Cross docking streamlines supply chains by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage time, reducing inventory costs and speeding delivery. Drop shipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory, as suppliers ship goods directly to customers, minimizing upfront investment but potentially extending delivery times. Explore the key differences between cross docking and drop shipping to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
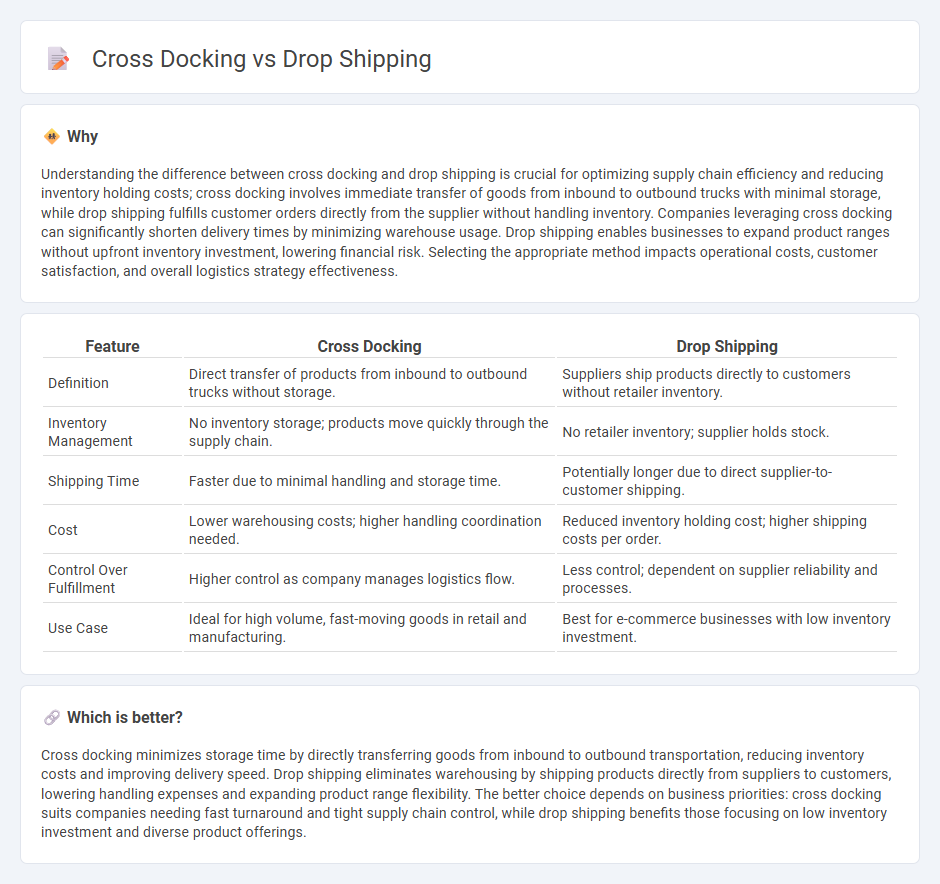
Understanding the difference between cross docking and drop shipping is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing inventory holding costs; cross docking involves immediate transfer of goods from inbound to outbound trucks with minimal storage, while drop shipping fulfills customer orders directly from the supplier without handling inventory. Companies leveraging cross docking can significantly shorten delivery times by minimizing warehouse usage. Drop shipping enables businesses to expand product ranges without upfront inventory investment, lowering financial risk. Selecting the appropriate method impacts operational costs, customer satisfaction, and overall logistics strategy effectiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cross Docking | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct transfer of products from inbound to outbound trucks without storage. | Suppliers ship products directly to customers without retailer inventory. |
| Inventory Management | No inventory storage; products move quickly through the supply chain. | No retailer inventory; supplier holds stock. |
| Shipping Time | Faster due to minimal handling and storage time. | Potentially longer due to direct supplier-to-customer shipping. |
| Cost | Lower warehousing costs; higher handling coordination needed. | Reduced inventory holding cost; higher shipping costs per order. |
| Control Over Fulfillment | Higher control as company manages logistics flow. | Less control; dependent on supplier reliability and processes. |
| Use Case | Ideal for high volume, fast-moving goods in retail and manufacturing. | Best for e-commerce businesses with low inventory investment. |
Which is better?
Cross docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, reducing inventory costs and improving delivery speed. Drop shipping eliminates warehousing by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, lowering handling expenses and expanding product range flexibility. The better choice depends on business priorities: cross docking suits companies needing fast turnaround and tight supply chain control, while drop shipping benefits those focusing on low inventory investment and diverse product offerings.
Connection
Cross docking and drop shipping streamline supply chain efficiency by minimizing storage and handling times. Cross docking consolidates inbound goods for immediate outbound distribution, while drop shipping enables direct shipping from suppliers to customers without inventory holding. Both methods reduce inventory costs and enhance order fulfillment speed, contributing to agile logistics operations.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Drop shipping minimizes inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing storage costs and inventory risks. Cross docking streamlines inventory flow by receiving goods and immediately transferring them to outbound shipments, enhancing warehouse efficiency and reducing handling time. Explore the benefits and challenges of both methods to optimize your inventory management strategy.
Order Fulfillment
Drop shipping enables order fulfillment by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, minimizing inventory holding and reducing shipping times. Cross docking streamlines fulfillment by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage, enhancing speed and efficiency in distribution centers. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Distribution Center
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, reducing the role of the distribution center. Cross docking relies heavily on distribution centers to quickly transfer goods from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage, optimizing inventory flow and reducing handling costs. Explore how your distribution center strategy impacts efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Drop Shipping - Drop shipping is a retail business model where sellers accept orders without holding inventory, instead transferring orders to suppliers who ship products directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - This article provides a step-by-step guide to starting a dropshipping business, including partnering with suppliers and setting up an online store on platforms like Shopify.
Drop-Shipping: What You Need to Know - This guide explains the basics of dropshipping and its implications for both buyers and sellers, including potential risks and benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com