Reducing empty miles significantly lowers transportation costs and minimizes environmental impact by optimizing vehicle utilization. Dynamic scheduling enhances route flexibility and improves delivery efficiency by adjusting plans in real-time based on current conditions. Explore effective strategies to balance empty miles reduction with dynamic scheduling for optimized logistics performance.
Why it is important
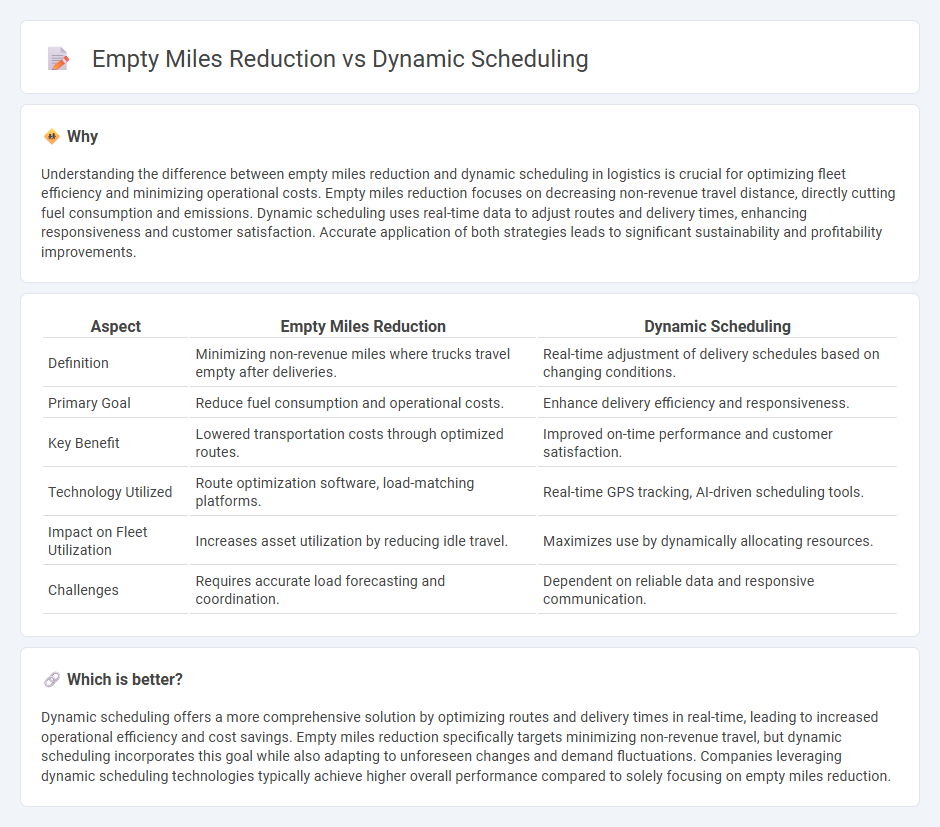
Understanding the difference between empty miles reduction and dynamic scheduling in logistics is crucial for optimizing fleet efficiency and minimizing operational costs. Empty miles reduction focuses on decreasing non-revenue travel distance, directly cutting fuel consumption and emissions. Dynamic scheduling uses real-time data to adjust routes and delivery times, enhancing responsiveness and customer satisfaction. Accurate application of both strategies leads to significant sustainability and profitability improvements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Dynamic Scheduling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing non-revenue miles where trucks travel empty after deliveries. | Real-time adjustment of delivery schedules based on changing conditions. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce fuel consumption and operational costs. | Enhance delivery efficiency and responsiveness. |
| Key Benefit | Lowered transportation costs through optimized routes. | Improved on-time performance and customer satisfaction. |
| Technology Utilized | Route optimization software, load-matching platforms. | Real-time GPS tracking, AI-driven scheduling tools. |
| Impact on Fleet Utilization | Increases asset utilization by reducing idle travel. | Maximizes use by dynamically allocating resources. |
| Challenges | Requires accurate load forecasting and coordination. | Dependent on reliable data and responsive communication. |
Which is better?
Dynamic scheduling offers a more comprehensive solution by optimizing routes and delivery times in real-time, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost savings. Empty miles reduction specifically targets minimizing non-revenue travel, but dynamic scheduling incorporates this goal while also adapting to unforeseen changes and demand fluctuations. Companies leveraging dynamic scheduling technologies typically achieve higher overall performance compared to solely focusing on empty miles reduction.
Connection
Reducing empty miles directly enhances operational efficiency by minimizing unproductive travel and cutting fuel costs, which aligns closely with dynamic scheduling strategies that optimize delivery routes in real-time based on demand and traffic conditions. Dynamic scheduling leverages advanced algorithms and data analytics to assign loads more effectively, ensuring trucks spend more time loaded and fewer miles empty. This synergy between empty miles reduction and dynamic scheduling leads to lower carbon emissions, improved asset utilization, and significant cost savings in logistics management.
Key Terms
**Dynamic Scheduling:**
Dynamic scheduling optimizes fleet operations by leveraging real-time data to adjust routes and delivery times, increasing efficiency and reducing idle times. The approach minimizes delays, improves resource allocation, and enhances customer satisfaction through flexible and adaptive planning. Explore how dynamic scheduling technology can transform logistics and elevate operational performance.
Real-time Optimization
Dynamic scheduling improves operational efficiency by adjusting delivery routes and times based on real-time data, reducing idle times and better responding to demand fluctuations. Empty miles reduction targets minimizing non-revenue generating mileage, cutting fuel costs and lowering carbon emissions, which enhances sustainability in transportation. Explore how real-time optimization synergizes these strategies to maximize fleet productivity and cost savings.
Resource Allocation
Dynamic scheduling optimizes resource allocation by adjusting delivery routes in real-time, reducing idle time and enhancing fleet utilization. Empty miles reduction targets minimizing non-revenue travel, which directly lowers fuel consumption and operational costs while maximizing asset productivity. Explore how integrating both strategies can revolutionize your logistics efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Dynamic Scheduling? - Totalmobile - Dynamic scheduling is an advanced workforce management tool that uses algorithms and machine learning to automatically optimise real-time employee allocation, considering availability, skills, travel time, and unexpected disruptions to maximize efficiency and reduce costs in fast-paced industries.
Dynamic priority scheduling - Wikipedia - Dynamic priority scheduling is a real-time algorithm where task priorities are computed during execution, allowing optimal resource use by adapting task order based on changing deadlines and progress, exemplified by algorithms like Earliest Deadline First (EDF).
Dynamic scheduling - Example - Computer Architecture - In computer architecture, dynamic scheduling rearranges instruction execution order to reduce pipeline stalls and handle data dependencies by using structures like reservation stations and common data buses, improving processor throughput without violating program correctness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com