Dynamic rerouting leverages real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and delivery priorities to continuously adjust delivery paths, minimizing delays and fuel consumption. Event-driven routing reacts specifically to unexpected incidents such as accidents, road closures, or urgent shipment requests, triggering immediate route changes to maintain supply chain efficiency. Explore the advantages and applications of dynamic rerouting versus event-driven routing in modern logistics to optimize your transportation network.
Why it is important
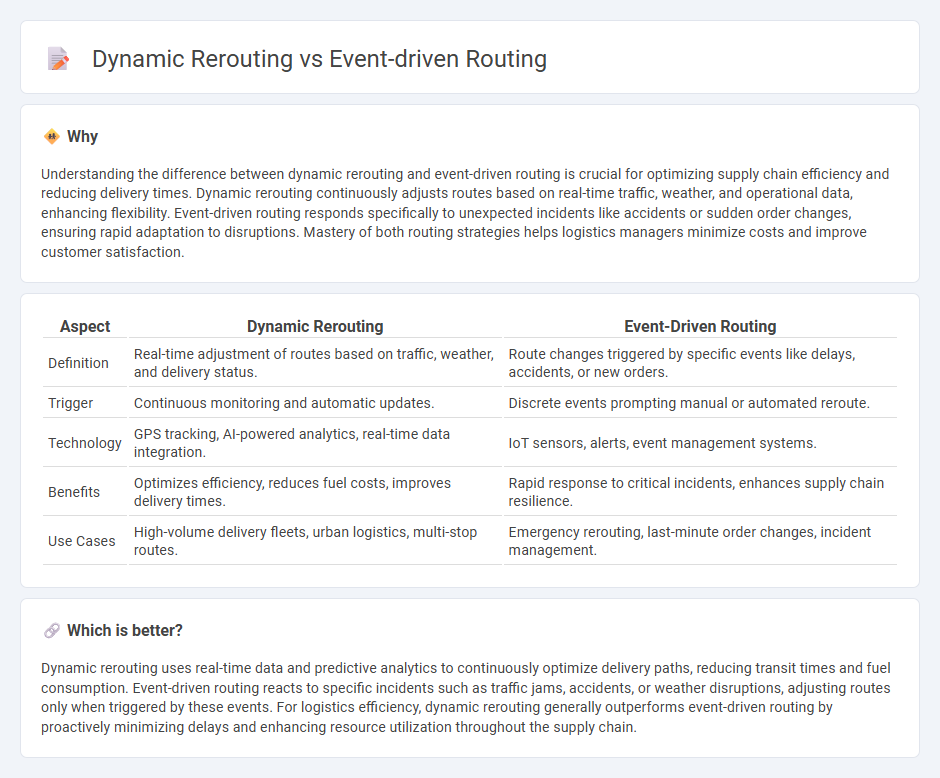
Understanding the difference between dynamic rerouting and event-driven routing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing delivery times. Dynamic rerouting continuously adjusts routes based on real-time traffic, weather, and operational data, enhancing flexibility. Event-driven routing responds specifically to unexpected incidents like accidents or sudden order changes, ensuring rapid adaptation to disruptions. Mastery of both routing strategies helps logistics managers minimize costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dynamic Rerouting | Event-Driven Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of routes based on traffic, weather, and delivery status. | Route changes triggered by specific events like delays, accidents, or new orders. |
| Trigger | Continuous monitoring and automatic updates. | Discrete events prompting manual or automated reroute. |
| Technology | GPS tracking, AI-powered analytics, real-time data integration. | IoT sensors, alerts, event management systems. |
| Benefits | Optimizes efficiency, reduces fuel costs, improves delivery times. | Rapid response to critical incidents, enhances supply chain resilience. |
| Use Cases | High-volume delivery fleets, urban logistics, multi-stop routes. | Emergency rerouting, last-minute order changes, incident management. |
Which is better?
Dynamic rerouting uses real-time data and predictive analytics to continuously optimize delivery paths, reducing transit times and fuel consumption. Event-driven routing reacts to specific incidents such as traffic jams, accidents, or weather disruptions, adjusting routes only when triggered by these events. For logistics efficiency, dynamic rerouting generally outperforms event-driven routing by proactively minimizing delays and enhancing resource utilization throughout the supply chain.
Connection
Dynamic rerouting in logistics leverages real-time data to adjust delivery paths based on current conditions, while event-driven routing triggers these adjustments in response to specific incidents such as traffic congestion, vehicle breakdowns, or urgent shipment requests. This interconnected approach enhances supply chain efficiency by minimizing delays and optimizing resource utilization. Integration of IoT sensors and advanced analytics platforms facilitates seamless communication between events and route recalculations, ensuring adaptive and resilient logistics operations.
Key Terms
Real-time Data Integration
Event-driven routing leverages real-time triggers from data events to immediately adjust traffic paths, enhancing responsiveness to current conditions. Dynamic rerouting continuously analyzes traffic data, using algorithms to optimize routes based on real-time information like congestion or accidents. Discover how integrating event-driven routing and dynamic rerouting can transform your traffic management strategies.
Trigger Points (Events)
Event-driven routing relies on specific trigger points such as sensor activations or system alerts to initiate route adjustments, optimizing responsiveness to real-time conditions. Dynamic rerouting continuously evaluates network data, including traffic flow and congestion levels, to recalibrate paths proactively without waiting for explicit triggers. Discover how these approaches enhance navigation efficiency by exploring their distinct event-handling mechanisms.
Route Optimization Algorithms
Event-driven routing leverages real-time data triggers to promptly adjust routes, enhancing responsiveness in fluctuating conditions, while dynamic rerouting continuously recalculates paths based on current traffic and network states to optimize travel efficiency. Route optimization algorithms such as Dijkstra's, A*, and genetic algorithms play crucial roles in both methods by processing traffic patterns, distances, and constraints to minimize travel time and costs. Explore the latest advancements in route optimization algorithms to understand their impact on intelligent transport and logistics systems.
Source and External Links
What is EDA? - Event-Driven Architecture Explained - AWS - Event-driven routing in event-driven architecture involves an event router acting as a centralized component that filters, routes, and audits events between decoupled services, enabling asynchronous communication and independent service management with policy controls for security and cost efficiency.
Event-Driven Architecture - AWS - Event-driven routing uses an event router to automatically push filtered events to consumers, removing the need for polling and coordination between services, supporting cross-account and cross-region data replication while providing centralized audit and security policy enforcement.
Event-driven architectures | Eventarc - Google Cloud - Event-driven routing is conducted by an event router that ingests, filters, and fans out immutable events from producers to appropriate consumers based on subscriptions or triggers, enabling decoupled microservices to react asynchronously and independently to state changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com