Urban logistics hubs enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by consolidating shipments close to city centers, reducing transit times and emissions. Forward stocking locations store inventory nearer to demand points, enabling faster replenishment and improved service levels for retailers and manufacturers. Explore the benefits and strategic differences between these two critical distribution models to optimize your supply chain.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between urban logistics hubs and forward stocking locations is crucial for optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Urban logistics hubs are centralized points within cities designed for transshipment and consolidation of goods, enhancing speed and reducing congestion. Forward stocking locations, located closer to end customers, enable rapid order fulfillment by holding inventory near demand points. Knowing their distinct roles helps businesses strategically balance inventory management and delivery speed in urban supply chains.
Comparison Table
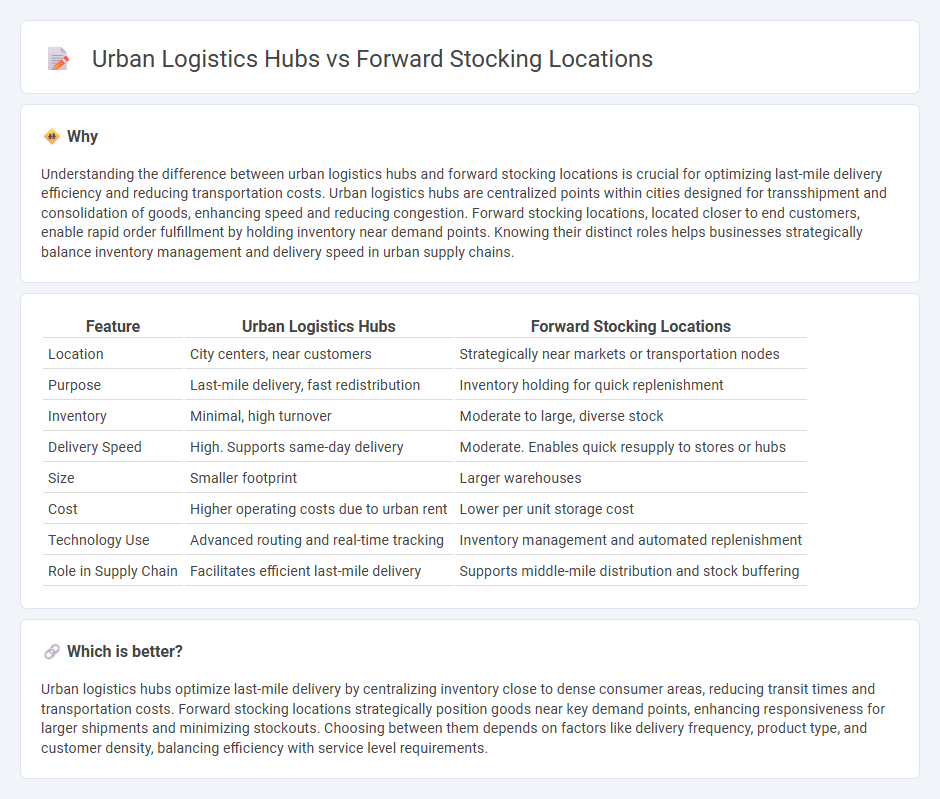
| Feature | Urban Logistics Hubs | Forward Stocking Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Location | City centers, near customers | Strategically near markets or transportation nodes |
| Purpose | Last-mile delivery, fast redistribution | Inventory holding for quick replenishment |
| Inventory | Minimal, high turnover | Moderate to large, diverse stock |
| Delivery Speed | High. Supports same-day delivery | Moderate. Enables quick resupply to stores or hubs |
| Size | Smaller footprint | Larger warehouses |
| Cost | Higher operating costs due to urban rent | Lower per unit storage cost |
| Technology Use | Advanced routing and real-time tracking | Inventory management and automated replenishment |
| Role in Supply Chain | Facilitates efficient last-mile delivery | Supports middle-mile distribution and stock buffering |
Which is better?
Urban logistics hubs optimize last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory close to dense consumer areas, reducing transit times and transportation costs. Forward stocking locations strategically position goods near key demand points, enhancing responsiveness for larger shipments and minimizing stockouts. Choosing between them depends on factors like delivery frequency, product type, and customer density, balancing efficiency with service level requirements.
Connection
Urban logistics hubs serve as central nodes facilitating the consolidation and redistribution of goods within metropolitan areas, optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency. Forward stocking locations act as decentralized inventory points strategically positioned near demand centers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. The seamless integration of these hubs with forward stocking locations enhances supply chain responsiveness and supports sustainable urban freight management.
Key Terms
Inventory Placement
Forward stocking locations prioritize decentralizing inventory close to end customers to minimize delivery times and enhance service levels, essential for efficient last-mile fulfillment. Urban logistics hubs concentrate on centralized inventory management within city centers to leverage higher shipment volumes and optimize transportation costs. Explore the strategic considerations and benefits of each approach to optimize your inventory placement effectively.
Last-Mile Delivery
Forward stocking locations (FSLs) strategically position inventory closer to end customers, significantly reducing last-mile delivery times and enhancing service responsiveness. Urban logistics hubs serve as centralized distribution points within metropolitan areas, optimizing route efficiency and lowering transportation costs while managing the complexity of dense urban environments. Explore how leveraging both FSLs and urban hubs can transform your last-mile delivery strategy for maximum efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Facility Proximity
Forward stocking locations minimize delivery times by placing inventory near end customers, enhancing supply chain responsiveness and reducing transportation costs. Urban logistics hubs serve as centralized distribution points within metropolitan areas, optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency and supporting sustainable urban freight management. Explore how facility proximity impacts operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in modern logistics networks.
Source and External Links
Forward Stocking Locations | American Expediting - Forward stocking locations are warehouses positioned close to customers to enhance warehouse reach and speed service, handling diverse inventory like medical equipment and industrial supplies while offering secure storage and real-time inventory tracking across the U.S. and Canada.
What Are Forward Stocking Locations? | Park Place Technologies - Forward stocking locations are mini-warehouses storing spare parts near end users globally, enabling faster regional delivery and helping companies meet strict service level agreements with over 900 locations worldwide covering multiple continents.
Understanding Forward Stocking Locations (FSL) - TecEx - FSLs are strategically positioned warehouses that bring inventory closer to key markets, reducing shipping times and costs, improving inventory management, and enhancing customer service by placing stock nearer to demand hubs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com