Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining temperature-controlled environments essential for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and fresh produce during transportation. Freight consolidation optimizes shipping efficiency by combining multiple smaller shipments into a single cargo load, reducing costs and environmental impact. Explore how integrating cold chain solutions with freight consolidation can enhance supply chain resilience and sustainability.
Why it is important
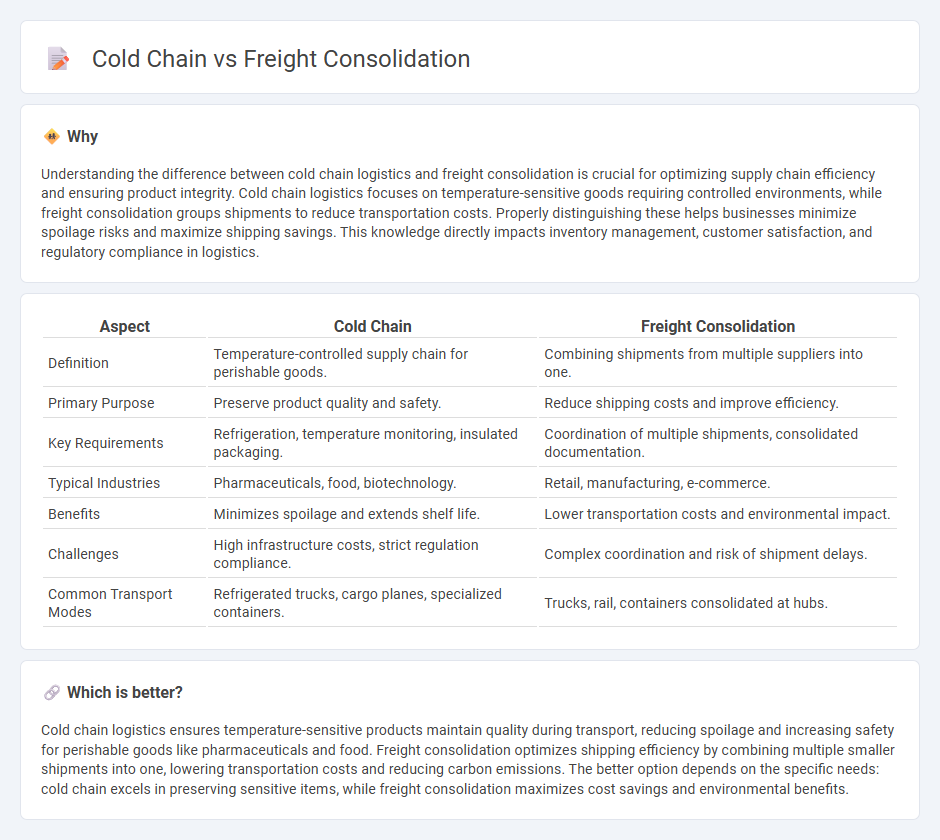
Understanding the difference between cold chain logistics and freight consolidation is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and ensuring product integrity. Cold chain logistics focuses on temperature-sensitive goods requiring controlled environments, while freight consolidation groups shipments to reduce transportation costs. Properly distinguishing these helps businesses minimize spoilage risks and maximize shipping savings. This knowledge directly impacts inventory management, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance in logistics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Freight Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Combining shipments from multiple suppliers into one. |
| Primary Purpose | Preserve product quality and safety. | Reduce shipping costs and improve efficiency. |
| Key Requirements | Refrigeration, temperature monitoring, insulated packaging. | Coordination of multiple shipments, consolidated documentation. |
| Typical Industries | Pharmaceuticals, food, biotechnology. | Retail, manufacturing, e-commerce. |
| Benefits | Minimizes spoilage and extends shelf life. | Lower transportation costs and environmental impact. |
| Challenges | High infrastructure costs, strict regulation compliance. | Complex coordination and risk of shipment delays. |
| Common Transport Modes | Refrigerated trucks, cargo planes, specialized containers. | Trucks, rail, containers consolidated at hubs. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products maintain quality during transport, reducing spoilage and increasing safety for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food. Freight consolidation optimizes shipping efficiency by combining multiple smaller shipments into one, lowering transportation costs and reducing carbon emissions. The better option depends on the specific needs: cold chain excels in preserving sensitive items, while freight consolidation maximizes cost savings and environmental benefits.
Connection
Cold chain logistics relies on freight consolidation to optimize the transportation of temperature-sensitive goods by combining shipments into fewer, larger loads, reducing transit times and minimizing exposure to temperature fluctuations. Consolidated freight in cold chain management enhances efficiency by lowering shipping costs and ensuring consistent refrigeration throughout the supply route. Effective integration of cold chain protocols with freight consolidation supports product integrity for pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and other sensitive items.
Key Terms
**Freight Consolidation:**
Freight consolidation combines multiple smaller shipments into one larger load to reduce transportation costs and improve efficiency, often by maximizing container space and decreasing the number of trips. This method optimizes logistics for non-perishable goods by minimizing handling and freight expenses without compromising delivery speed. Discover how freight consolidation can streamline your supply chain and enhance cost savings.
Hub-and-Spoke
Freight consolidation in a hub-and-spoke model optimizes cargo volume by grouping shipments at central hubs, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery efficiency. Cold chain logistics within this system ensures temperature-sensitive goods maintain their integrity through refrigerated hubs and specialized handling protocols. Explore how integrating freight consolidation with cold chain management enhances supply chain reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Less-than-Truckload (LTL)
Freight consolidation in Less-than-Truckload (LTL) shipping maximizes efficiency by grouping multiple smaller shipments into a single load, reducing costs and transit times. Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive goods remain within specified thermal ranges during LTL transport, maintaining product quality and regulatory compliance. Explore more on optimizing LTL operations through integrated freight consolidation and cold chain management strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Freight Consolidation? Trinity Explains. - Freight consolidation is the process where a shipper combines multiple smaller shipments within a region into a single load transported to the destination region, optimizing space, reducing costs, and saving time by paying bulk rates instead of individual shipment fees.
Freight Consolidation: What It Is and When to use it. - Freight consolidation lowers shipping costs by allowing businesses to combine freight volumes in order to secure full truckload pricing at less-than-truckload volumes, also improving supply chain performance through fewer transitions and faster deliveries.
Freight Consolidation: The Benefits and Drawbacks - Averitt - Freight consolidation combines multiple LTL shipments bound for the same region into a full truckload shipment, reducing per-unit costs and freight damages while meeting the demand for smaller, frequent shipments in dynamic markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com