Digital collectibles transform ownership through blockchain-verified scarcity and uniqueness, offering creators direct monetization opportunities without intermediaries. Intellectual property licensing enables rights holders to authorize usage of their creations in exchange for fees or royalties, maintaining controlled distribution across markets. Explore the benefits and challenges of both models in driving innovative revenue streams.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital collectibles and intellectual property licensing is crucial for entrepreneurs to navigate legal rights and monetize assets effectively. Digital collectibles, such as NFTs, represent unique, blockchain-verified items, while intellectual property licensing grants permission to use protected creations like trademarks or patents. Accurate knowledge prevents potential infringement disputes and maximizes revenue streams in the digital economy. Entrepreneurs leveraging these distinctions can strategically protect and exploit their innovations.
Comparison Table
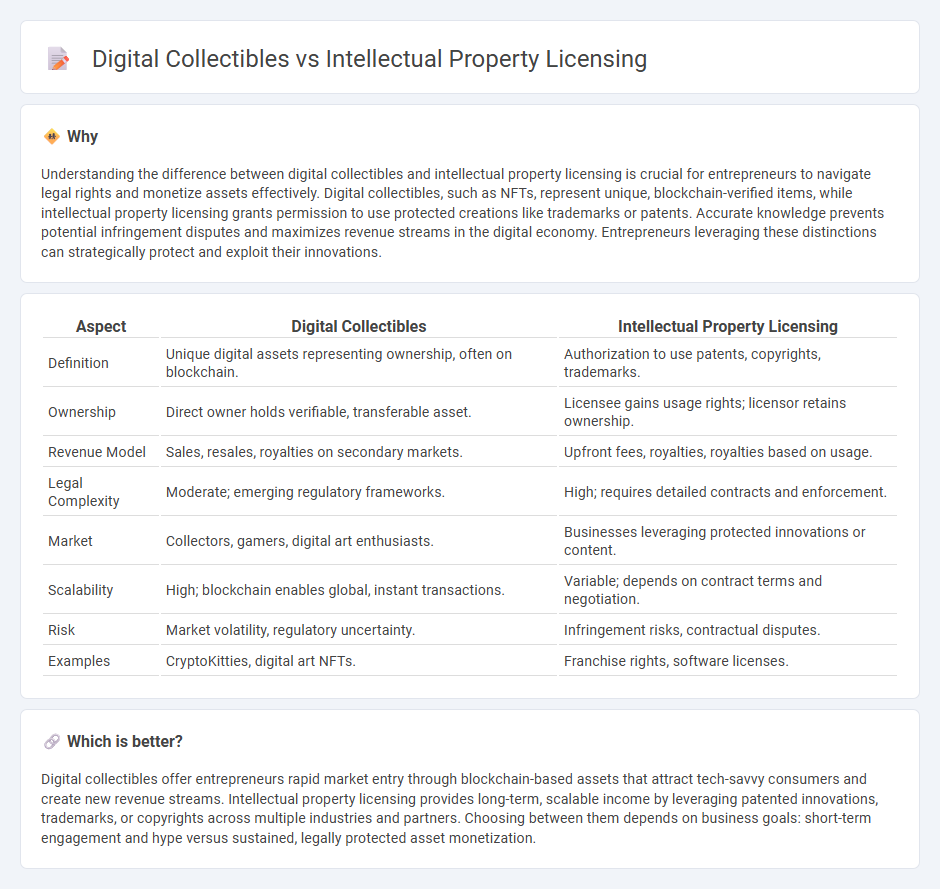
| Aspect | Digital Collectibles | Intellectual Property Licensing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unique digital assets representing ownership, often on blockchain. | Authorization to use patents, copyrights, trademarks. |
| Ownership | Direct owner holds verifiable, transferable asset. | Licensee gains usage rights; licensor retains ownership. |
| Revenue Model | Sales, resales, royalties on secondary markets. | Upfront fees, royalties, royalties based on usage. |
| Legal Complexity | Moderate; emerging regulatory frameworks. | High; requires detailed contracts and enforcement. |
| Market | Collectors, gamers, digital art enthusiasts. | Businesses leveraging protected innovations or content. |
| Scalability | High; blockchain enables global, instant transactions. | Variable; depends on contract terms and negotiation. |
| Risk | Market volatility, regulatory uncertainty. | Infringement risks, contractual disputes. |
| Examples | CryptoKitties, digital art NFTs. | Franchise rights, software licenses. |
Which is better?
Digital collectibles offer entrepreneurs rapid market entry through blockchain-based assets that attract tech-savvy consumers and create new revenue streams. Intellectual property licensing provides long-term, scalable income by leveraging patented innovations, trademarks, or copyrights across multiple industries and partners. Choosing between them depends on business goals: short-term engagement and hype versus sustained, legally protected asset monetization.
Connection
Digital collectibles, such as NFTs, represent unique digital assets whose ownership and authenticity are protected through blockchain technology, creating new opportunities for intellectual property licensing in entrepreneurship. Licensing digital collectibles allows creators to monetize their work by granting usage rights while retaining control over their intellectual property. This intersection empowers entrepreneurs to leverage digital scarcity and rights management for innovative business models and revenue streams.
Key Terms
Patent Licensing
Patent licensing involves granting permission to use patented inventions, providing legal protection and revenue streams for innovators. Digital collectibles, often based on blockchain technology, represent ownership of unique digital items without necessarily involving patent rights. Explore how patent licensing intersects with the growing market for digital collectibles to unlock new opportunities.
Smart Contracts
Intellectual property licensing leverages smart contracts to automate rights management, enabling precise royalty distribution and usage tracking. Digital collectibles utilize smart contracts to establish unique ownership, provenance, and transferability on blockchain platforms, ensuring authenticity and scarcity. Explore how integrating smart contracts transforms both intellectual property licensing and digital collectibles for enhanced security and efficiency.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Intellectual property licensing involves granting rights to use protected creations under specific terms, whereas digital collectibles like Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent unique blockchain-based assets linked to digital content, often embedding IP rights in a decentralized manner. NFTs leverage smart contracts to ensure provenance, authenticity, and ownership transparency, contrasting traditional licensing frameworks dependent on centralized enforcement. Explore the evolving intersection of IP law and digital assets to understand how NFTs redefine rights management and monetization strategies.
Source and External Links
How To License Your Intellectual Property - Intellectual property licensing is a legal agreement where the IP owner (licensor) authorizes another party (licensee) to use the IP rights for agreed purposes, typically in exchange for fees or royalties, and can involve patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets.
Licensing Intellectual Property 101: What Every Entrepreneur and ... - An IP license is a contract between licensor and licensee detailing rights and obligations for using intellectual property including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, designed to enable business growth and product expansion.
Intellectual Property Licensing Toolkit | Practical Law - Westlaw - Licensing allows IP owners to authorize others to use their patents, trademarks, copyrights, or trade secrets while retaining ownership, and license agreements vary depending on the type of IP and business context such as revenue generation or technology sharing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com