Roll-up acquisitions streamline growth by consolidating multiple smaller companies into a single, larger entity, boosting market share and operational efficiency. Crowdsourcing leverages the collective intelligence and resources of diverse participants to solve problems, generate ideas, or fund projects, fostering innovation and community engagement. Explore how these strategic approaches can transform your entrepreneurial ventures and drive scalable success.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between roll-up acquisition, which consolidates multiple smaller companies into a larger entity, and crowdsourcing, which gathers ideas or services from a large group of people, is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right growth or innovation strategy. Roll-up acquisitions enable rapid market expansion and operational efficiencies, while crowdsourcing fosters creativity and cost-effective problem-solving. Selecting the appropriate approach directly impacts resource allocation, business scalability, and competitive advantage. Entrepreneurs equipped with this knowledge can optimize funding strategies and stakeholder engagement to drive sustainable success.
Comparison Table
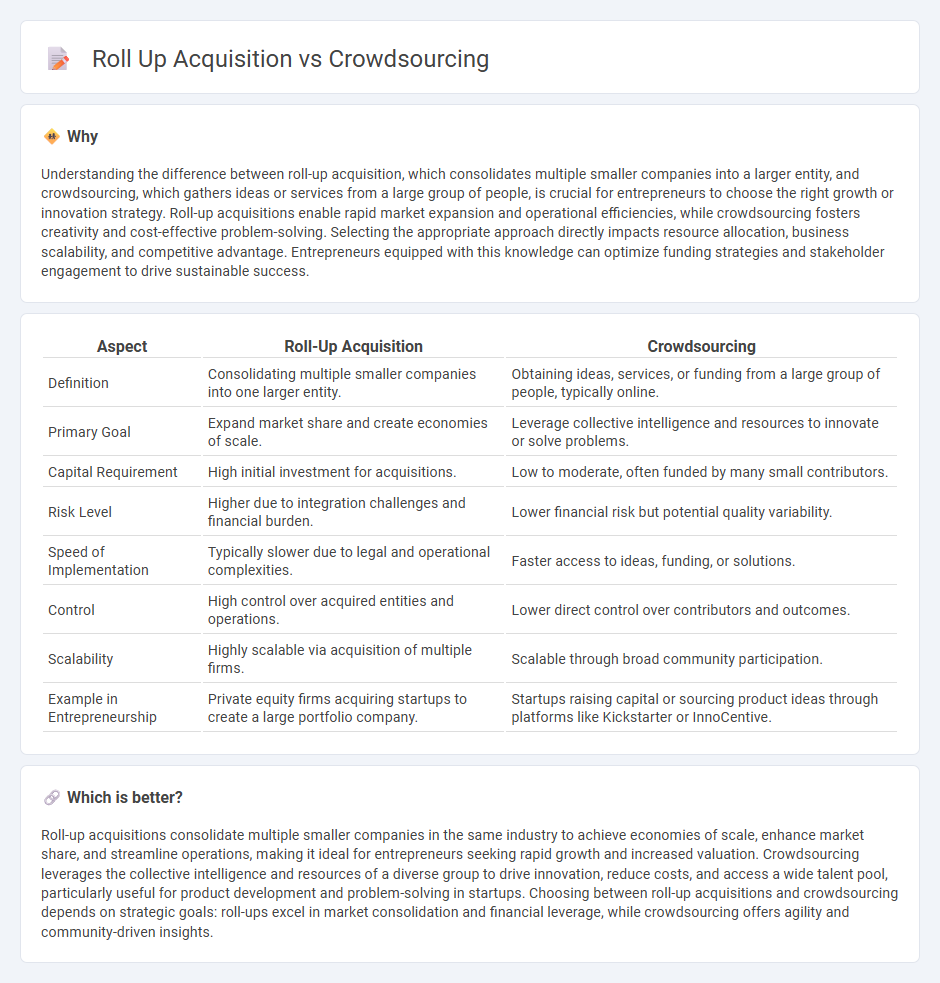
| Aspect | Roll-Up Acquisition | Crowdsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidating multiple smaller companies into one larger entity. | Obtaining ideas, services, or funding from a large group of people, typically online. |
| Primary Goal | Expand market share and create economies of scale. | Leverage collective intelligence and resources to innovate or solve problems. |
| Capital Requirement | High initial investment for acquisitions. | Low to moderate, often funded by many small contributors. |
| Risk Level | Higher due to integration challenges and financial burden. | Lower financial risk but potential quality variability. |
| Speed of Implementation | Typically slower due to legal and operational complexities. | Faster access to ideas, funding, or solutions. |
| Control | High control over acquired entities and operations. | Lower direct control over contributors and outcomes. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via acquisition of multiple firms. | Scalable through broad community participation. |
| Example in Entrepreneurship | Private equity firms acquiring startups to create a large portfolio company. | Startups raising capital or sourcing product ideas through platforms like Kickstarter or InnoCentive. |
Which is better?
Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies in the same industry to achieve economies of scale, enhance market share, and streamline operations, making it ideal for entrepreneurs seeking rapid growth and increased valuation. Crowdsourcing leverages the collective intelligence and resources of a diverse group to drive innovation, reduce costs, and access a wide talent pool, particularly useful for product development and problem-solving in startups. Choosing between roll-up acquisitions and crowdsourcing depends on strategic goals: roll-ups excel in market consolidation and financial leverage, while crowdsourcing offers agility and community-driven insights.
Connection
Roll-up acquisitions and crowdsourcing connect through the strategic aggregation of resources and expertise to accelerate business growth. Roll-up acquisitions consolidate smaller companies within the same industry to create operational efficiencies and market dominance, while crowdsourcing leverages a distributed network of individuals to generate innovative ideas, solutions, and funding. Together, they enhance scalability, minimize costs, and foster innovation, driving entrepreneurial ventures toward competitive advantage and sustainable expansion.
Key Terms
Collective Intelligence
Crowdsourcing leverages Collective Intelligence by tapping into a diverse, distributed group to solve problems, generate ideas, or complete tasks through platforms like Amazon Mechanical Turk or Wikipedia. Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple small companies in the same industry to achieve economies of scale and faster market penetration, relying more on traditional management integration than broad collective input. Explore how these strategies differ in harnessing Collective Intelligence and driving business growth.
Capital Consolidation
Crowdsourcing leverages a large pool of independent contributors to quickly gather capital, distributing ownership among many small investors, which can lead to diverse but fragmented equity stakes. Roll-up acquisitions involve acquiring multiple smaller companies to consolidate capital and operational control under a single entity, often resulting in more centralized financial management and increased market influence. Explore further to understand how each strategy impacts capital consolidation and investor returns.
Synergy
Crowdsourcing leverages diverse, decentralized contributions to innovate and solve problems, creating synergy through collective intelligence and varied expertise. Roll-up acquisition focuses on consolidating smaller companies to achieve operational efficiencies, scale economies, and market power, generating synergy via cost reduction and resource integration. Explore how each approach maximizes synergy for strategic growth and competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
What is Crowdsourcing? Definition - Examples - Applications - Crowdsourcing, coined by Jeff Howe in 2006, is the process where businesses outsource tasks or ideas to a large community (the crowd) rather than individual providers, leveraging the collective intelligence of the masses, with examples ranging from unpaid projects like Wikipedia to paid crowdsourcing work.
What is crowdsourcing? | Definition from TechTarget - Crowdsourcing is the practice of soliciting knowledge, goods, or services from a broad group of people via the internet or platforms, enabling entities to tap into a wider range of expertise faster and often at lower cost than traditional methods, although managing large volumes of responses can be complex.
Crowdsourcing - Wikipedia - Crowdsourcing involves large, dispersed groups contributing goods, services, ideas, or work (paid or volunteer) often via digital platforms, with advantages such as cost reduction, improved speed and quality, and it spans methods like competitions, virtual labor markets, and open collaboration for commercial or nonprofit goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com