Urban consolidation centres optimize last-mile logistics by aggregating deliveries to multiple retailers in a single location, reducing congestion and emissions in dense city areas. Direct store delivery bypasses central distribution, shipping products straight from manufacturers to stores, enhancing speed and freshness but increasing urban traffic. Discover how these logistics strategies balance efficiency and sustainability in urban supply chains.
Why it is important
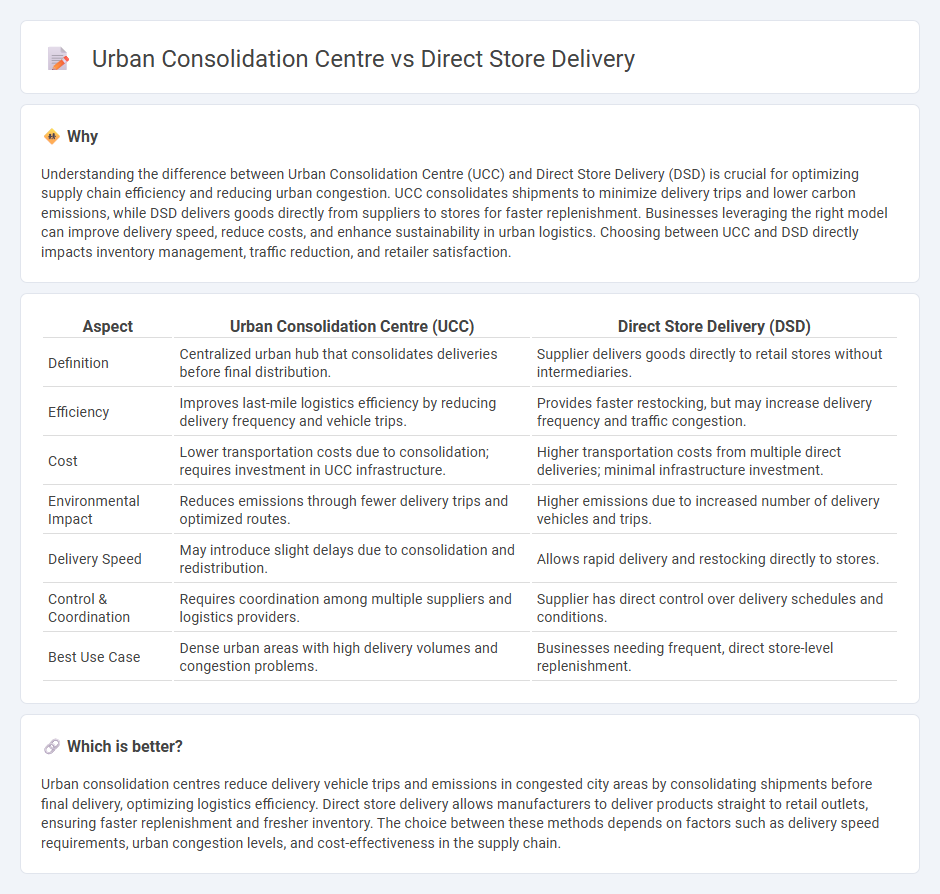
Understanding the difference between Urban Consolidation Centre (UCC) and Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing urban congestion. UCC consolidates shipments to minimize delivery trips and lower carbon emissions, while DSD delivers goods directly from suppliers to stores for faster replenishment. Businesses leveraging the right model can improve delivery speed, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability in urban logistics. Choosing between UCC and DSD directly impacts inventory management, traffic reduction, and retailer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Consolidation Centre (UCC) | Direct Store Delivery (DSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized urban hub that consolidates deliveries before final distribution. | Supplier delivers goods directly to retail stores without intermediaries. |
| Efficiency | Improves last-mile logistics efficiency by reducing delivery frequency and vehicle trips. | Provides faster restocking, but may increase delivery frequency and traffic congestion. |
| Cost | Lower transportation costs due to consolidation; requires investment in UCC infrastructure. | Higher transportation costs from multiple direct deliveries; minimal infrastructure investment. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces emissions through fewer delivery trips and optimized routes. | Higher emissions due to increased number of delivery vehicles and trips. |
| Delivery Speed | May introduce slight delays due to consolidation and redistribution. | Allows rapid delivery and restocking directly to stores. |
| Control & Coordination | Requires coordination among multiple suppliers and logistics providers. | Supplier has direct control over delivery schedules and conditions. |
| Best Use Case | Dense urban areas with high delivery volumes and congestion problems. | Businesses needing frequent, direct store-level replenishment. |
Which is better?
Urban consolidation centres reduce delivery vehicle trips and emissions in congested city areas by consolidating shipments before final delivery, optimizing logistics efficiency. Direct store delivery allows manufacturers to deliver products straight to retail outlets, ensuring faster replenishment and fresher inventory. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as delivery speed requirements, urban congestion levels, and cost-effectiveness in the supply chain.
Connection
Urban consolidation centres (UCCs) streamline last-mile logistics by centralizing shipments before distributing them to stores, reducing traffic and emissions in city centers. Direct store delivery (DSD) benefits from UCCs by receiving consolidated, just-in-time deliveries, which improve inventory turnover and enhance supply chain efficiency. This integration optimizes urban freight movement and supports sustainable retail distribution models.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Direct store delivery (DSD) streamlines inventory management by bypassing central warehouses, enabling faster replenishment and reducing stockouts in retail stores. Urban consolidation centres (UCCs) consolidate shipments from multiple suppliers, optimizing inventory flow through centralized distribution, lowering transportation costs, and minimizing urban congestion. Explore the comparative benefits of DSD and UCC strategies to enhance inventory efficiency and sustainability in retail logistics.
Transportation Efficiency
Direct store delivery (DSD) reduces handling and storage costs by delivering products straight from the supplier to retail outlets, optimizing transportation routes and minimizing delivery time. Urban consolidation centres (UCCs) centralize last-mile deliveries by aggregating shipments, decreasing delivery vehicles in urban areas and reducing traffic congestion and emissions. Explore further to understand how DSD and UCC strategies impact transportation efficiency in supply chain logistics.
Last-Mile Delivery
Direct store delivery (DSD) streamlines last-mile delivery by shipping goods directly from manufacturers to retail outlets, reducing handling times and inventory costs. Urban consolidation centres (UCCs) optimize last-mile logistics by consolidating deliveries from multiple suppliers, minimizing traffic congestion, and lowering carbon emissions in dense city areas. Explore how DSD and UCC models transform urban logistics and enhance delivery efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Direct-Store Delivery (DSD)? What Are Its Benefits? - FarEye - Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a distribution method where manufacturers or suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores, bypassing distribution centers, enhancing product freshness, merchandising, and streamlining invoicing and payments for perishable goods.
What Is Direct Store Delivery? - Bernick's - DSD involves delivering products straight from supplier to retail store, often with in-store merchandising, frequent deliveries, and close supplier-retailer relationships, ideal for fast-selling and perishable items to maximize shelf control and profits.
What is Direct Store Delivery? Logistics Glossary - Penske - Direct Store Delivery ships products directly from manufacturers or suppliers to retail stores, reducing touchpoints and labor costs while supporting just-in-time deliveries, inventory management, and special handling requirements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com