Productized services offer entrepreneurs a fixed-scope, scalable solution by standardizing expert services into repeatable packages, reducing customization and client onboarding time. In contrast, SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers cloud-based software applications on a subscription model, enabling continuous updates and broad user access without traditional software installation. Explore how choosing between productized services and SaaS can impact your business growth strategy.
Why it is important
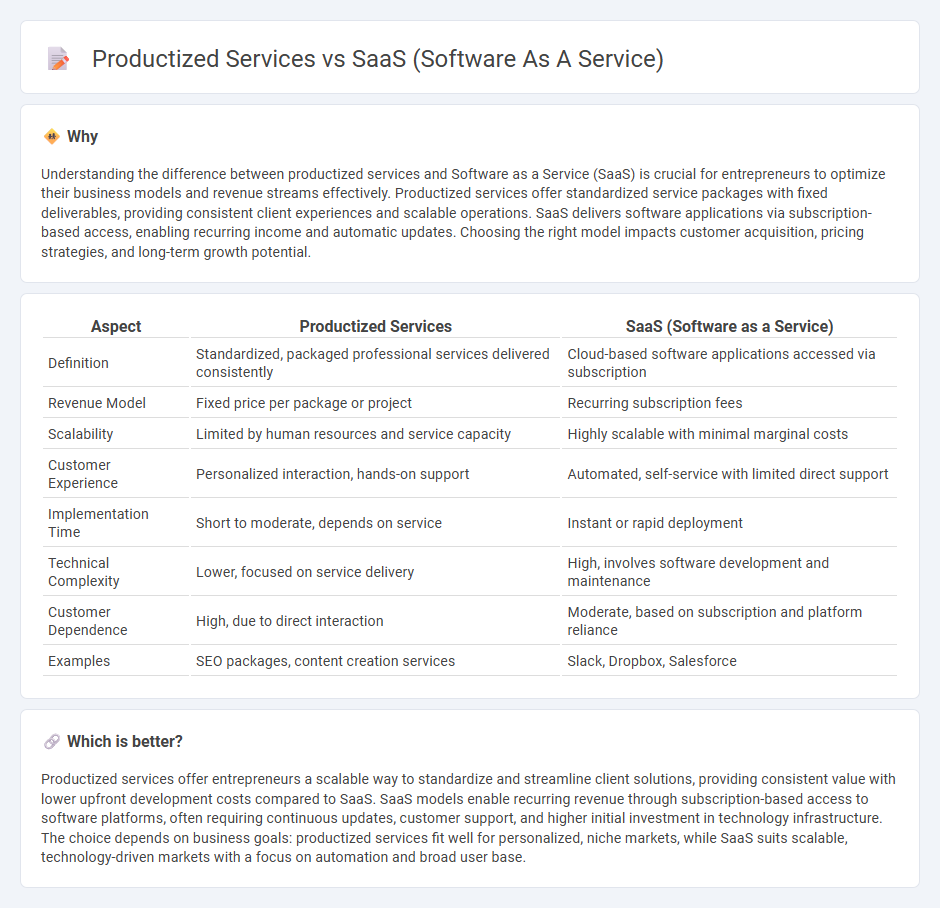
Understanding the difference between productized services and Software as a Service (SaaS) is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize their business models and revenue streams effectively. Productized services offer standardized service packages with fixed deliverables, providing consistent client experiences and scalable operations. SaaS delivers software applications via subscription-based access, enabling recurring income and automatic updates. Choosing the right model impacts customer acquisition, pricing strategies, and long-term growth potential.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Productized Services | SaaS (Software as a Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardized, packaged professional services delivered consistently | Cloud-based software applications accessed via subscription |
| Revenue Model | Fixed price per package or project | Recurring subscription fees |
| Scalability | Limited by human resources and service capacity | Highly scalable with minimal marginal costs |
| Customer Experience | Personalized interaction, hands-on support | Automated, self-service with limited direct support |
| Implementation Time | Short to moderate, depends on service | Instant or rapid deployment |
| Technical Complexity | Lower, focused on service delivery | High, involves software development and maintenance |
| Customer Dependence | High, due to direct interaction | Moderate, based on subscription and platform reliance |
| Examples | SEO packages, content creation services | Slack, Dropbox, Salesforce |
Which is better?
Productized services offer entrepreneurs a scalable way to standardize and streamline client solutions, providing consistent value with lower upfront development costs compared to SaaS. SaaS models enable recurring revenue through subscription-based access to software platforms, often requiring continuous updates, customer support, and higher initial investment in technology infrastructure. The choice depends on business goals: productized services fit well for personalized, niche markets, while SaaS suits scalable, technology-driven markets with a focus on automation and broad user base.
Connection
Productized services and SaaS are connected through their scalable, subscription-based business models that streamline service delivery and software access. Entrepreneurs leverage productized services to package expertise into repeatable offerings, while SaaS platforms provide cloud-based software solutions that automate and enhance business processes. This synergy allows startups to reduce operational costs, increase recurring revenue, and accelerate market entry.
Key Terms
Scalability
SaaS platforms offer unparalleled scalability by enabling automated, cloud-based software delivery that supports rapid user growth without significant infrastructure investment. Productized services scale through standardized workflows and repeatable processes but often require additional human resources as demand increases, limiting rapid expansion. Explore further to understand which model best suits your business scalability goals.
Revenue Model
SaaS revenue models rely on subscription fees, often tiered by usage, features, or number of users, ensuring predictable recurring income and scalability. Productized services generate revenue through fixed-price packages for clearly defined deliverables, offering simpler billing but potentially limited scalability. Explore detailed comparisons and growth strategies to optimize your business revenue model.
Customization
SaaS platforms often provide scalable software solutions with limited customization options tailored to broad user needs, while productized services emphasize predefined, standardized offerings with minimal flexibility to maintain efficiency. Businesses seeking highly personalized workflows typically find productized services less adaptable compared to SaaS's configurable interfaces and integration capabilities. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which model aligns best with your customization requirements.
Source and External Links
Software as a service - Wikipedia - SaaS is a cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet, centrally managed by the provider, and accessed via web applications, typically on a subscription basis without local installation or ownership of the software.
What is SaaS (Software as a Service)? | Salesforce US - SaaS delivers applications remotely via the internet, freeing users from hardware, licensing, and maintenance concerns, enabling collaboration and on-demand software access through web browsers.
What is SaaS (Software as a Service) - Oracle - SaaS is a cloud-based delivery model where the provider develops, maintains, and updates software accessible via the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis, offering scalability, lower costs, and integration across various business functions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com