No code startups leverage visual development tools and platforms to build software products quickly without traditional coding, enabling faster market entry and reduced initial costs. Bootstrapped startups rely on personal savings and revenue to fund growth, maintaining full control but often facing slower expansion compared to externally funded ventures. Explore the advantages and challenges of both startup approaches to determine which aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between no-code startups and bootstrapped startups is crucial for effective resource allocation and strategic planning. No-code startups leverage visual development tools to rapidly build applications without traditional coding, enabling faster market entry and lower initial investment. Bootstrapped startups rely on self-funding and organic growth, emphasizing financial discipline and sustainable scaling. Understanding these distinctions helps entrepreneurs choose the best approach for product development, funding needs, and long-term business goals.
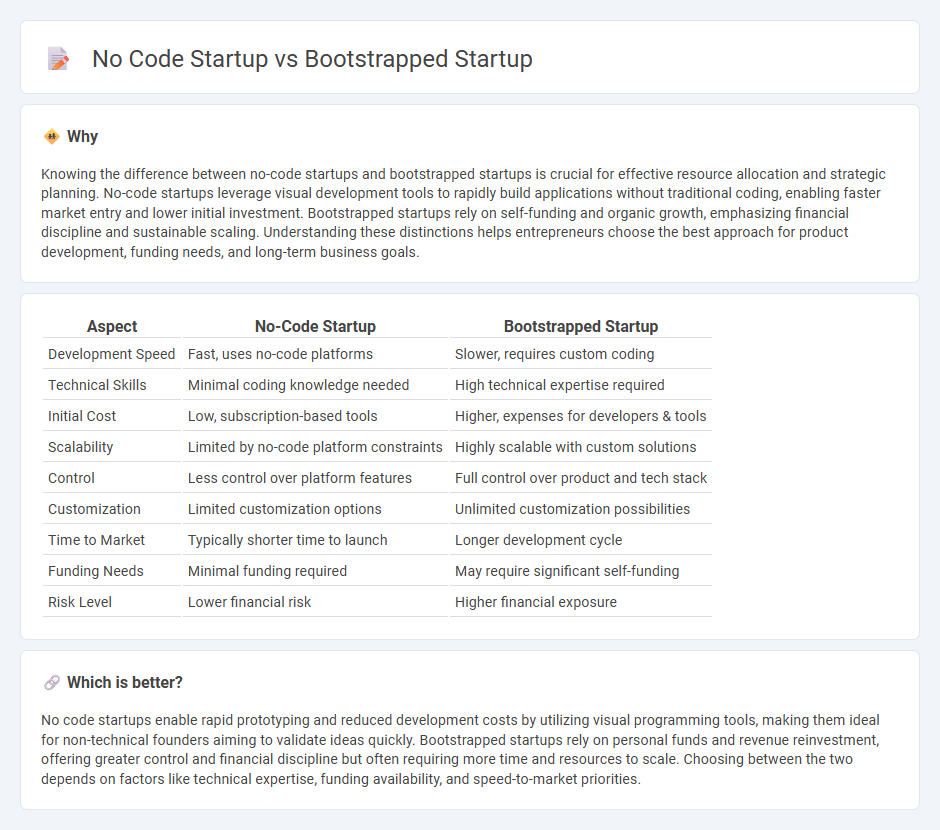
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Code Startup | Bootstrapped Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Development Speed | Fast, uses no-code platforms | Slower, requires custom coding |
| Technical Skills | Minimal coding knowledge needed | High technical expertise required |
| Initial Cost | Low, subscription-based tools | Higher, expenses for developers & tools |
| Scalability | Limited by no-code platform constraints | Highly scalable with custom solutions |
| Control | Less control over platform features | Full control over product and tech stack |
| Customization | Limited customization options | Unlimited customization possibilities |
| Time to Market | Typically shorter time to launch | Longer development cycle |
| Funding Needs | Minimal funding required | May require significant self-funding |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk | Higher financial exposure |
Which is better?
No code startups enable rapid prototyping and reduced development costs by utilizing visual programming tools, making them ideal for non-technical founders aiming to validate ideas quickly. Bootstrapped startups rely on personal funds and revenue reinvestment, offering greater control and financial discipline but often requiring more time and resources to scale. Choosing between the two depends on factors like technical expertise, funding availability, and speed-to-market priorities.
Connection
No code startups and bootstrapped startups share a strong connection through their emphasis on minimizing initial capital expenditures by leveraging no code platforms to build products rapidly without hiring expensive development teams. This approach accelerates time-to-market and empowers entrepreneurs to maintain full ownership and control while validating business ideas efficiently. Both strategies democratize entrepreneurship, enabling founders to focus resources on growth and customer acquisition instead of heavy infrastructure investments.
Key Terms
**Bootstrapped Startup:**
Bootstrapped startups rely on personal savings and revenue generated to fund growth, avoiding external investors and maintaining full control over operations. This approach fosters financial discipline, agile decision-making, and organic scalability with limited resources. Explore the advantages and strategies to successfully build a resilient bootstrapped startup.
Self-funding
Bootstrapped startups rely primarily on self-funding, enabling founders to maintain full control and equity while minimizing external financial dependencies. In contrast, no-code startups often leverage drag-and-drop platforms to rapidly develop prototypes with minimal upfront costs, sometimes attracting early investment due to their quick market validation. Explore deeper insights into funding strategies and growth opportunities for both startup models.
Lean operations
Bootstrapped startups operate with minimal external funding, emphasizing cost efficiency and rapid iteration to maintain lean operations. No code startups leverage visual development platforms to speed up product launches and reduce technical overhead, aligning with the lean startup methodology. Explore deeper insights on how bootstrapped and no code approaches optimize lean operations.
Source and External Links
Bootstrapping - Overview, Stages, and Advantages - Bootstrapping is building a business from scratch without attracting investment or with minimal external capital, relying mainly on internal funding sources like personal savings and credit, and involving stages from initial personal funds to operating using customer revenue and eventually credit.
Bootstrapping: How to Bootstrap Your Startup - Carta - Bootstrapping means starting and growing a startup using your own resources without outside capital, often including personal savings, credit cards, and reinvesting early profits, enabling founders to maintain control and validate their idea before seeking external funding.
What is bootstrapping? Pros and cons of self-financing - Brex - Bootstrapping refers to self-financing a business using only existing resources without venture capital or major loans, which allows founders to keep ownership and control but involves financial risk, with famous examples like GitHub and Spanx proving its potential success.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com