Side Hustle Stack offers entrepreneurs a flexible platform to launch multiple income streams with minimal upfront investment, contrasting with traditional small business ownership that demands significant capital and long-term commitment. Small business ownership involves managing extensive operations, regulatory compliance, and employee oversight, whereas Side Hustle Stack emphasizes agility and scalability through digital opportunities. Explore more about how each approach can align with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
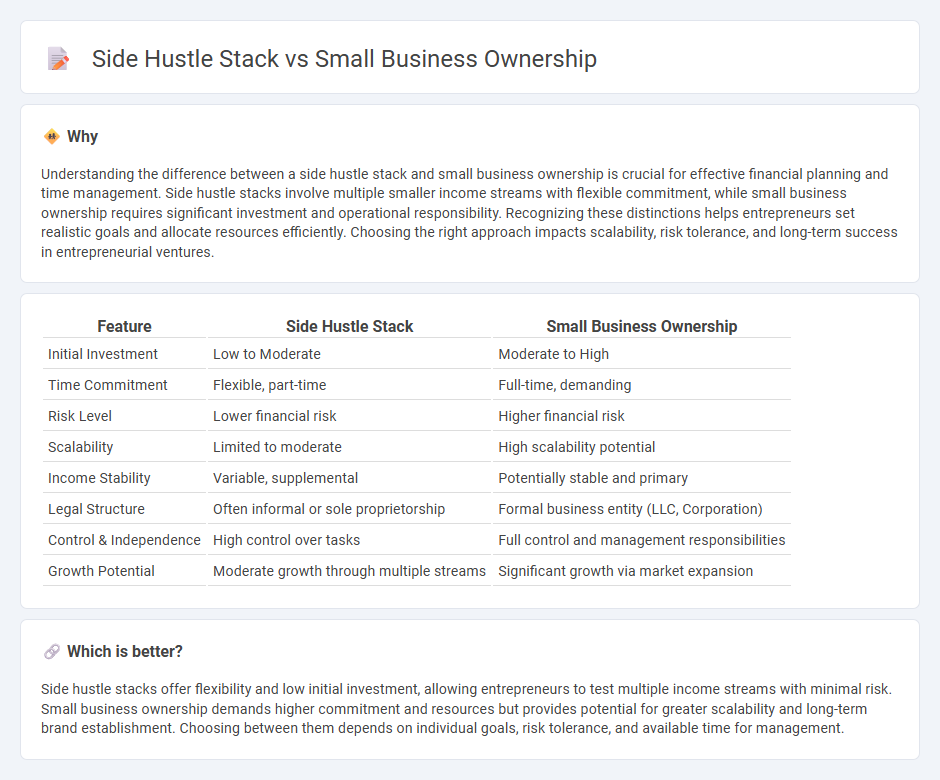
Understanding the difference between a side hustle stack and small business ownership is crucial for effective financial planning and time management. Side hustle stacks involve multiple smaller income streams with flexible commitment, while small business ownership requires significant investment and operational responsibility. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs set realistic goals and allocate resources efficiently. Choosing the right approach impacts scalability, risk tolerance, and long-term success in entrepreneurial ventures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Side Hustle Stack | Small Business Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Time Commitment | Flexible, part-time | Full-time, demanding |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk | Higher financial risk |
| Scalability | Limited to moderate | High scalability potential |
| Income Stability | Variable, supplemental | Potentially stable and primary |
| Legal Structure | Often informal or sole proprietorship | Formal business entity (LLC, Corporation) |
| Control & Independence | High control over tasks | Full control and management responsibilities |
| Growth Potential | Moderate growth through multiple streams | Significant growth via market expansion |
Which is better?
Side hustle stacks offer flexibility and low initial investment, allowing entrepreneurs to test multiple income streams with minimal risk. Small business ownership demands higher commitment and resources but provides potential for greater scalability and long-term brand establishment. Choosing between them depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and available time for management.
Connection
Side hustles often serve as practical learning platforms for entrepreneurship, allowing individuals to test business ideas and develop essential skills with low risk. These experiences create a foundation for transitioning into small business ownership by building customer relationships, managing finances, and understanding market demands. The progression from side hustle to small business ownership exemplifies a scalable growth model within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Business Structure
Small business ownership typically involves formal business structures such as LLCs, S-corporations, or sole proprietorships that provide legal protection and tax benefits, whereas side hustles often start with minimal legal setup and rely on informal arrangements or sole proprietorship status. The choice of business structure impacts liability, taxation, and operational complexity, making it crucial for entrepreneurs to evaluate their growth goals and risk tolerance. Explore detailed comparisons of business structures to determine the best fit for your venture.
Time Commitment
Small business ownership demands a significant time commitment, often requiring owners to manage operations, marketing, and finances full-time. Side hustles typically involve fewer hours, allowing for flexible scheduling around a primary job or personal commitments. Explore detailed time management strategies and comparisons to determine the best fit for your lifestyle.
Revenue Model
Small business ownership offers scalable revenue models that often rely on diversified income streams such as recurring sales, subscriptions, and wholesale partnerships, providing long-term financial stability. Side hustles typically generate supplemental income through flexible, task-based gigs or freelance projects, limiting their revenue potential but allowing quick monetization with minimal upfront investment. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize your revenue model and maximize profit in both small business and side hustle ventures.
Source and External Links
The 8 Small Business Owner Structures - PeopleKeep - Small business ownership can take eight forms including sole proprietorship, partnership, C corporation, S corporation, B corporation, close corporation, LLC, and nonprofit corporation; sole proprietorship is the simplest type where the owner has full control but also unlimited personal liability.
10 steps to start your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Key steps to start small business ownership include choosing and registering a business name, getting federal and state tax IDs, applying for necessary licenses and permits, and opening a business bank account.
Small business - Wikipedia - Small businesses are typically defined by having fewer employees and lower revenues than larger corporations, and can be structured as corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships, varying by country and industry.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com