Last mile delivery ensures products reach customers quickly by handling final shipment from distribution centers to their doorsteps, emphasizing speed and reliability. Dropshipping bypasses inventory management by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, reducing overhead but potentially increasing delivery times. Explore the advantages and challenges of these fulfillment methods to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
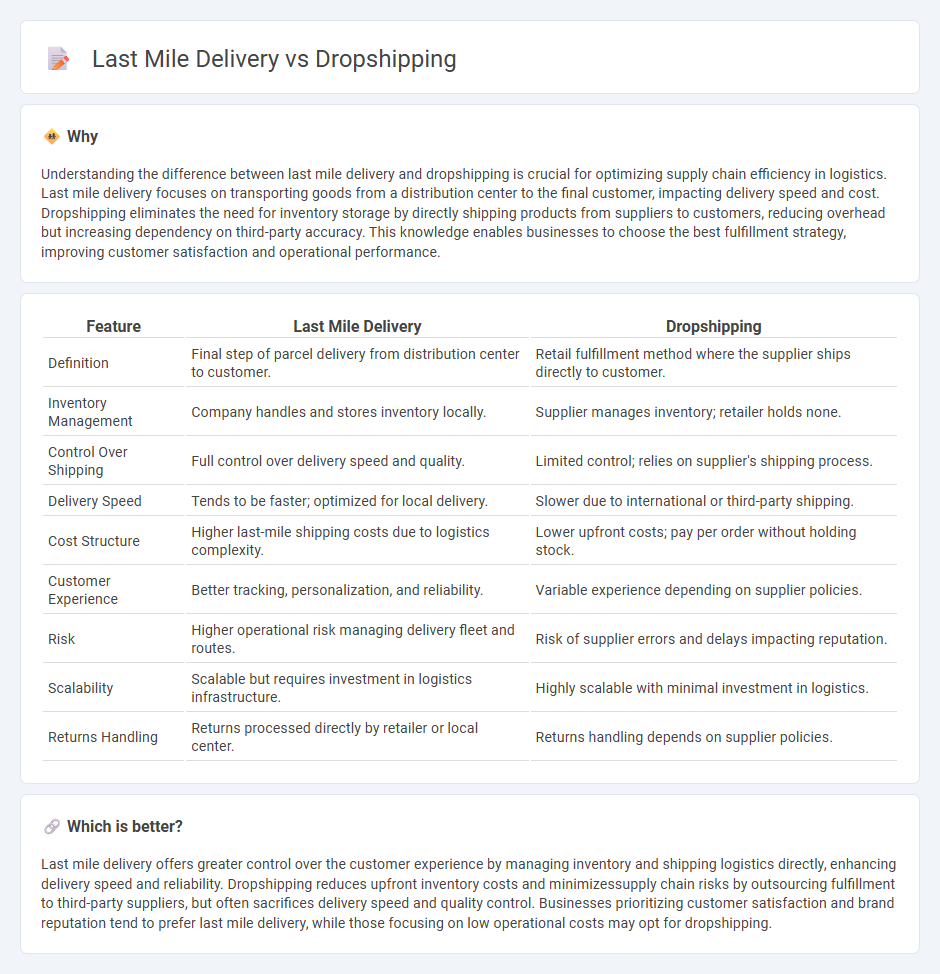
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and dropshipping is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency in logistics. Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a distribution center to the final customer, impacting delivery speed and cost. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing overhead but increasing dependency on third-party accuracy. This knowledge enables businesses to choose the best fulfillment strategy, improving customer satisfaction and operational performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Last Mile Delivery | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final step of parcel delivery from distribution center to customer. | Retail fulfillment method where the supplier ships directly to customer. |
| Inventory Management | Company handles and stores inventory locally. | Supplier manages inventory; retailer holds none. |
| Control Over Shipping | Full control over delivery speed and quality. | Limited control; relies on supplier's shipping process. |
| Delivery Speed | Tends to be faster; optimized for local delivery. | Slower due to international or third-party shipping. |
| Cost Structure | Higher last-mile shipping costs due to logistics complexity. | Lower upfront costs; pay per order without holding stock. |
| Customer Experience | Better tracking, personalization, and reliability. | Variable experience depending on supplier policies. |
| Risk | Higher operational risk managing delivery fleet and routes. | Risk of supplier errors and delays impacting reputation. |
| Scalability | Scalable but requires investment in logistics infrastructure. | Highly scalable with minimal investment in logistics. |
| Returns Handling | Returns processed directly by retailer or local center. | Returns handling depends on supplier policies. |
Which is better?
Last mile delivery offers greater control over the customer experience by managing inventory and shipping logistics directly, enhancing delivery speed and reliability. Dropshipping reduces upfront inventory costs and minimizessupply chain risks by outsourcing fulfillment to third-party suppliers, but often sacrifices delivery speed and quality control. Businesses prioritizing customer satisfaction and brand reputation tend to prefer last mile delivery, while those focusing on low operational costs may opt for dropshipping.
Connection
Last mile delivery plays a crucial role in dropshipping by ensuring efficient product movement from suppliers to end customers without the need for inventory holding. Dropshipping relies heavily on last mile logistics to minimize delivery time and reduce shipping costs, enhancing customer satisfaction. Optimizing last mile delivery routes and leveraging real-time tracking systems directly improves the operational efficiency of dropshipping businesses.
Key Terms
Inventory Management (dropshipping)
Dropshipping inventory management eliminates the need to hold stock by relying on suppliers to fulfill orders directly, reducing overhead costs and inventory risks. Efficient communication and accurate real-time data sharing between retailers and suppliers are crucial to prevent stockouts and delays in dropshipping models. Explore how mastering these inventory strategies can enhance your dropshipping success and operational efficiency.
Order Fulfillment (dropshipping)
Dropshipping order fulfillment involves suppliers directly shipping products to customers, eliminating the need for inventory management and warehousing by the retailer, which reduces overhead costs and speeds up the process. In contrast, last mile delivery focuses on the final step of the delivery journey, ensuring fast, accurate, and cost-effective delivery from a local warehouse or distribution center to the customer's doorstep, often involving real-time tracking and route optimization. Explore how optimizing order fulfillment strategies can enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Route Optimization (last mile delivery)
Route optimization in last mile delivery significantly enhances efficiency by minimizing travel distance and delivery time, directly reducing operational costs and carbon emissions. Dropshipping bypasses inventory storage but still relies on effective last mile logistics to ensure timely order fulfillment and customer satisfaction. Explore advanced route optimization technologies to maximize last mile delivery performance and drive business growth.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping is a business model where products sold in an online store are shipped directly to customers by the supplier, eliminating the need for the seller to hold inventory or handle shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where the seller creates and markets an online store but outsources storage, packaging, and shipping to third-party suppliers who fulfill customer orders directly.
Drop shipping - Drop shipping lets sellers accept orders without keeping stock, passing order and shipping details to suppliers who ship directly to customers, allowing sellers to avoid inventory costs and operate with minimal upfront investment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com