Cold chain logistics focuses on temperature-controlled transportation to preserve perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals, ensuring product integrity from origin to destination. Freight forwarding involves the coordination and shipment of goods across various transportation modes, optimizing routes, costs, and compliance for diverse cargo types. Explore the key differences and critical roles each plays in global supply chain management.
Why it is important
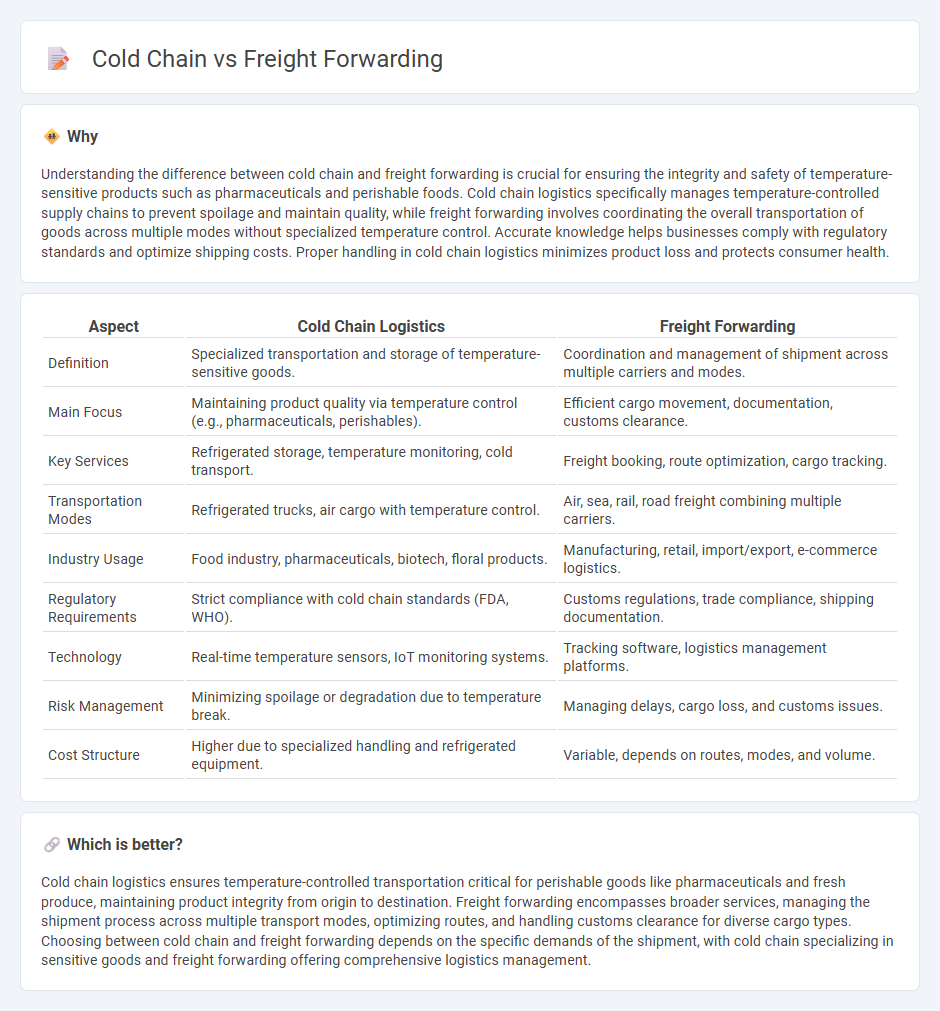
Understanding the difference between cold chain and freight forwarding is crucial for ensuring the integrity and safety of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods. Cold chain logistics specifically manages temperature-controlled supply chains to prevent spoilage and maintain quality, while freight forwarding involves coordinating the overall transportation of goods across multiple modes without specialized temperature control. Accurate knowledge helps businesses comply with regulatory standards and optimize shipping costs. Proper handling in cold chain logistics minimizes product loss and protects consumer health.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods. | Coordination and management of shipment across multiple carriers and modes. |
| Main Focus | Maintaining product quality via temperature control (e.g., pharmaceuticals, perishables). | Efficient cargo movement, documentation, customs clearance. |
| Key Services | Refrigerated storage, temperature monitoring, cold transport. | Freight booking, route optimization, cargo tracking. |
| Transportation Modes | Refrigerated trucks, air cargo with temperature control. | Air, sea, rail, road freight combining multiple carriers. |
| Industry Usage | Food industry, pharmaceuticals, biotech, floral products. | Manufacturing, retail, import/export, e-commerce logistics. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Strict compliance with cold chain standards (FDA, WHO). | Customs regulations, trade compliance, shipping documentation. |
| Technology | Real-time temperature sensors, IoT monitoring systems. | Tracking software, logistics management platforms. |
| Risk Management | Minimizing spoilage or degradation due to temperature break. | Managing delays, cargo loss, and customs issues. |
| Cost Structure | Higher due to specialized handling and refrigerated equipment. | Variable, depends on routes, modes, and volume. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled transportation critical for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and fresh produce, maintaining product integrity from origin to destination. Freight forwarding encompasses broader services, managing the shipment process across multiple transport modes, optimizing routes, and handling customs clearance for diverse cargo types. Choosing between cold chain and freight forwarding depends on the specific demands of the shipment, with cold chain specializing in sensitive goods and freight forwarding offering comprehensive logistics management.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled transportation of perishable goods, maintaining product quality from origin to destination. Freight forwarding coordinates the movement of these temperature-sensitive shipments by managing routes, compliance, and documentation across multiple carriers and modes of transport. Integration of cold chain protocols with freight forwarding enhances efficiency and reduces spoilage risks in global supply chains.
Key Terms
Freight Forwarding:
Freight forwarding involves coordinating and transporting goods efficiently across global supply chains, encompassing activities such as customs clearance, warehousing, and shipment tracking. It optimizes logistics for a wide variety of cargo, including containerized freight, bulk shipments, and perishable goods, ensuring timely delivery and cost-effective solutions. Discover more about how freight forwarding streamlines international trade and enhances supply chain management.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding specializes in managing the logistics of customs clearance across various cargo types, ensuring timely and compliant border processing. Cold chain logistics demands strict customs protocols to maintain temperature-sensitive products' integrity while navigating import/export regulations. Discover how efficient customs clearance strategies enhance both freight forwarding and cold chain operations.
Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading (BOL) plays a crucial role in freight forwarding by serving as a legal document that details cargo ownership, shipment terms, and receipt confirmation, ensuring smooth transportation of general goods. In cold chain logistics, the BOL must also specify temperature control requirements and handling instructions to maintain the integrity of perishable products throughout transit. Explore further to understand the critical differences in BOL usage between freight forwarding and cold chain management.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding is the strategic coordination of international goods movement via air, sea, rail, and highway, where a freight forwarder plans shipping steps, selects routes, handles customs, and ensures timely delivery but does not transport the goods themselves.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key Stages - A freight forwarder acts as an intermediary arranging export haulage, export customs clearance, and origin handling to ensure shipments are legal, safe, and comply with destination regulations, including handling of restricted or perishable items.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding involves services relating to carriage, consolidation, storage, handling, packing, customs, insurance, and supply chain management to ensure goods arrive at the right place, time, condition, and cost in international trade.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com