Solopreneurship involves individuals launching and managing businesses single-handedly, focusing on personal expertise and flexible operations, whereas startup entrepreneurship emphasizes building scalable companies with growth potential and external investment. Solopreneurs prioritize self-sufficiency and direct control, while startups seek innovation, market disruption, and often rapid expansion. Explore the distinctions and strategic approaches to decide which entrepreneurial path best suits your goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between solopreneurship and startup entrepreneurship is crucial because solopreneurs typically operate independently with limited scalability, while startups focus on rapid growth and attracting investment. Solopreneurs prioritize personal control and steady income, whereas startups aim to disrupt markets and build scalable business models. Knowing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs align their strategies, goals, and resource allocation effectively. This clarity improves decision-making, funding opportunities, and long-term business success.
Comparison Table
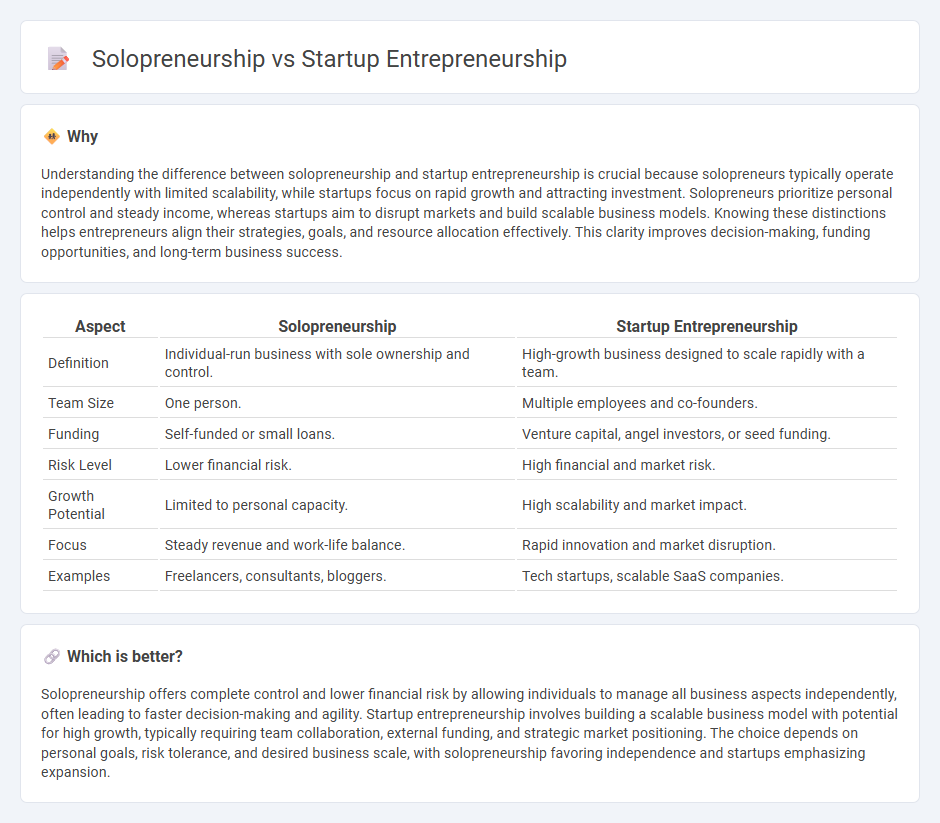
| Aspect | Solopreneurship | Startup Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual-run business with sole ownership and control. | High-growth business designed to scale rapidly with a team. |
| Team Size | One person. | Multiple employees and co-founders. |
| Funding | Self-funded or small loans. | Venture capital, angel investors, or seed funding. |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk. | High financial and market risk. |
| Growth Potential | Limited to personal capacity. | High scalability and market impact. |
| Focus | Steady revenue and work-life balance. | Rapid innovation and market disruption. |
| Examples | Freelancers, consultants, bloggers. | Tech startups, scalable SaaS companies. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers complete control and lower financial risk by allowing individuals to manage all business aspects independently, often leading to faster decision-making and agility. Startup entrepreneurship involves building a scalable business model with potential for high growth, typically requiring team collaboration, external funding, and strategic market positioning. The choice depends on personal goals, risk tolerance, and desired business scale, with solopreneurship favoring independence and startups emphasizing expansion.
Connection
Solopreneurship and startup entrepreneurship are interconnected through their focus on innovation and business creation, where solopreneurs often serve as the initial driving force behind startup ventures. Both emphasize agility, risk-taking, and independent decision-making, fostering environments conducive to rapid growth and market disruption. The transition from solopreneurship to startup entrepreneurship frequently involves scaling operations, securing funding, and expanding teams to transform individual ideas into scalable enterprises.
Key Terms
Team Building
Startup entrepreneurship emphasizes assembling a diverse team with complementary skills to drive innovation, scalability, and competitive advantage in dynamic markets. Solopreneurship prioritizes individual expertise and autonomy, often leveraging outsourcing or freelance partnerships instead of permanent team structures. Explore further to understand strategic approaches in team building across both models.
Scalability
Startup entrepreneurship emphasizes rapid growth and scalability by leveraging external funding, team expansion, and market disruption, aiming to capture significant market share quickly. Solopreneurship prioritizes personal control and sustainable income, often relying on niche markets and low overhead without the intent for massive scaling. Explore detailed strategies to understand which path best aligns with your business goals and growth expectations.
Autonomy
Startup entrepreneurship involves building a scalable business with teams, aiming for rapid growth and external funding, while solopreneurship emphasizes complete autonomy and direct control over all business aspects, often operating solo without outside investors. Autonomy in solopreneurship allows for flexible decision-making and personalized work structures, contrasting with startup entrepreneurs who must align with stakeholder expectations and investor pressures. Explore the nuances between these paths to determine which autonomy level suits your entrepreneurial goals best.
Source and External Links
What is a startup company? Here's what startup means - Stripe - A startup is a business in its early stages aimed at bringing new products or services to market, progressing through ideation, launch, and growth phases with sources of funding evolving from personal savings to venture capital as the company scales.
What Is A Startup: Types, Operations And Career Benefits - Indeed - A startup is an entrepreneurial venture in its early operations designed to solve real-life problems, focusing on rapid market growth and typically seeking funding from venture capitalists and angel investors to develop and scale innovative products or services.
Startup company - Wikipedia - A startup is a new company founded by entrepreneurs to develop and validate scalable business models, often funded through multiple stages including angel investment, seed funding, and venture capital rounds, with high uncertainty and high potential for growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com