Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies within the same industry to create a larger, more competitive entity, achieving rapid market expansion and operational synergies. Direct investment involves injecting capital directly into a single business, enabling focused growth and strategic control over operations and innovation. Explore deeper insights on how each approach can shape entrepreneurial success and investment strategy.
Why it is important
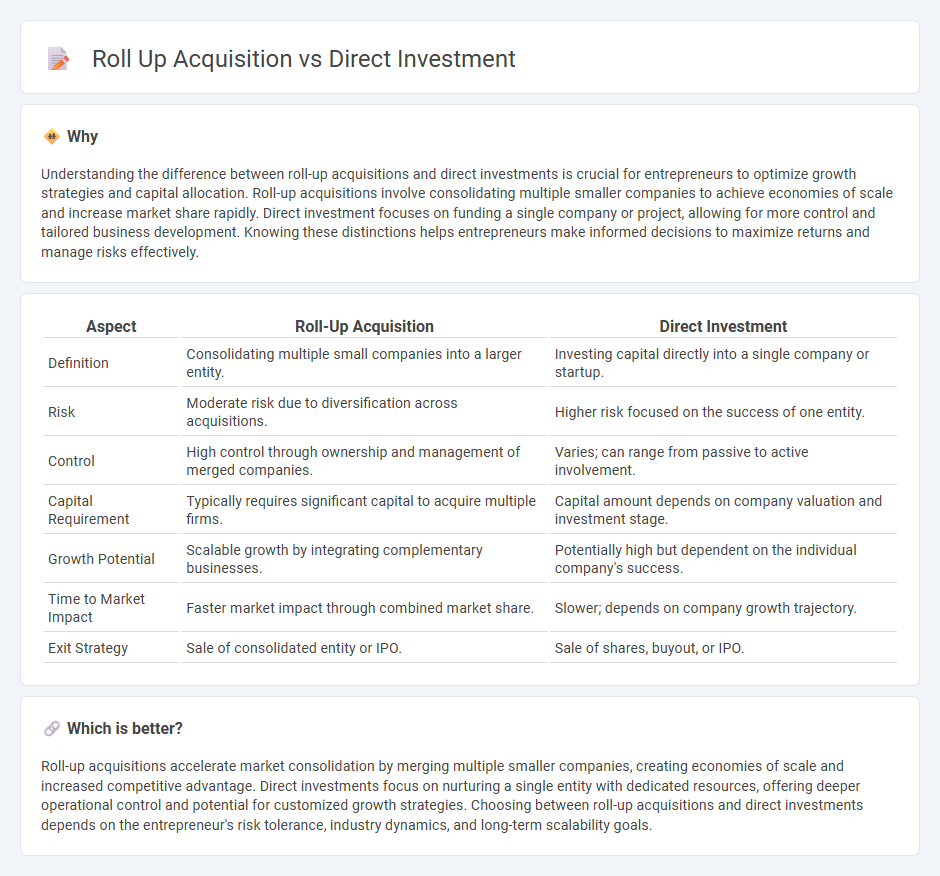
Understanding the difference between roll-up acquisitions and direct investments is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize growth strategies and capital allocation. Roll-up acquisitions involve consolidating multiple smaller companies to achieve economies of scale and increase market share rapidly. Direct investment focuses on funding a single company or project, allowing for more control and tailored business development. Knowing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Roll-Up Acquisition | Direct Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidating multiple small companies into a larger entity. | Investing capital directly into a single company or startup. |
| Risk | Moderate risk due to diversification across acquisitions. | Higher risk focused on the success of one entity. |
| Control | High control through ownership and management of merged companies. | Varies; can range from passive to active involvement. |
| Capital Requirement | Typically requires significant capital to acquire multiple firms. | Capital amount depends on company valuation and investment stage. |
| Growth Potential | Scalable growth by integrating complementary businesses. | Potentially high but dependent on the individual company's success. |
| Time to Market Impact | Faster market impact through combined market share. | Slower; depends on company growth trajectory. |
| Exit Strategy | Sale of consolidated entity or IPO. | Sale of shares, buyout, or IPO. |
Which is better?
Roll-up acquisitions accelerate market consolidation by merging multiple smaller companies, creating economies of scale and increased competitive advantage. Direct investments focus on nurturing a single entity with dedicated resources, offering deeper operational control and potential for customized growth strategies. Choosing between roll-up acquisitions and direct investments depends on the entrepreneur's risk tolerance, industry dynamics, and long-term scalability goals.
Connection
Roll-up acquisitions and direct investments are connected through their strategic approach to scaling businesses by consolidating multiple smaller companies into a larger entity. Direct investment provides the necessary capital for roll-up acquisitions, enabling entrepreneurs to expand market share and achieve economies of scale. This synergy accelerates growth, enhances operational efficiency, and increases competitive advantage in the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Capital Allocation
Capital allocation in direct investment involves deploying funds directly into new or existing ventures, emphasizing control and long-term growth potential. Roll-up acquisitions allocate capital to strategically consolidate smaller companies within an industry, achieving economies of scale and increased market share efficiently. Explore detailed strategies and metrics to optimize your capital allocation decisions in both investment approaches.
Consolidation Strategy
Direct investment enables companies to acquire stakes in target firms, fostering control and long-term growth, while roll-up acquisitions focus on consolidating fragmented markets by merging multiple smaller companies to achieve economies of scale and increased market share. Consolidation strategies using roll-ups streamline operations, reduce competition, and enhance valuation through synergies and cost efficiencies. Explore how these approaches impact market dominance and financial performance in detail.
Ownership Structure
Direct investment involves acquiring a controlling interest directly in a target company, leading to full ownership and decision-making authority, which allows for strategic control and integration aligned with the investor's goals. Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies into a larger entity under a unified ownership structure, aiming to achieve economies of scale and market dominance while maintaining a streamlined management hierarchy. Explore further to understand how these ownership structures impact growth strategies and operational efficiencies.
Source and External Links
Direct Investments - CAIA - Direct investment refers to a standalone investment or co-investment in a company or asset, favored by wealthy individuals and family offices as it avoids intermediary fees and aligns with investor values, with increasing allocation trends compared to private equity funds managed by third parties.
Direct Investment in: Balance of Payments Textbook - Direct investment capital encompasses equity capital, reinvested earnings, and intercompany debt transactions where a direct investor gains lasting interest in a foreign or domestic enterprise, reflected in ownership and financial flows between related entities.
Direct Investing - U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission - Direct investing involves buying stock directly from a company through direct stock plans or dividend reinvestment plans, allowing investors to bypass brokers, potentially saving commissions and automating stock purchases and dividend reinvestments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com