Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishables remain within controlled environments throughout transportation and storage, preserving quality and safety. Cross docking streamlines supply chain efficiency by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and reducing handling costs. Discover how integrating cold chain and cross docking solutions can enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
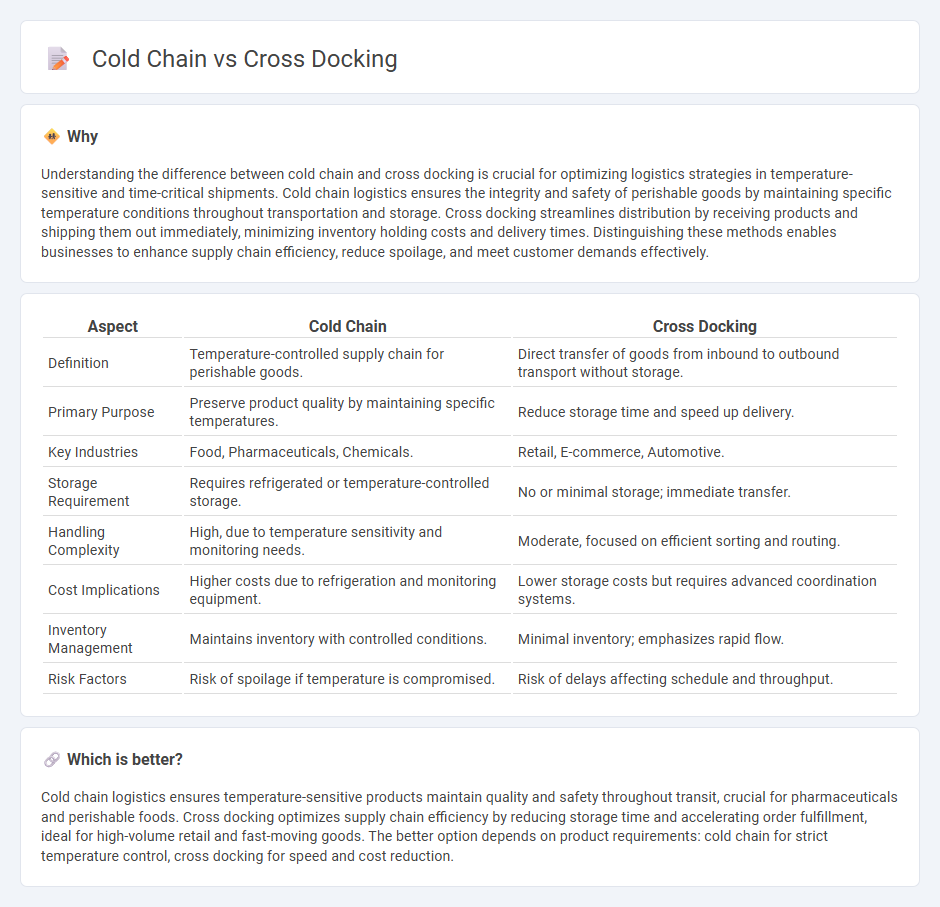
Understanding the difference between cold chain and cross docking is crucial for optimizing logistics strategies in temperature-sensitive and time-critical shipments. Cold chain logistics ensures the integrity and safety of perishable goods by maintaining specific temperature conditions throughout transportation and storage. Cross docking streamlines distribution by receiving products and shipping them out immediately, minimizing inventory holding costs and delivery times. Distinguishing these methods enables businesses to enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce spoilage, and meet customer demands effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Cross Docking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transport without storage. |
| Primary Purpose | Preserve product quality by maintaining specific temperatures. | Reduce storage time and speed up delivery. |
| Key Industries | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals. | Retail, E-commerce, Automotive. |
| Storage Requirement | Requires refrigerated or temperature-controlled storage. | No or minimal storage; immediate transfer. |
| Handling Complexity | High, due to temperature sensitivity and monitoring needs. | Moderate, focused on efficient sorting and routing. |
| Cost Implications | Higher costs due to refrigeration and monitoring equipment. | Lower storage costs but requires advanced coordination systems. |
| Inventory Management | Maintains inventory with controlled conditions. | Minimal inventory; emphasizes rapid flow. |
| Risk Factors | Risk of spoilage if temperature is compromised. | Risk of delays affecting schedule and throughput. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products maintain quality and safety throughout transit, crucial for pharmaceuticals and perishable foods. Cross docking optimizes supply chain efficiency by reducing storage time and accelerating order fulfillment, ideal for high-volume retail and fast-moving goods. The better option depends on product requirements: cold chain for strict temperature control, cross docking for speed and cost reduction.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products remain within a controlled environment from origin to destination, minimizing spoilage and maintaining product quality. Cross docking accelerates the transfer of goods by unloading inbound shipments directly onto outbound vehicles, reducing storage time and preserving the cold chain integrity. Integrating cross docking with cold chain enables faster distribution of perishable items such as pharmaceuticals and food, optimizing supply chain efficiency and product freshness.
Key Terms
**Cross Docking:**
Cross docking streamlines supply chain operations by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and reducing inventory costs. This method enhances efficiency and accelerates distribution, particularly for time-sensitive goods, by eliminating the need for warehousing. Discover more about how cross docking can optimize logistics and improve delivery speed.
Transshipment
Cross docking streamlines the transshipment process by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation without long-term storage, significantly reducing handling time and inventory costs. Cold chain transshipment emphasizes maintaining precise temperature control throughout the transfer to preserve perishable goods' quality and safety. Explore how integrating cross docking with cold chain logistics enhances efficiency in temperature-sensitive supply chains.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Cross docking accelerates Just-in-Time (JIT) delivery by minimizing inventory holding and enabling rapid transfer of goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation. Cold chain logistics incorporate temperature-controlled environments essential for perishable items, ensuring product integrity during JIT delivery. Discover how integrating cross docking with cold chain systems optimizes supply chain efficiency and responsiveness.
Source and External Links
Cross Docking: Definition, History, and Process - Cross docking is a shipping method transferring goods directly from incoming to outgoing transportation modes, with key methods including continuous cross docking, consolidation arrangements, and de-consolidation to efficiently handle shipments and reduce costs.
What Is Cross-Docking? Definition, Types & Advantages - Cross-docking is a supply chain technique that rapidly transfers goods from inbound to outbound vehicles with minimal storage, accelerating delivery, reducing costs, and improving inventory control used by various industries like retail and manufacturing.
Understanding cross-docking: A comprehensive guide - Cross-docking involves direct transfer of products from suppliers to customers with minimal storage, categorized by pre-distribution and post-distribution sorting approaches, and by process types such as continuous, consolidation, and deconsolidation to suit different logistics needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com