Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data and algorithms to improve delivery efficiency by continuously adjusting routes based on traffic, weather, and demand fluctuations. Hub-and-spoke distribution relies on centralized hubs to consolidate shipments, streamlining operations but often sacrificing flexibility. Explore the benefits and trade-offs of each approach to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
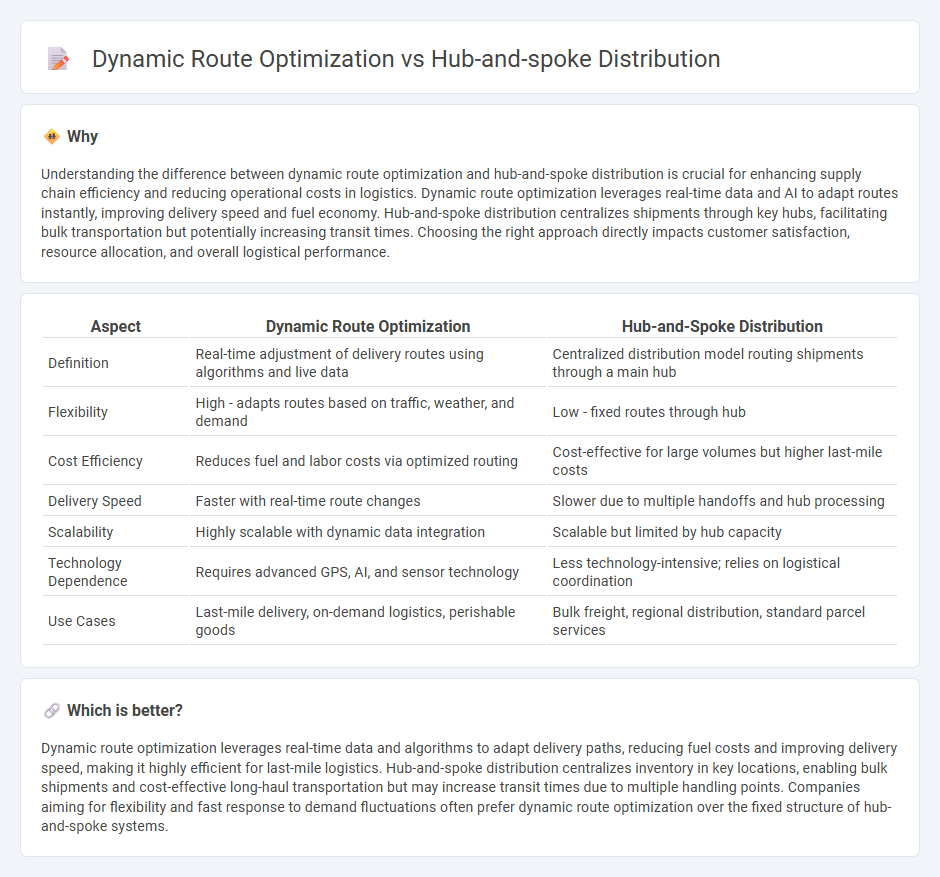
Understanding the difference between dynamic route optimization and hub-and-spoke distribution is crucial for enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs in logistics. Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data and AI to adapt routes instantly, improving delivery speed and fuel economy. Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes shipments through key hubs, facilitating bulk transportation but potentially increasing transit times. Choosing the right approach directly impacts customer satisfaction, resource allocation, and overall logistical performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dynamic Route Optimization | Hub-and-Spoke Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of delivery routes using algorithms and live data | Centralized distribution model routing shipments through a main hub |
| Flexibility | High - adapts routes based on traffic, weather, and demand | Low - fixed routes through hub |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces fuel and labor costs via optimized routing | Cost-effective for large volumes but higher last-mile costs |
| Delivery Speed | Faster with real-time route changes | Slower due to multiple handoffs and hub processing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with dynamic data integration | Scalable but limited by hub capacity |
| Technology Dependence | Requires advanced GPS, AI, and sensor technology | Less technology-intensive; relies on logistical coordination |
| Use Cases | Last-mile delivery, on-demand logistics, perishable goods | Bulk freight, regional distribution, standard parcel services |
Which is better?
Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data and algorithms to adapt delivery paths, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery speed, making it highly efficient for last-mile logistics. Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory in key locations, enabling bulk shipments and cost-effective long-haul transportation but may increase transit times due to multiple handling points. Companies aiming for flexibility and fast response to demand fluctuations often prefer dynamic route optimization over the fixed structure of hub-and-spoke systems.
Connection
Dynamic route optimization enhances the efficiency of hub-and-spoke distribution by continuously adjusting delivery paths based on real-time traffic, weather, and demand data. This integration reduces transit times and operational costs while maximizing hub capacity utilization. Leveraging advanced algorithms, logistics companies can synchronize routes to ensure timely shipments from centralized hubs to multiple spokes, improving overall network responsiveness.
Key Terms
**Hub-and-Spoke Distribution:**
Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory in a main hub, enabling efficient bulk shipments to regional spokes, reducing transportation costs and improving inventory management accuracy. This model supports predictable demand patterns and simplifies logistics by consolidating routes, but can lead to slower delivery times compared to decentralized methods. Explore how hub-and-spoke systems enhance supply chain scalability and cost-efficiency for your business needs.
Centralized Hub
Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory and order processing at a main hub, enhancing control and reducing fixed transportation costs through scheduled routes connecting peripheral spokes. Dynamic route optimization uses real-time data and algorithms to adjust delivery paths, minimizing travel time and fuel consumption on decentralized networks. Explore how centralized hubs leverage these strategies for efficient supply chain management.
Spoke Nodes
Hub-and-spoke distribution systems concentrate on central hub nodes dispersing goods to multiple spoke nodes, optimizing fixed routes and predictable scheduling, which simplifies inventory management at the spokes. Dynamic route optimization adapts delivery paths in real-time based on variables like traffic, demand, and delivery windows, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs at spoke nodes by minimizing transit times and fuel consumption. Explore further to understand how integrating these methods can improve logistics performance at spoke nodes.
Source and External Links
Hub and Spoke Model In Logistics And Its Importance - NimbusPost - The hub-and-spoke distribution model simplifies supply chains by centralizing inventory and delivery routes around a main hub, reducing costs for warehousing and transportation while improving workforce productivity and enabling faster delivery to multiple destinations efficiently.
The Hub and Spoke Distribution Model for SMB's - Ware2Go - This distribution model minimizes transit times and final mile costs by positioning inventory close to consumers through a central hub that forwards shipments, improving service levels and allowing efficient freight cost management and inventory control for merchants.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - The hub-and-spoke system organizes routes as spokes connecting outlying points to a central hub, originally popularized by airlines like Delta for optimizing passenger and freight transport, later adopted by logistics and telecommunications for efficient network and route management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com