Middle mile optimization enhances supply chain efficiency by streamlining transportation between warehouses and distribution centers using real-time data and advanced routing algorithms. Reverse logistics focuses on managing product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to minimize waste and recover value. Explore effective strategies to improve your logistics operations and reduce costs.
Why it is important
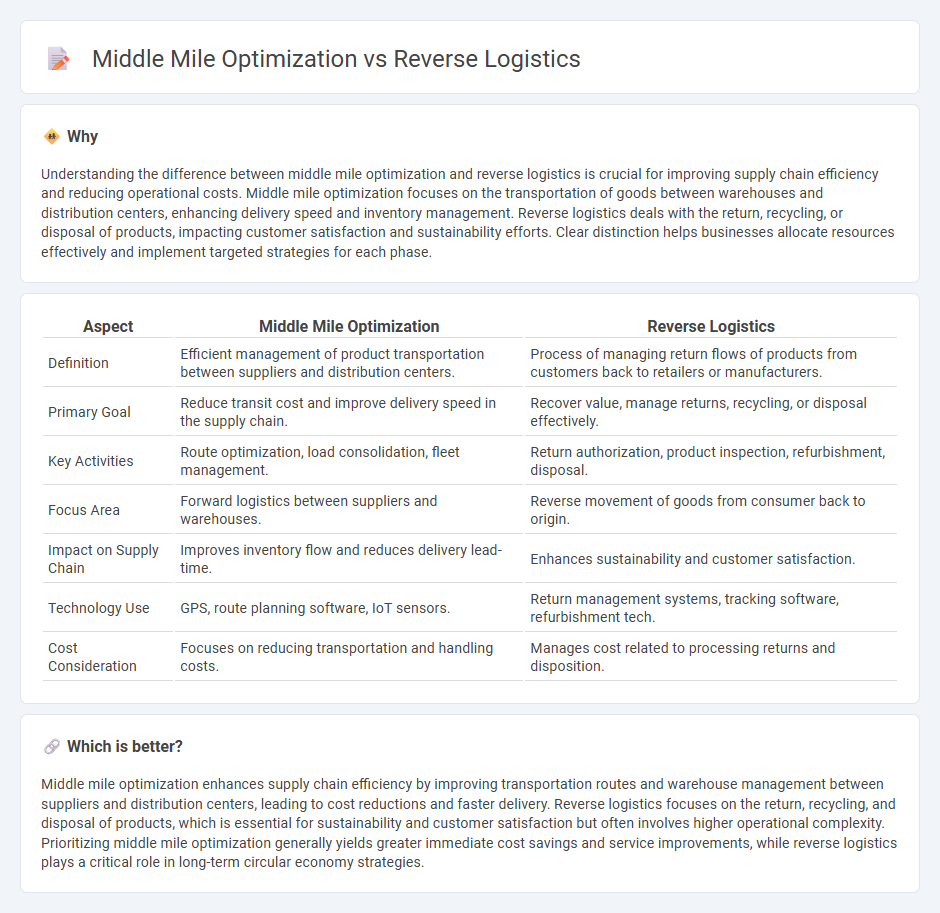
Understanding the difference between middle mile optimization and reverse logistics is crucial for improving supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Middle mile optimization focuses on the transportation of goods between warehouses and distribution centers, enhancing delivery speed and inventory management. Reverse logistics deals with the return, recycling, or disposal of products, impacting customer satisfaction and sustainability efforts. Clear distinction helps businesses allocate resources effectively and implement targeted strategies for each phase.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Middle Mile Optimization | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Efficient management of product transportation between suppliers and distribution centers. | Process of managing return flows of products from customers back to retailers or manufacturers. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce transit cost and improve delivery speed in the supply chain. | Recover value, manage returns, recycling, or disposal effectively. |
| Key Activities | Route optimization, load consolidation, fleet management. | Return authorization, product inspection, refurbishment, disposal. |
| Focus Area | Forward logistics between suppliers and warehouses. | Reverse movement of goods from consumer back to origin. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Improves inventory flow and reduces delivery lead-time. | Enhances sustainability and customer satisfaction. |
| Technology Use | GPS, route planning software, IoT sensors. | Return management systems, tracking software, refurbishment tech. |
| Cost Consideration | Focuses on reducing transportation and handling costs. | Manages cost related to processing returns and disposition. |
Which is better?
Middle mile optimization enhances supply chain efficiency by improving transportation routes and warehouse management between suppliers and distribution centers, leading to cost reductions and faster delivery. Reverse logistics focuses on the return, recycling, and disposal of products, which is essential for sustainability and customer satisfaction but often involves higher operational complexity. Prioritizing middle mile optimization generally yields greater immediate cost savings and service improvements, while reverse logistics plays a critical role in long-term circular economy strategies.
Connection
Middle mile optimization enhances supply chain efficiency by streamlining transportation and inventory management between warehouses and distribution centers, directly impacting reverse logistics processes. Efficient middle mile operations reduce return transit times and costs, facilitating quicker processing of returned goods and improving overall reverse logistics performance. Integrating data from both middle mile and reverse logistics enables better route planning, inventory tracking, and resource allocation, ultimately driving cost savings and sustainability in logistics management.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics focuses on managing the return flow of goods from consumers to manufacturers, including product returns, recycling, and refurbishing. Effective reverse logistics reduces waste, recovers value, and improves customer satisfaction through efficient handling of returned items. Discover how optimizing reverse logistics can enhance your supply chain sustainability and profitability.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics centers on the efficient handling of product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to minimize waste and recover value. Middle mile optimization streamlines transportation between warehouses and distribution centers, reducing costs and improving delivery speed. Discover effective strategies to enhance returns management and optimize your supply chain.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics in refurbishment emphasizes the return flow of used products for repair, testing, and quality assurance to restore value. Middle mile optimization streamlines transportation and storage between manufacturing and distribution centers, reducing costs and improving turnaround times for refurbished items. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these processes enhance refurbishment efficiency and profitability.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, or recycling, aiming to implement a cost-effective flow from consumption to origin while supporting sustainability and lean supply chain principles.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages returns, surplus goods, and refurbishments by controlling product flows from customers back to sellers or manufacturers, with varied applications across industries like beverage, construction, and food.
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics integrates shipping and returns to reduce operational waste, making supply chains more efficient and sustainable by optimizing resources and adapting to environmental responsibilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com