Entrepreneurship often involves navigating eco anxiety, a growing concern driven by environmental challenges and climate change impacts on market stability and resource availability. Proactive coping strategies empower entrepreneurs to anticipate environmental risks, innovate sustainable solutions, and build resilient business models. Discover how integrating proactive coping can transform eco anxiety into entrepreneurial opportunities for a greener economy.
Why it is important
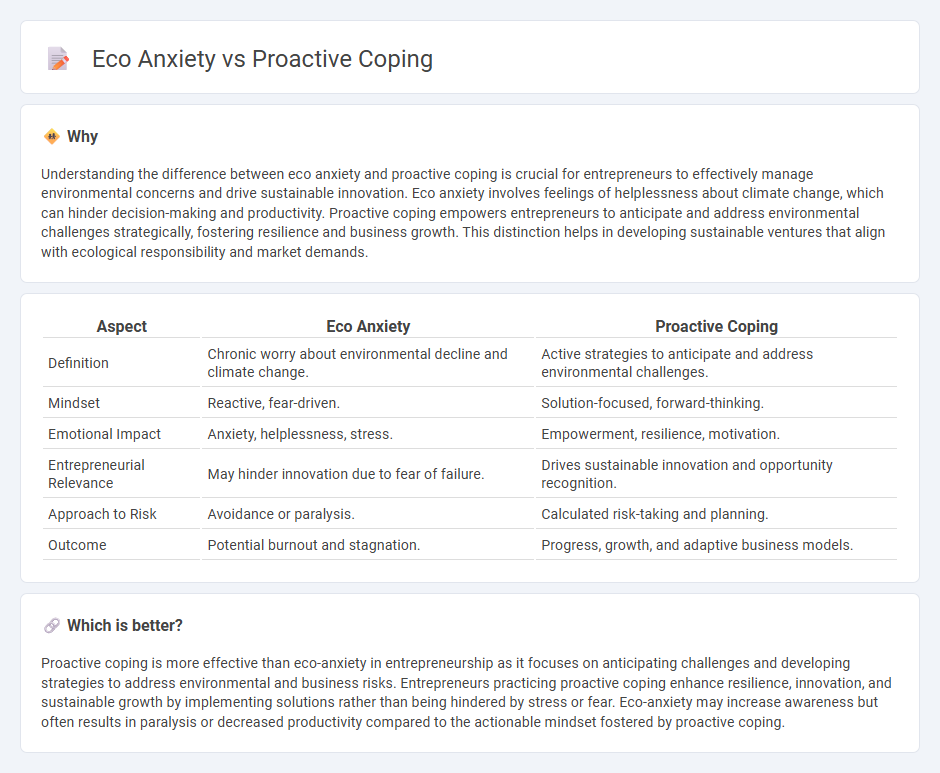
Understanding the difference between eco anxiety and proactive coping is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively manage environmental concerns and drive sustainable innovation. Eco anxiety involves feelings of helplessness about climate change, which can hinder decision-making and productivity. Proactive coping empowers entrepreneurs to anticipate and address environmental challenges strategically, fostering resilience and business growth. This distinction helps in developing sustainable ventures that align with ecological responsibility and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Eco Anxiety | Proactive Coping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic worry about environmental decline and climate change. | Active strategies to anticipate and address environmental challenges. |
| Mindset | Reactive, fear-driven. | Solution-focused, forward-thinking. |
| Emotional Impact | Anxiety, helplessness, stress. | Empowerment, resilience, motivation. |
| Entrepreneurial Relevance | May hinder innovation due to fear of failure. | Drives sustainable innovation and opportunity recognition. |
| Approach to Risk | Avoidance or paralysis. | Calculated risk-taking and planning. |
| Outcome | Potential burnout and stagnation. | Progress, growth, and adaptive business models. |
Which is better?
Proactive coping is more effective than eco-anxiety in entrepreneurship as it focuses on anticipating challenges and developing strategies to address environmental and business risks. Entrepreneurs practicing proactive coping enhance resilience, innovation, and sustainable growth by implementing solutions rather than being hindered by stress or fear. Eco-anxiety may increase awareness but often results in paralysis or decreased productivity compared to the actionable mindset fostered by proactive coping.
Connection
Eco anxiety drives entrepreneurs to develop innovative solutions addressing environmental challenges, fostering proactive coping strategies that enhance resilience and adaptability. This synergy promotes sustainable business practices and encourages long-term planning to mitigate climate-related risks. Effective proactive coping in entrepreneurship transforms eco anxiety into motivation for impactful environmental and economic change.
Key Terms
Resilience
Proactive coping involves anticipating stressors and engaging in adaptive strategies to build resilience before challenges arise, whereas eco-anxiety reflects emotional distress related to environmental threats, often leading to feelings of helplessness. Developing resilience through proactive coping techniques, such as problem-solving, planning, and social support, empowers individuals to manage eco-anxiety more effectively and fosters psychological well-being. Explore practical methods to enhance resilience and transform eco-anxiety into constructive action for environmental sustainability.
Adaptability
Proactive coping enhances adaptability by encouraging individuals to anticipate potential environmental stressors and develop strategies to manage them effectively, unlike eco-anxiety which often triggers reactive responses rooted in fear and uncertainty. This adaptive mindset fosters resilience, allowing people to transform ecological concerns into actionable plans that promote sustainable living. Explore how integrating proactive coping can empower communities to face climate challenges with confidence and hope.
Sustainability
Proactive coping involves anticipating potential environmental challenges and actively implementing sustainable practices to mitigate future risks, while eco-anxiety reflects the emotional distress linked to concerns about ecological degradation and climate change. Emphasizing resilience-building strategies, proactive coping enhances individual and community capacity to adopt renewable energy, reduce carbon footprints, and support conservation efforts. Explore effective methods to integrate proactive coping into sustainability initiatives for better environmental and mental health outcomes.
Source and External Links
Proactive Coping Strategies: Building Resilience and ... - Proactive coping involves preparing for and managing expected or unexpected challenges ahead of time by identifying stressors, developing plans, building social support, practicing self-care, and other strategies to build resilience and reduce stress.
The Psychology of Proactive Coping: Strategies for Building ... - Proactive coping refers to actions taken before stressors occur to prevent or diminish their impact, including developing coping mechanisms, setting attainable goals, enhancing problem-solving skills, and creating strong social support networks.
Proactive Coping - PMC - Proactive coping is a future-oriented self-regulatory behavior focused on striving for positive outcomes through resource accumulation and realistic goal-setting, which is strongly linked with improved well-being and optimism.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com