Roll-up acquisition involves strategically purchasing and integrating multiple smaller companies to rapidly scale operations and market presence, leveraging synergies and economies of scale. Organic growth focuses on expanding a business internally through increased sales, product development, and customer acquisition without external mergers or acquisitions. Explore how each strategy can impact your entrepreneurial journey and business scalability.
Why it is important
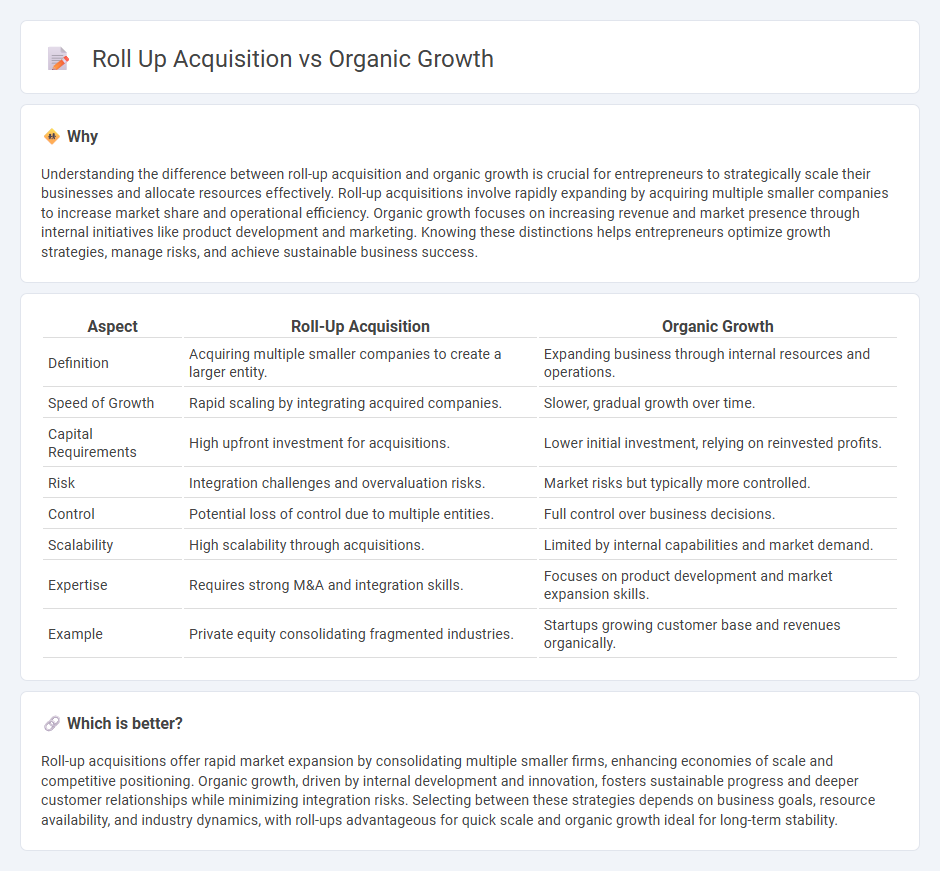
Understanding the difference between roll-up acquisition and organic growth is crucial for entrepreneurs to strategically scale their businesses and allocate resources effectively. Roll-up acquisitions involve rapidly expanding by acquiring multiple smaller companies to increase market share and operational efficiency. Organic growth focuses on increasing revenue and market presence through internal initiatives like product development and marketing. Knowing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs optimize growth strategies, manage risks, and achieve sustainable business success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Roll-Up Acquisition | Organic Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring multiple smaller companies to create a larger entity. | Expanding business through internal resources and operations. |
| Speed of Growth | Rapid scaling by integrating acquired companies. | Slower, gradual growth over time. |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for acquisitions. | Lower initial investment, relying on reinvested profits. |
| Risk | Integration challenges and overvaluation risks. | Market risks but typically more controlled. |
| Control | Potential loss of control due to multiple entities. | Full control over business decisions. |
| Scalability | High scalability through acquisitions. | Limited by internal capabilities and market demand. |
| Expertise | Requires strong M&A and integration skills. | Focuses on product development and market expansion skills. |
| Example | Private equity consolidating fragmented industries. | Startups growing customer base and revenues organically. |
Which is better?
Roll-up acquisitions offer rapid market expansion by consolidating multiple smaller firms, enhancing economies of scale and competitive positioning. Organic growth, driven by internal development and innovation, fosters sustainable progress and deeper customer relationships while minimizing integration risks. Selecting between these strategies depends on business goals, resource availability, and industry dynamics, with roll-ups advantageous for quick scale and organic growth ideal for long-term stability.
Connection
Roll-up acquisitions accelerate entrepreneurship by consolidating multiple smaller companies to achieve rapid market expansion and increased operational efficiency. Organic growth complements this strategy through internal development, strengthening core competencies, and fostering innovation within the acquired entities. Combining roll-up acquisitions with organic growth enhances competitive advantage and drives sustainable business scalability in dynamic markets.
Key Terms
Internal Expansion
Organic growth emphasizes internal expansion through enhancing existing capabilities, optimizing processes, and increasing market share via innovation and customer retention. Roll-up acquisitions involve consolidating smaller companies to quickly scale operations and capture market dominance, often requiring integration of diverse systems and cultures. Explore in-depth strategies to determine the best approach for sustainable business growth.
Synergy
Organic growth leverages internal resources to enhance operational efficiencies and foster innovation, driving sustainable revenue expansion without external dependencies. Roll-up acquisitions create synergy by consolidating fragmented markets, reducing costs, and accelerating scale through integration of complementary businesses. Discover strategic approaches to maximize synergy effects in both organic growth and roll-up acquisition models.
Economies of Scale
Organic growth leverages internal resources to increase production efficiency, resulting in cost savings through streamlined operations and improved labor productivity. Roll-up acquisitions achieve economies of scale by consolidating multiple companies, reducing overlapping costs, enhancing bargaining power with suppliers, and optimizing supply chain logistics. Explore detailed strategies to maximize economies of scale through both growth approaches.
Source and External Links
Organic Growth | Definition + Examples - Wall Street Prep - Organic growth is growth achieved from a company's internal initiatives improving its business model, leading to increased revenue, profit margins, and operating efficiency through methods like expanding markets, innovating products, and enhancing sales strategies.
Organic Growth - Overview, How It Works, Primary Strategies - Organic growth is the expansion of a company using its own capacity and resources without external financing, typically marked by increased output, efficiency, revenue, and cash flow, with major growth strategies focusing on improving internal operations.
Organic growth - Wikipedia - Organic growth is business expansion from increased output and customer base within existing businesses, as opposed to growth by mergers and acquisitions, and involves strategies like market penetration, product development, and content marketing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com