Bootstrapped SaaS businesses rely on self-funding and organic growth, offering proprietary software solutions with controlled quality and consistent revenue streams. Open Source Software enables community-driven development, fostering innovation and flexibility through freely accessible code, but often faces challenges in monetization and support. Explore the advantages and trade-offs between these models to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial venture.
Why it is important
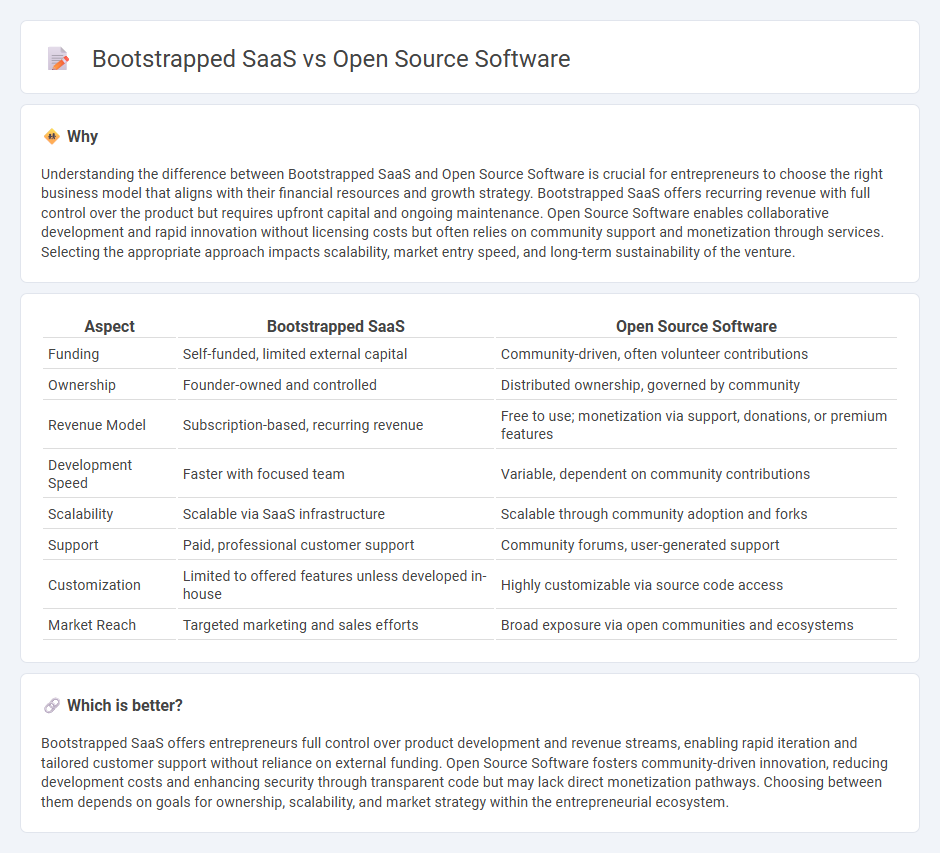
Understanding the difference between Bootstrapped SaaS and Open Source Software is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their financial resources and growth strategy. Bootstrapped SaaS offers recurring revenue with full control over the product but requires upfront capital and ongoing maintenance. Open Source Software enables collaborative development and rapid innovation without licensing costs but often relies on community support and monetization through services. Selecting the appropriate approach impacts scalability, market entry speed, and long-term sustainability of the venture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bootstrapped SaaS | Open Source Software |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Self-funded, limited external capital | Community-driven, often volunteer contributions |
| Ownership | Founder-owned and controlled | Distributed ownership, governed by community |
| Revenue Model | Subscription-based, recurring revenue | Free to use; monetization via support, donations, or premium features |
| Development Speed | Faster with focused team | Variable, dependent on community contributions |
| Scalability | Scalable via SaaS infrastructure | Scalable through community adoption and forks |
| Support | Paid, professional customer support | Community forums, user-generated support |
| Customization | Limited to offered features unless developed in-house | Highly customizable via source code access |
| Market Reach | Targeted marketing and sales efforts | Broad exposure via open communities and ecosystems |
Which is better?
Bootstrapped SaaS offers entrepreneurs full control over product development and revenue streams, enabling rapid iteration and tailored customer support without reliance on external funding. Open Source Software fosters community-driven innovation, reducing development costs and enhancing security through transparent code but may lack direct monetization pathways. Choosing between them depends on goals for ownership, scalability, and market strategy within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Connection
Bootstrapped SaaS companies often leverage open source software to reduce initial development costs and accelerate product deployment, fostering innovation without external funding. This synergy allows entrepreneurs to maintain full control while benefiting from community-driven improvements and scalability inherent in open source projects. Leveraging open source tools enhances bootstrapped SaaS viability by providing robust, customizable solutions that align with limited budgets and agile growth strategies.
Key Terms
Licensing Models
Open source software offers users the freedom to inspect, modify, and distribute code under licenses such as GPL, MIT, or Apache, fostering collaboration and transparency. Bootstrapped SaaS typically operates under proprietary licenses that restrict code access but provide ongoing updates, customer support, and hosted solutions without upfront infrastructure costs. Explore detailed comparisons of licensing models to determine the ideal approach for your software deployment strategy.
Funding Strategies
Open Source Software relies on community contributions and transparency to drive innovation, often minimizing upfront costs and attracting organic growth without heavy external funding. Bootstrapped SaaS companies prioritize self-funding and reinvestment of early revenues to maintain full control and sustainable growth, avoiding dilution from venture capital. Explore detailed insights on funding strategies to determine the best approach for your software venture.
Revenue Streams
Open source software generates revenue primarily through support services, custom development, and donations, leveraging community contributions to enhance product innovation without huge upfront costs. Bootstrapped SaaS companies focus on recurring subscription fees, upselling premium features, and customer retention to build sustainable cash flow without external funding. Explore how these distinct revenue streams impact business growth and long-term profitability.
Source and External Links
What Is Open Source Software and How Does It Work? | Black Duck - Open source software (OSS) is software distributed with its source code that anyone can use, modify, and redistribute, originally promoted by Richard Stallman and formalized by the Open Source Initiative in 1998.
What Is Open Source Software? - IBM - Open source software is developed via open collaboration with publicly available source code, allowing anyone to examine, alter, redistribute it, and is widely used within modern software development practices like DevOps.
What Is Open-Source Software? (With Examples) | Indeed.com - Open-source software allows anyone to use, study, modify, and distribute it freely, with popular examples including Linux, Apache, Firefox, WordPress, and Android.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com