Subscription boxes deliver curated products on a recurring basis, building customer loyalty through convenience and surprise. The rental model offers temporary access to high-value or specialized items, reducing upfront costs and encouraging sustainable consumption. Explore the advantages and challenges of both business models to determine the best entrepreneurial approach.
Why it is important
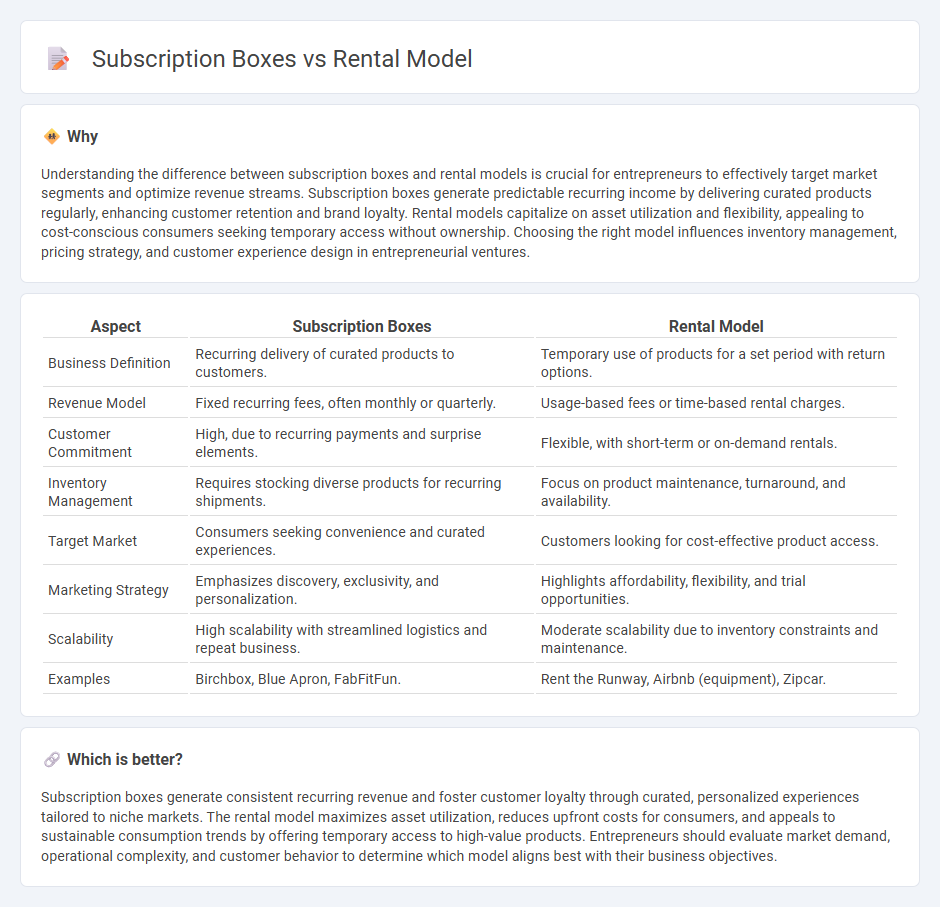
Understanding the difference between subscription boxes and rental models is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively target market segments and optimize revenue streams. Subscription boxes generate predictable recurring income by delivering curated products regularly, enhancing customer retention and brand loyalty. Rental models capitalize on asset utilization and flexibility, appealing to cost-conscious consumers seeking temporary access without ownership. Choosing the right model influences inventory management, pricing strategy, and customer experience design in entrepreneurial ventures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Subscription Boxes | Rental Model |
|---|---|---|
| Business Definition | Recurring delivery of curated products to customers. | Temporary use of products for a set period with return options. |
| Revenue Model | Fixed recurring fees, often monthly or quarterly. | Usage-based fees or time-based rental charges. |
| Customer Commitment | High, due to recurring payments and surprise elements. | Flexible, with short-term or on-demand rentals. |
| Inventory Management | Requires stocking diverse products for recurring shipments. | Focus on product maintenance, turnaround, and availability. |
| Target Market | Consumers seeking convenience and curated experiences. | Customers looking for cost-effective product access. |
| Marketing Strategy | Emphasizes discovery, exclusivity, and personalization. | Highlights affordability, flexibility, and trial opportunities. |
| Scalability | High scalability with streamlined logistics and repeat business. | Moderate scalability due to inventory constraints and maintenance. |
| Examples | Birchbox, Blue Apron, FabFitFun. | Rent the Runway, Airbnb (equipment), Zipcar. |
Which is better?
Subscription boxes generate consistent recurring revenue and foster customer loyalty through curated, personalized experiences tailored to niche markets. The rental model maximizes asset utilization, reduces upfront costs for consumers, and appeals to sustainable consumption trends by offering temporary access to high-value products. Entrepreneurs should evaluate market demand, operational complexity, and customer behavior to determine which model aligns best with their business objectives.
Connection
Subscription boxes and the rental model share a common business strategy focused on recurring revenue streams by offering curated product access through regular delivery or temporary usage. Both models leverage customer preferences for variety, convenience, and affordability, enabling businesses to capitalize on ongoing consumer engagement and reduce inventory risks. This connection enhances customer retention by providing continuous value without the commitment of ownership, fueling growth in lifestyle and niche markets.
Key Terms
Revenue Stream
Rental models generate revenue primarily through recurring fees for temporary product access, enabling higher customer retention and steady cash flow. Subscription boxes rely on periodic shipments and upfront payments, fostering customer loyalty through curated experiences and predictable income. Explore the nuances of each revenue stream to optimize your business strategy effectively.
Customer Retention
Rental models enhance customer retention by offering flexible, cost-effective access to products without long-term commitments, encouraging repeat usage and brand loyalty. Subscription boxes create consistent engagement through curated, personalized deliveries that build anticipation and foster ongoing relationships. Explore our insights to understand which model best boosts your customer retention strategy.
Inventory Management
Rental models require dynamic inventory management to track item availability, condition, and turnaround times for multiple users, ensuring efficient utilization and minimizing stockouts. Subscription boxes focus on forecasting demand and maintaining sufficient stock levels for curated products, prioritizing timely replenishment and diversification of inventory to meet subscriber preferences. Explore more about optimizing inventory strategies for rental and subscription businesses.
Source and External Links
Rent to Rent: A Guide to Increasing Rental Profitability - The Rent to Rent model is where a company leases a property long-term from the owner and sublets it to tenants, managing all aspects including maintenance, tenant sourcing, and payments, providing owners fixed monthly income without management hassle.
Rental Business Model: A Complete Guide - The rental business model is structured using a business model canvas consisting of desirability (customer demand), feasibility (resources and operations), and viability (financial revenue streams and costs) to build a successful rental marketplace.
Top 8 Rental Models and How to Implement Them - Common rental models include short-term rentals, subscription-based rentals, peer-to-peer rentals, long-term leasing, and on-demand rentals, each suited for different customer needs and operational strategies with specific pros and cons.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com