Marketplace flipping involves purchasing undervalued items from online or physical marketplaces and reselling them at a higher price, capitalizing on market inefficiencies. Wholesale arbitrage focuses on buying bulk products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates to resell individually for profit. Explore the distinct strategies and benefits of each approach to enhance your entrepreneurial success.
Why it is important
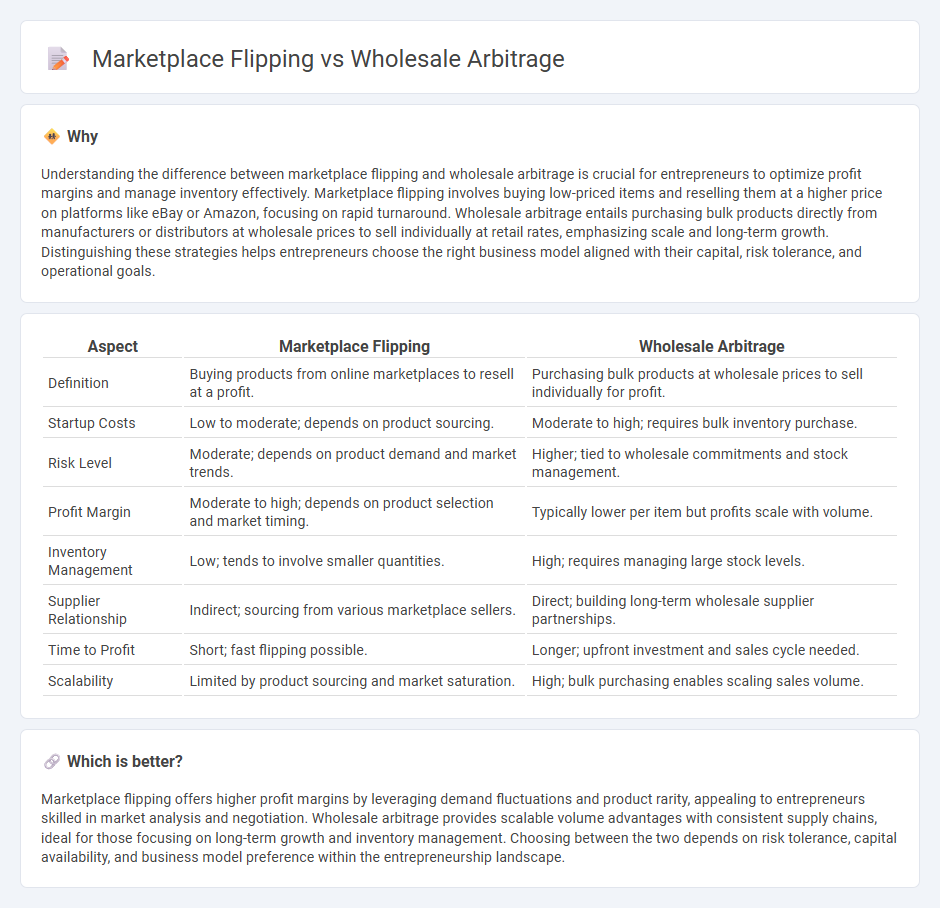
Understanding the difference between marketplace flipping and wholesale arbitrage is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize profit margins and manage inventory effectively. Marketplace flipping involves buying low-priced items and reselling them at a higher price on platforms like eBay or Amazon, focusing on rapid turnaround. Wholesale arbitrage entails purchasing bulk products directly from manufacturers or distributors at wholesale prices to sell individually at retail rates, emphasizing scale and long-term growth. Distinguishing these strategies helps entrepreneurs choose the right business model aligned with their capital, risk tolerance, and operational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Marketplace Flipping | Wholesale Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying products from online marketplaces to resell at a profit. | Purchasing bulk products at wholesale prices to sell individually for profit. |
| Startup Costs | Low to moderate; depends on product sourcing. | Moderate to high; requires bulk inventory purchase. |
| Risk Level | Moderate; depends on product demand and market trends. | Higher; tied to wholesale commitments and stock management. |
| Profit Margin | Moderate to high; depends on product selection and market timing. | Typically lower per item but profits scale with volume. |
| Inventory Management | Low; tends to involve smaller quantities. | High; requires managing large stock levels. |
| Supplier Relationship | Indirect; sourcing from various marketplace sellers. | Direct; building long-term wholesale supplier partnerships. |
| Time to Profit | Short; fast flipping possible. | Longer; upfront investment and sales cycle needed. |
| Scalability | Limited by product sourcing and market saturation. | High; bulk purchasing enables scaling sales volume. |
Which is better?
Marketplace flipping offers higher profit margins by leveraging demand fluctuations and product rarity, appealing to entrepreneurs skilled in market analysis and negotiation. Wholesale arbitrage provides scalable volume advantages with consistent supply chains, ideal for those focusing on long-term growth and inventory management. Choosing between the two depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and business model preference within the entrepreneurship landscape.
Connection
Marketplace flipping and wholesale arbitrage both involve capitalizing on price differences across platforms or markets to generate profit. Entrepreneurs purchase products at lower wholesale prices or discounted rates, then resell them on marketplaces like Amazon or eBay at higher retail values. This connection highlights strategic sourcing and market knowledge as key skills for maximizing returns in e-commerce ventures.
Key Terms
Bulk Purchasing
Wholesale arbitrage leverages bulk purchasing by acquiring large quantities of products at discounted rates directly from manufacturers or distributors, maximizing profit margins through volume sales. Marketplace flipping involves sourcing items from various sellers at lower prices, then reselling them individually on platforms like Amazon or eBay for a markup. Explore detailed strategies and benefits to optimize bulk purchasing for your business success.
Resale Platforms
Wholesale arbitrage involves purchasing bulk products at discounted rates from suppliers to resell at a profit on resale platforms like Amazon or eBay. Marketplace flipping focuses on finding undervalued or clearance items within online marketplaces and relisting them at higher prices to capitalize on demand. Explore effective strategies for maximizing profits on popular resale platforms and scaling your ecommerce business.
Price Discrepancy
Wholesale arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between bulk wholesale purchases and retail marketplaces, allowing sellers to acquire goods at significantly lower costs and resell them at a higher retail price. Marketplace flipping capitalizes on temporal or listing-based price variations within online platforms, where sellers buy underpriced items and quickly resell them for profit. Explore these strategies further to maximize your ecommerce profitability through price discrepancy optimization.
Source and External Links
Amazon Stores: Retail Arbitrage vs. Wholesale - Payability - Wholesale arbitrage involves buying products in bulk directly from suppliers, manufacturers, or distributors at lower per-unit costs, allowing sellers to maximize profit margins, in contrast to retail or online arbitrage where individual discounted products are bought from retailers to resell.
Online arbitrage vs. wholesale on Amazon - 8fig - Wholesale sellers purchase large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors, often requiring high upfront capital to meet minimum order quantities, while online arbitrage sellers source low-priced items from anywhere online without necessarily dealing directly with manufacturers.
Online Arbitrage vs Wholesale on Amazon. What is the difference? - Wholesale offers higher profit margins, more stable inventory, and easier scaling by buying bulk quantities directly from brands, but requires significant upfront investment and supplier approval, whereas online arbitrage involves buying smaller quantities at retail prices with lower startup costs and risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com