Liquidity staking allows investors to earn rewards while maintaining asset liquidity by enabling token transfers and trading, unlike traditional staking that locks assets. Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) improves network scalability and governance by allowing token holders to elect delegates who validate transactions on their behalf. Explore the advantages and use cases of liquidity staking and DPoS to enhance your crypto investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between liquidity staking and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) is crucial for optimizing returns and managing risks in cryptocurrency investments. Liquidity staking allows users to earn rewards while maintaining token liquidity through tradable staking derivatives, enhancing capital efficiency. Delegated proof-of-stake involves delegating voting power to validators who secure the network, influencing decentralization and governance. Differentiating these mechanisms helps investors align strategies with their liquidity needs and risk tolerance in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Comparison Table
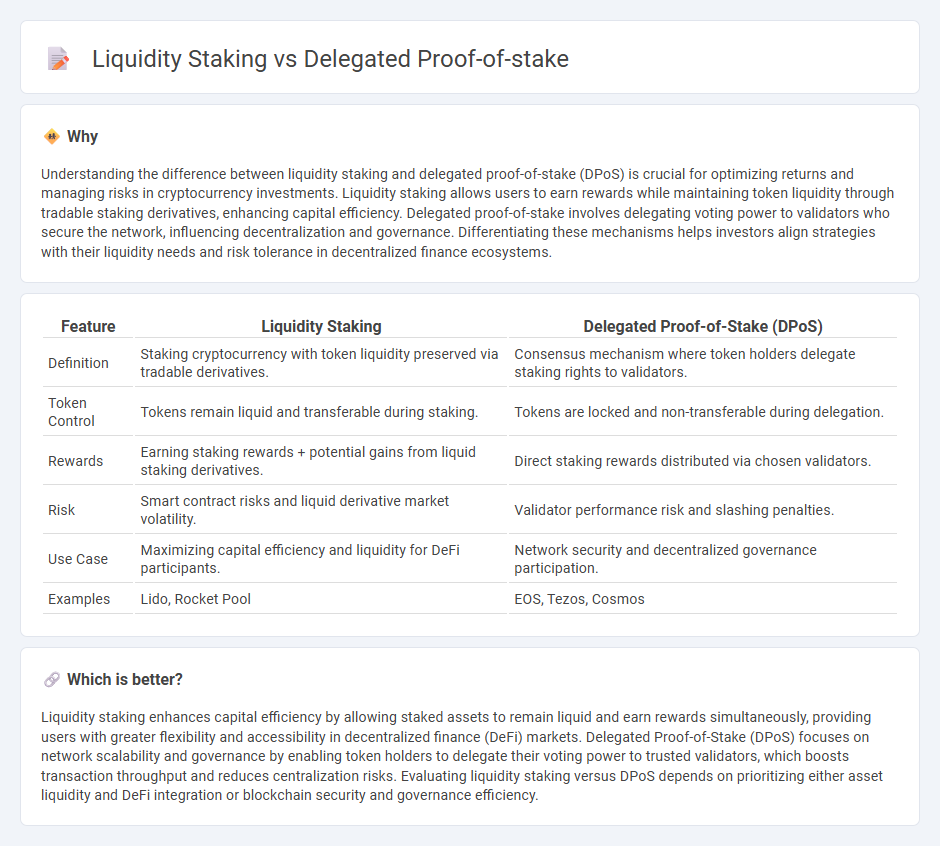
| Feature | Liquidity Staking | Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staking cryptocurrency with token liquidity preserved via tradable derivatives. | Consensus mechanism where token holders delegate staking rights to validators. |
| Token Control | Tokens remain liquid and transferable during staking. | Tokens are locked and non-transferable during delegation. |
| Rewards | Earning staking rewards + potential gains from liquid staking derivatives. | Direct staking rewards distributed via chosen validators. |
| Risk | Smart contract risks and liquid derivative market volatility. | Validator performance risk and slashing penalties. |
| Use Case | Maximizing capital efficiency and liquidity for DeFi participants. | Network security and decentralized governance participation. |
| Examples | Lido, Rocket Pool | EOS, Tezos, Cosmos |
Which is better?
Liquidity staking enhances capital efficiency by allowing staked assets to remain liquid and earn rewards simultaneously, providing users with greater flexibility and accessibility in decentralized finance (DeFi) markets. Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) focuses on network scalability and governance by enabling token holders to delegate their voting power to trusted validators, which boosts transaction throughput and reduces centralization risks. Evaluating liquidity staking versus DPoS depends on prioritizing either asset liquidity and DeFi integration or blockchain security and governance efficiency.
Connection
Liquidity staking enhances delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) by allowing token holders to earn staking rewards while maintaining the ability to trade or use their staked assets. In DPoS networks like EOS and Tezos, liquidity staking tokens represent delegated stakes, providing increased market liquidity without compromising network security or decentralization. This integration drives higher participation rates and strengthens consensus mechanisms through more flexible asset management.
Key Terms
Validator
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) relies on token holders electing validators who confirm transactions and maintain network security, emphasizing trust and voting power distribution. Liquidity staking allows users to stake assets while retaining liquidity through tokenized derivatives, enabling validators to secure the network and provide capital efficiency simultaneously. Explore how these staking mechanisms impact validator incentives, network performance, and user benefits in detail.
Staking Pool
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) enables token holders to delegate their voting power to trusted validators, enhancing network security and transaction speed through a consensus pool. Liquidity staking involves locking assets in a staking pool that provides liquidity, allowing users to earn rewards while maintaining asset flexibility. Explore the mechanisms and benefits of Staking Pools to understand their impact on blockchain participation and earning potential.
Governance
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) enhances blockchain governance by enabling token holders to elect delegates who validate transactions and propose protocol changes, ensuring a more democratic and scalable decision-making process. Liquidity staking improves governance participation by allowing stakers to retain transferable tokens while earning rewards, increasing voter engagement and flexibility within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Explore deeper insights into how these consensus mechanisms impact governance models and token holder influence.
Source and External Links
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)? - DPoS is a consensus mechanism evolving from Proof of Stake, where users vote for delegates who validate blocks, aiming for a democratic and efficient blockchain process originally designed by Daniel Larimer in 2013.
What Is Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)? - DPoS features a voting system where participants elect delegates to validate blocks, offering an accessible and scalable variation of Proof of Stake with a focus on democratic participation.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) - DPoS is a consensus algorithm designed to secure blockchains through a democratic voting and election system of witnesses/delegates, emphasizing efficiency, decentralization, and flexibility, created by Daniel Larimer and used in projects like BitShares and EOS.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com