Entrepreneurship in the alternative protein sector is revolutionizing food innovation by developing plant-based products and lab-grown meat that address sustainability and ethical concerns. Companies like Beyond Meat and Memphis Meats are leading market growth with scalable, eco-friendly protein solutions that reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional livestock farming. Explore deeper insights into how these startups are shaping the future of food technology.
Why it is important
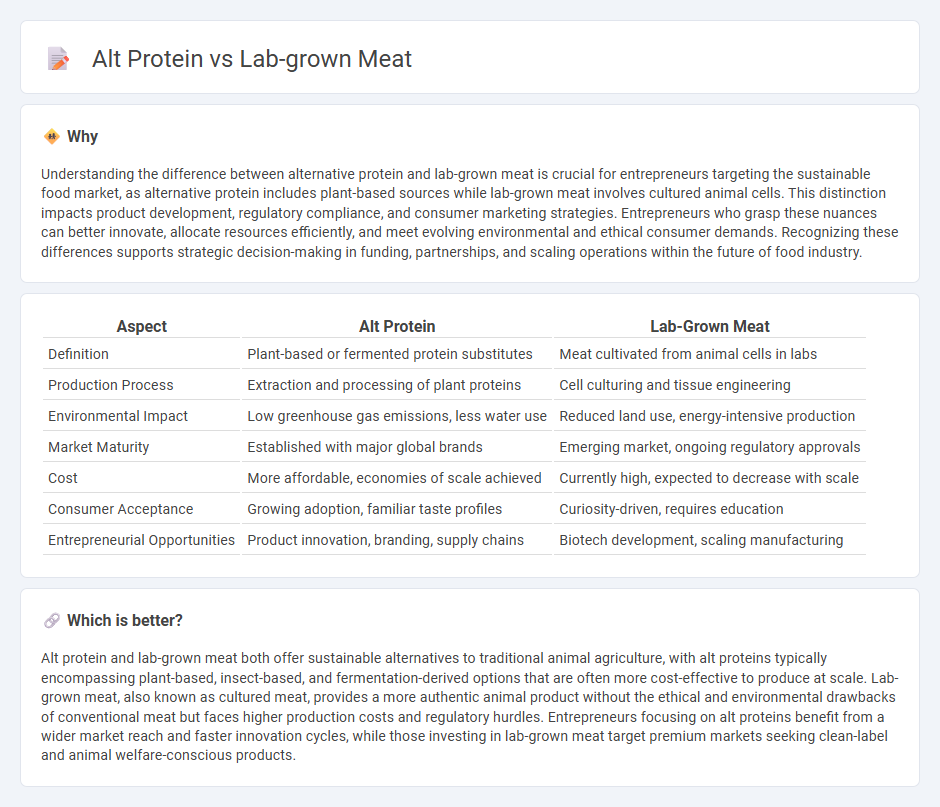
Understanding the difference between alternative protein and lab-grown meat is crucial for entrepreneurs targeting the sustainable food market, as alternative protein includes plant-based sources while lab-grown meat involves cultured animal cells. This distinction impacts product development, regulatory compliance, and consumer marketing strategies. Entrepreneurs who grasp these nuances can better innovate, allocate resources efficiently, and meet evolving environmental and ethical consumer demands. Recognizing these differences supports strategic decision-making in funding, partnerships, and scaling operations within the future of food industry.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Lab-Grown Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plant-based or fermented protein substitutes | Meat cultivated from animal cells in labs |
| Production Process | Extraction and processing of plant proteins | Cell culturing and tissue engineering |
| Environmental Impact | Low greenhouse gas emissions, less water use | Reduced land use, energy-intensive production |
| Market Maturity | Established with major global brands | Emerging market, ongoing regulatory approvals |
| Cost | More affordable, economies of scale achieved | Currently high, expected to decrease with scale |
| Consumer Acceptance | Growing adoption, familiar taste profiles | Curiosity-driven, requires education |
| Entrepreneurial Opportunities | Product innovation, branding, supply chains | Biotech development, scaling manufacturing |
Which is better?
Alt protein and lab-grown meat both offer sustainable alternatives to traditional animal agriculture, with alt proteins typically encompassing plant-based, insect-based, and fermentation-derived options that are often more cost-effective to produce at scale. Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat, provides a more authentic animal product without the ethical and environmental drawbacks of conventional meat but faces higher production costs and regulatory hurdles. Entrepreneurs focusing on alt proteins benefit from a wider market reach and faster innovation cycles, while those investing in lab-grown meat target premium markets seeking clean-label and animal welfare-conscious products.
Connection
Alt protein and lab-grown meat represent innovative solutions in entrepreneurship focused on sustainable food production, leveraging biotechnology to create meat alternatives without traditional animal farming. Startups and investors are driving growth in these sectors by developing scalable, cost-effective production methods that reduce environmental impact and address ethical concerns. Market trends indicate a rising consumer demand for plant-based and cellular agriculture products, positioning alt protein and lab-grown meat as key components in the future of food entrepreneurship.
Key Terms
Cellular Agriculture
Cellular agriculture, a key branch of lab-grown meat production, cultivates animal cells directly to create meat without raising animals, offering a scalable solution to traditional livestock farming's environmental impacts. Alternative proteins, including plant-based and fermentation-derived options, provide diverse nutritional profiles and lower carbon footprints but differ fundamentally in production methods and sensory attributes. Explore the advancements in cellular agriculture to understand how it revolutionizes sustainable protein sources.
Plant-Based Protein
Plant-based protein offers a sustainable alternative to traditional animal meat by utilizing ingredients like peas, soy, and lentils, providing high-quality nutrition with lower environmental impact. Unlike lab-grown meat, which involves cellular agriculture, plant-based options are available at scale and favored for their cost-effectiveness and versatility in food products. Explore more about the benefits and innovations in plant-based protein sources to understand their growing role in the alternative protein landscape.
Cultivation Bioreactor
Cultivation bioreactors are essential for scaling lab-grown meat production by providing controlled environments for muscle cell growth, optimizing parameters like temperature, oxygen, and nutrient supply. This technology contrasts with alternative protein production, which often relies on fermentation or plant-based processing methods that do not require cellular cultivation. Explore how advancements in bioreactor design are transforming the future of sustainable meat alternatives.
Source and External Links
The Myth of Cultured Meat: A Review - PMC - Lab-grown meat is produced by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment but faces challenges such as replacing costly fetal bovine serum and ensuring safe, large-scale production without animal-derived inputs.
How lab-grown meat is revolutionizing what we eat - ThinkLandscape - Lab-grown meat comes from stem cells fed a nutrient-rich media, creating meat identical at the molecular level to conventional meat, with potential benefits like lower emissions and the ability to customize nutritional content.
The science of cultivated meat | GFI - The Good Food Institute - Cultivated meat is real animal meat grown from stem cells in bioreactors, aiming to offer a more sustainable and humane alternative to conventional meat with growing global industry investment and research efforts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com