Ghost kitchens operate as professional, delivery-only food service facilities that eliminate the need for physical dining spaces, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing overhead costs compared to traditional restaurants. Home-based food businesses leverage personal kitchens to create artisanal or niche food products, benefiting from low startup costs and flexible work environments but facing regulatory and scalability challenges. Explore the advantages and limitations of each model to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial food venture.
Why it is important
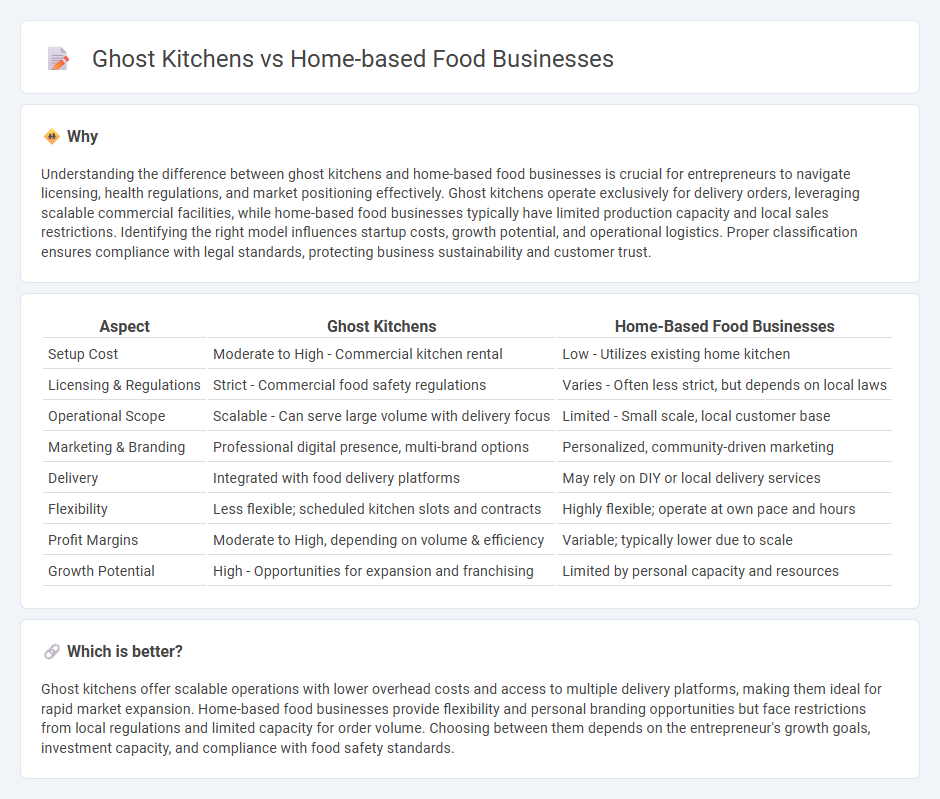
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchens and home-based food businesses is crucial for entrepreneurs to navigate licensing, health regulations, and market positioning effectively. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively for delivery orders, leveraging scalable commercial facilities, while home-based food businesses typically have limited production capacity and local sales restrictions. Identifying the right model influences startup costs, growth potential, and operational logistics. Proper classification ensures compliance with legal standards, protecting business sustainability and customer trust.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchens | Home-Based Food Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Cost | Moderate to High - Commercial kitchen rental | Low - Utilizes existing home kitchen |
| Licensing & Regulations | Strict - Commercial food safety regulations | Varies - Often less strict, but depends on local laws |
| Operational Scope | Scalable - Can serve large volume with delivery focus | Limited - Small scale, local customer base |
| Marketing & Branding | Professional digital presence, multi-brand options | Personalized, community-driven marketing |
| Delivery | Integrated with food delivery platforms | May rely on DIY or local delivery services |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; scheduled kitchen slots and contracts | Highly flexible; operate at own pace and hours |
| Profit Margins | Moderate to High, depending on volume & efficiency | Variable; typically lower due to scale |
| Growth Potential | High - Opportunities for expansion and franchising | Limited by personal capacity and resources |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchens offer scalable operations with lower overhead costs and access to multiple delivery platforms, making them ideal for rapid market expansion. Home-based food businesses provide flexibility and personal branding opportunities but face restrictions from local regulations and limited capacity for order volume. Choosing between them depends on the entrepreneur's growth goals, investment capacity, and compliance with food safety standards.
Connection
Ghost kitchens and home-based food businesses share a reliance on low-overhead models that maximize culinary output through minimal physical storefronts. Both leverage digital platforms for order management, delivery coordination, and customer engagement, enabling entrepreneurs to scale operations flexibly. This synergy enhances market entry opportunities for food innovators by reducing capital investment and operational barriers in the competitive food industry.
Key Terms
Licensing and Permits
Home-based food businesses require obtaining a Cottage Food License or home kitchen permit, which limits the types of foods and scales of production allowed under local health regulations. Ghost kitchens must secure commercial kitchen licenses and comply with stringent health and safety standards, including zoning laws and fire safety codes, due to their commercial operation nature. Explore detailed licensing requirements and the step-by-step permit process to ensure compliance for your food business venture.
Commercial Kitchen Space
Home-based food businesses often face strict regulations and limited space constraints that can hinder large-scale production, whereas ghost kitchens benefit from fully equipped commercial kitchen spaces designed for efficiency and scalability. Commercial kitchen space in ghost kitchens provides advanced appliances, compliance with health codes, and flexible rental options that support diverse culinary operations. Explore how choosing the right commercial kitchen can transform your food business and boost growth potential.
Delivery Platforms
Home-based food businesses often leverage delivery platforms like Uber Eats and DoorDash to reach local customers with minimal overhead costs. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively through delivery services, optimizing kitchen space for multiple brands and maximizing order efficiency without a storefront. Explore how these delivery platforms shape the future of food entrepreneurship by connecting diverse culinary concepts to a broad audience.
Source and External Links
Homebased Food Operations in Los Angeles County - Los Angeles County supports legal home food businesses through Cottage Food Operations for non-potentially hazardous prepackaged foods and Microenterprise Home Kitchen Operations for fresh, hot meals, providing permits, inspections, and safety education to ensure compliance and public health protection.
How to Sell Food From Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Starting ... - Successful home food businesses often focus on niche categories like specialized baked goods, preserved foods, specialty desserts, snack foods, dry mixes, and specialty beverages that meet both market demand and regulatory requirements.
How to Start a Food Business from Home - Escoffier - Starting a home-based food business involves selecting a niche that fits your passion and market demand, such as baked goods or meal prepping, and complying with relevant food laws and licensing to reach customers through farmers' markets, online platforms, or delivery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com