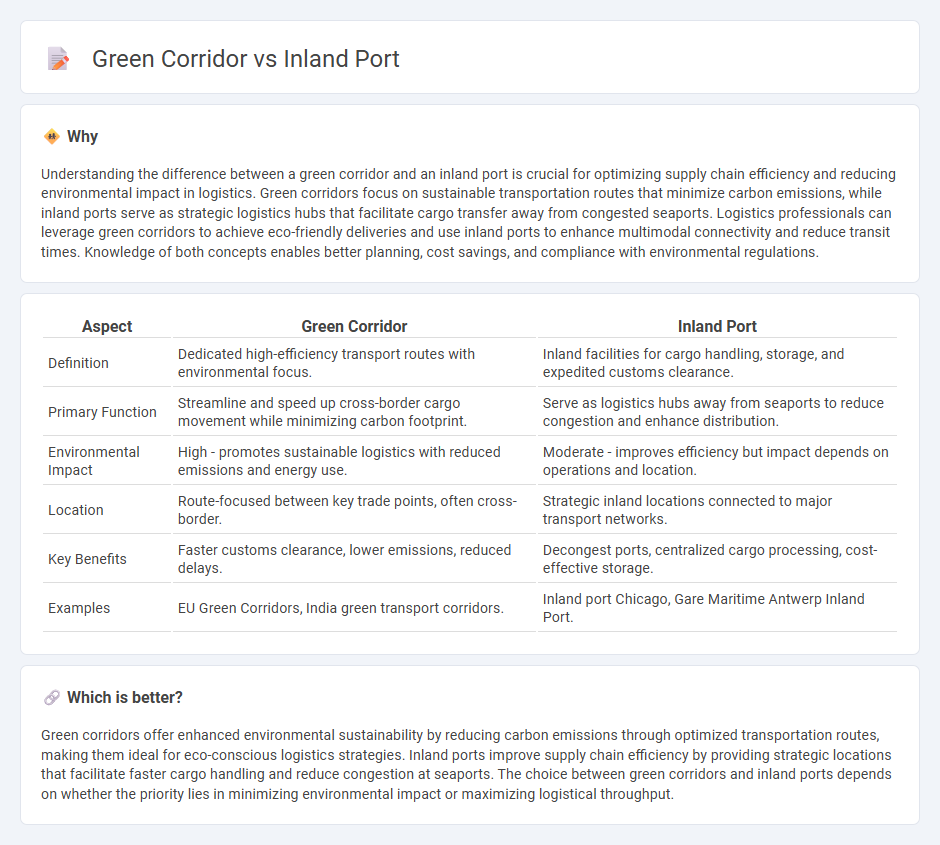
| Aspect | Green Corridor | Inland Port |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated high-efficiency transport routes with environmental focus. | Inland facilities for cargo handling, storage, and expedited customs clearance. |
| Primary Function | Streamline and speed up cross-border cargo movement while minimizing carbon footprint. | Serve as logistics hubs away from seaports to reduce congestion and enhance distribution. |
| Environmental Impact | High - promotes sustainable logistics with reduced emissions and energy use. | Moderate - improves efficiency but impact depends on operations and location. |
| Location | Route-focused between key trade points, often cross-border. | Strategic inland locations connected to major transport networks. |
| Key Benefits | Faster customs clearance, lower emissions, reduced delays. | Decongest ports, centralized cargo processing, cost-effective storage. |
| Examples | EU Green Corridors, India green transport corridors. | Inland port Chicago, Gare Maritime Antwerp Inland Port. |
Which is better?
Green corridors offer enhanced environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions through optimized transportation routes, making them ideal for eco-conscious logistics strategies. Inland ports improve supply chain efficiency by providing strategic locations that facilitate faster cargo handling and reduce congestion at seaports. The choice between green corridors and inland ports depends on whether the priority lies in minimizing environmental impact or maximizing logistical throughput.
Connection
Green corridors enhance logistics sustainability by enabling low-emission transport routes that prioritize eco-friendly practices, while inland ports act as strategic hubs that facilitate efficient cargo handling and reduce congestion at seaports. The integration of inland ports within green corridors optimizes supply chain efficiency by shortening transit times and minimizing carbon footprints through multimodal transport options. This connection supports sustainable logistics by promoting resource-efficient freight movement and reducing environmental impacts across transportation networks.
Key Terms
**Inland Port:**
Inland ports are strategic logistics hubs located away from coastal areas, designed to facilitate the efficient transfer of goods between different transportation modes such as rail, road, and sometimes air. These facilities help reduce congestion at seaports, lower transportation costs, and improve supply chain resilience by serving as distribution centers closer to inland markets. Explore more about how inland ports are transforming global logistics and trade networks.
Intermodal Terminal
Inland ports serve as critical intermodal terminals, linking rail, road, and sometimes air transport to streamline cargo flow between seaports and inland destinations, reducing congestion and improving supply chain efficiency. Green corridors emphasize environmentally sustainable logistics by prioritizing low-emission transport modes and optimized routing within these terminals to minimize carbon footprints. Explore the distinct roles of inland ports and green corridors in sustainable intermodal terminal operations for a comprehensive understanding.
Hinterland Connectivity
Inland ports act as strategic logistics hubs, enhancing hinterland connectivity by facilitating efficient cargo transfer between seaports and inland destinations, reducing congestion at coastal terminals. Green corridors prioritize sustainable transportation routes that minimize carbon emissions while optimizing the flow of goods through dedicated, eco-friendly infrastructure spanning key hinterland regions. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of inland ports and green corridors to understand their role in transforming hinterland connectivity.
Source and External Links
What is an inland port? - InTek Logistics - An inland port is a large-scale shipping and trade center located away from the coast, serving as a distribution hub with direct rail connection to seaports to facilitate international trade and alleviate congestion at coastal ports through intermodal transport.
Chapter 2.3 - Inland Ports / Dry Ports - Inland ports (also called dry ports) are inland terminals integrated with maritime terminals, providing efficient access to inland markets via connected logistics activities like distribution centers and container depots.
Inland port - Wikipedia - An inland port is a port located on an inland waterway or a dry port that may not be connected directly to the sea but serves as a major logistics hub for freight distribution via rivers, canals, or rail.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com